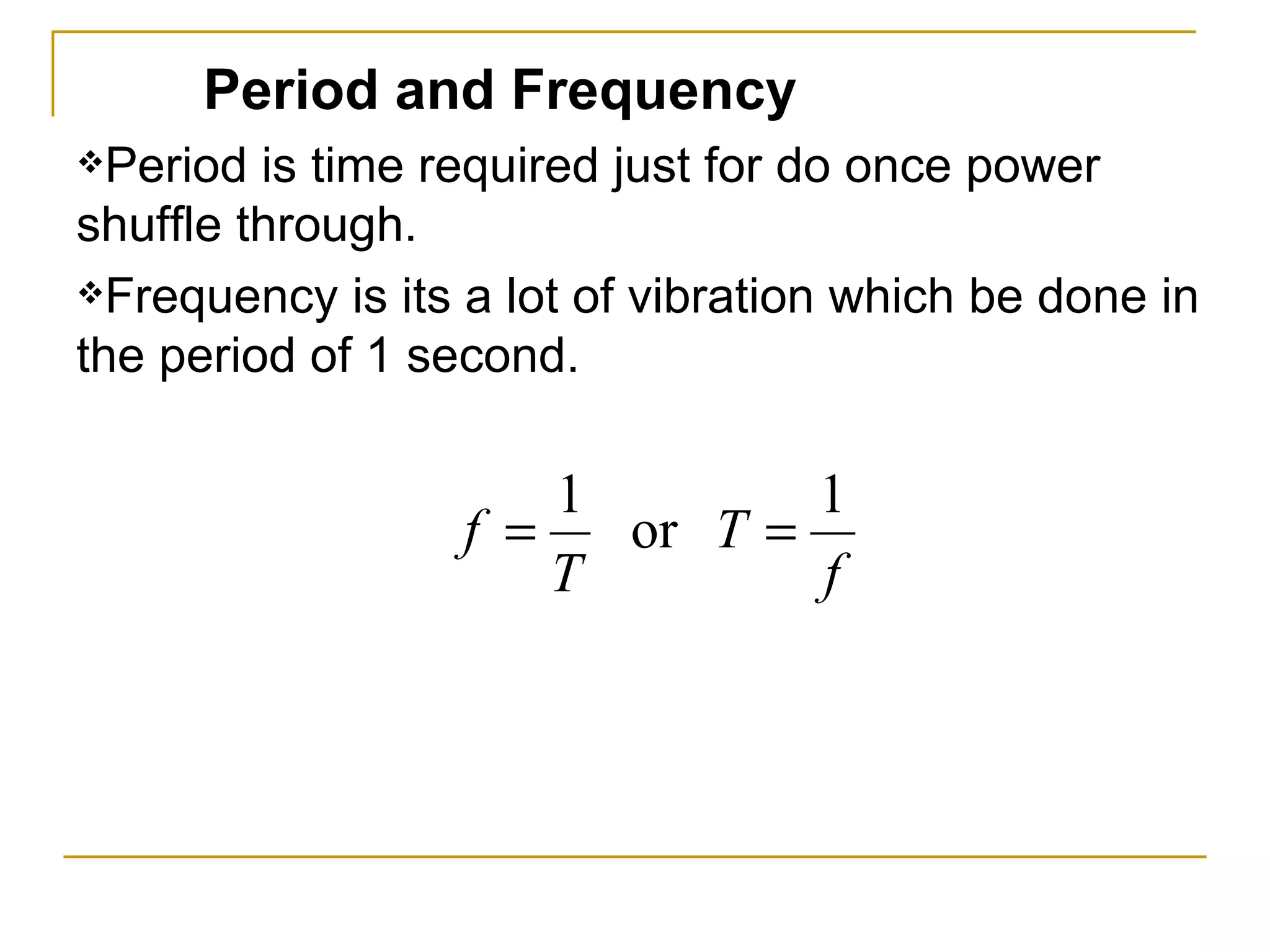
