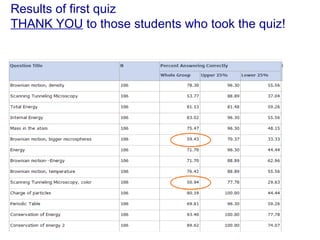
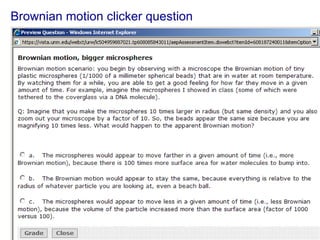
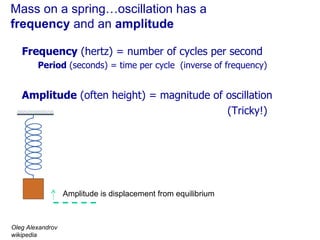
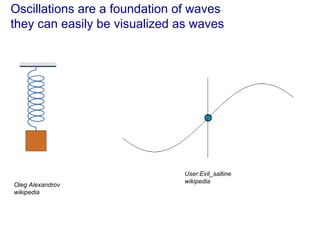
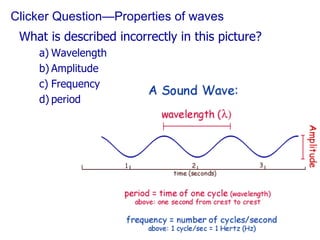
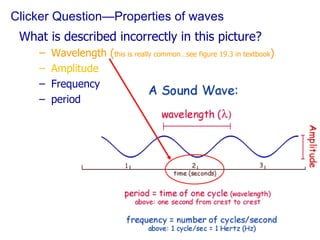
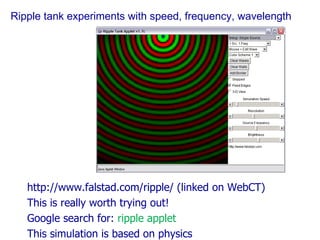
The document contains notes about a quiz covering oscillations, waves, and the Doppler effect, with upcoming exercises and due dates noted. It explains concepts such as self-sustaining oscillations, wave properties (frequency, amplitude, wavelength), and types of waves while providing examples from physics. Additionally, it discusses the Doppler effect and includes clicker questions and resources for visualization and simulations related to wave properties.