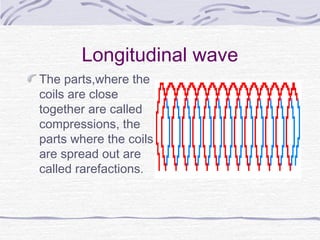
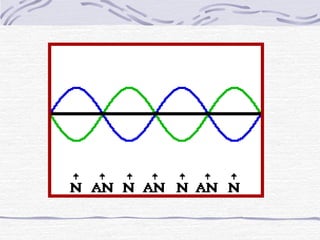
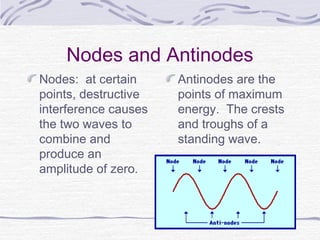
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium. They are caused by vibrations in the medium and can be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination. Key properties of waves include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Waves interact with each other and surfaces through reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and can form standing waves through the combination of incoming and reflected waves.