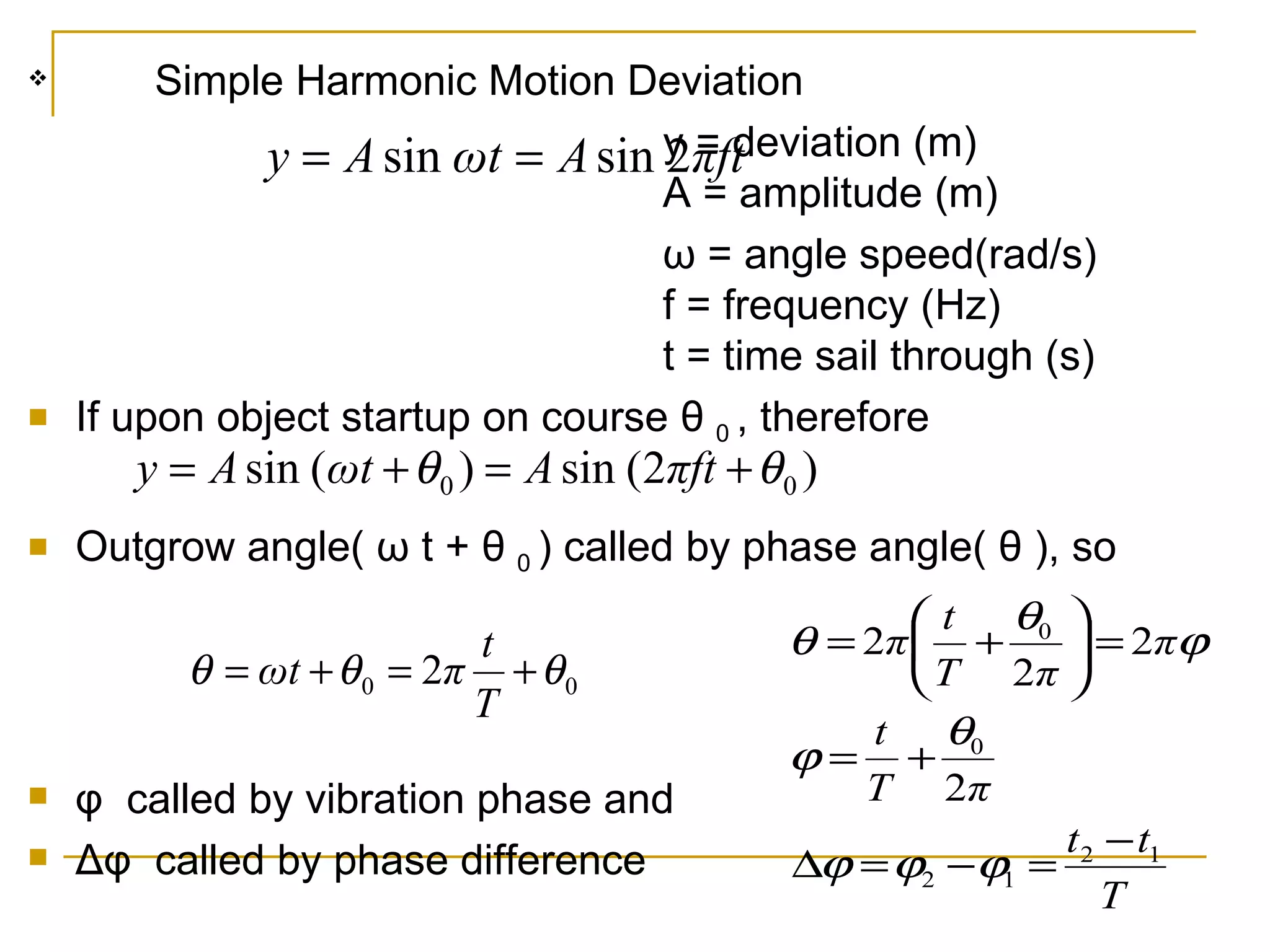
