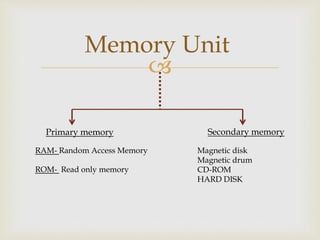
The document discusses different types of computer memory including primary memory like RAM and ROM, and secondary memory like magnetic disks, magnetic drums, CD-ROMs, and hard disks. It defines a hard disk drive as using rapidly rotating disks coated with magnetic material to store and retrieve digital data in a random-access manner. The document also covers optical discs which encode data in the form of pits and lands on a circular disc, and defines common units of data storage like kilobytes, megabytes, and terabytes in terms of bytes.