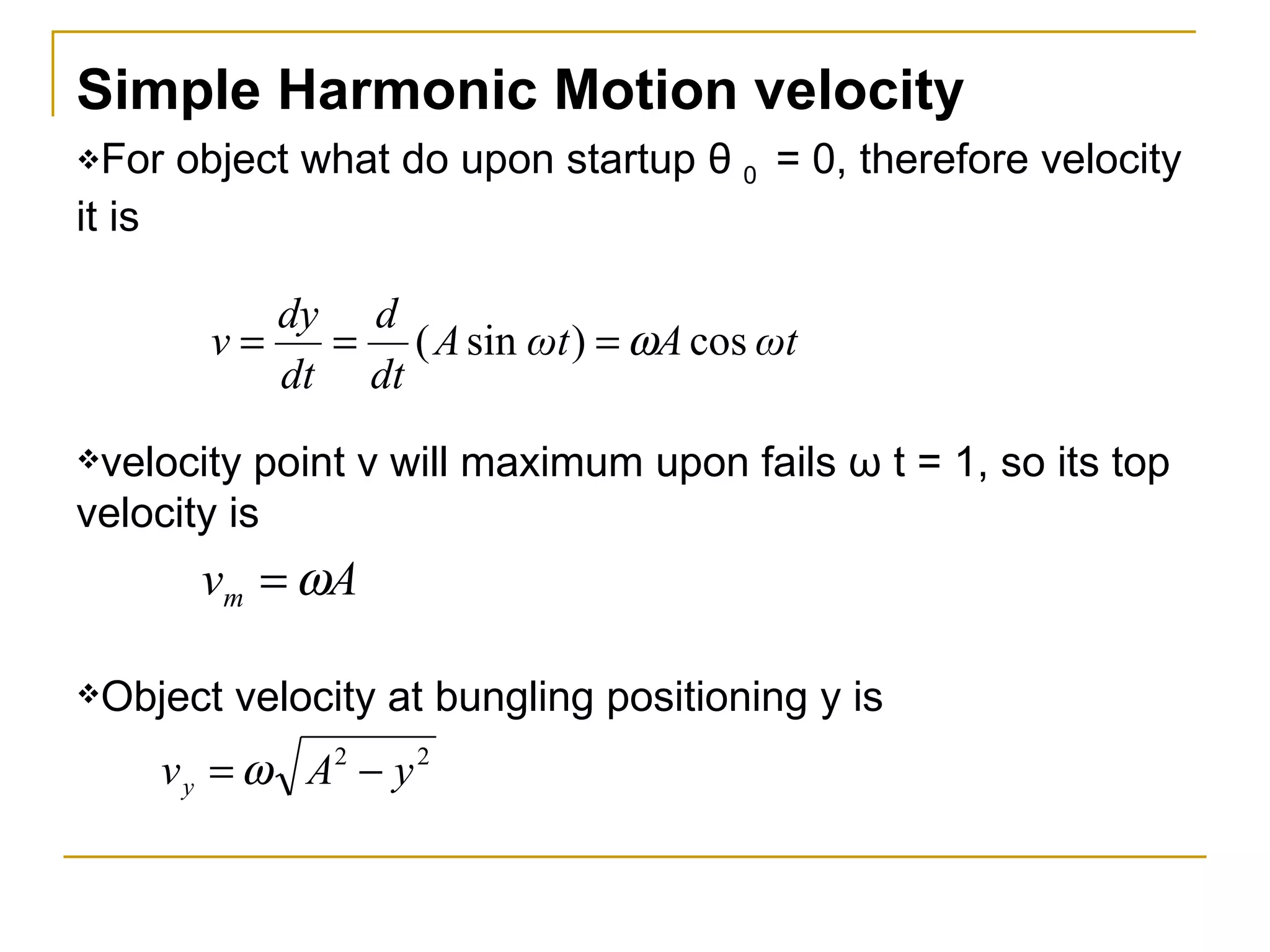
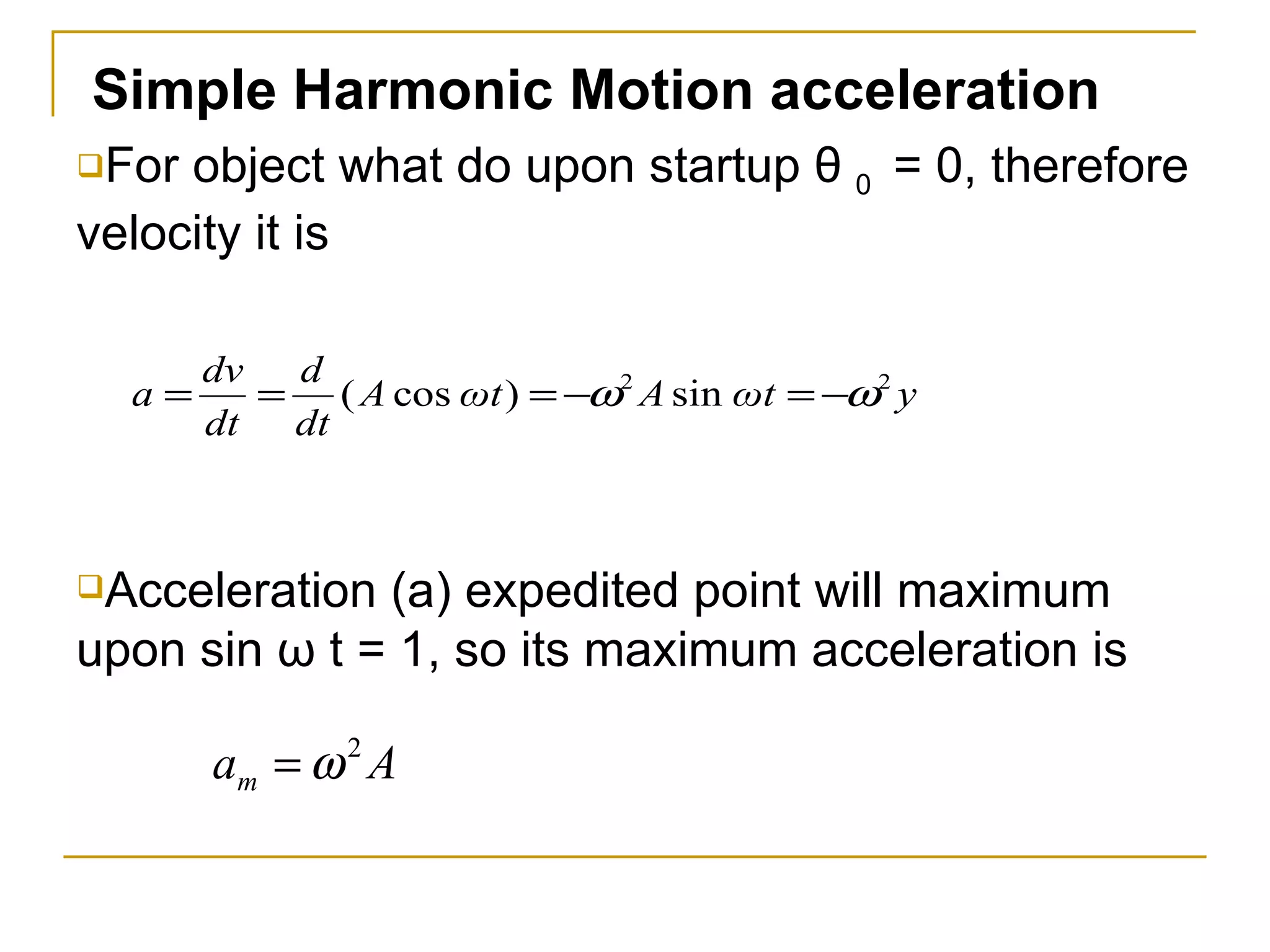
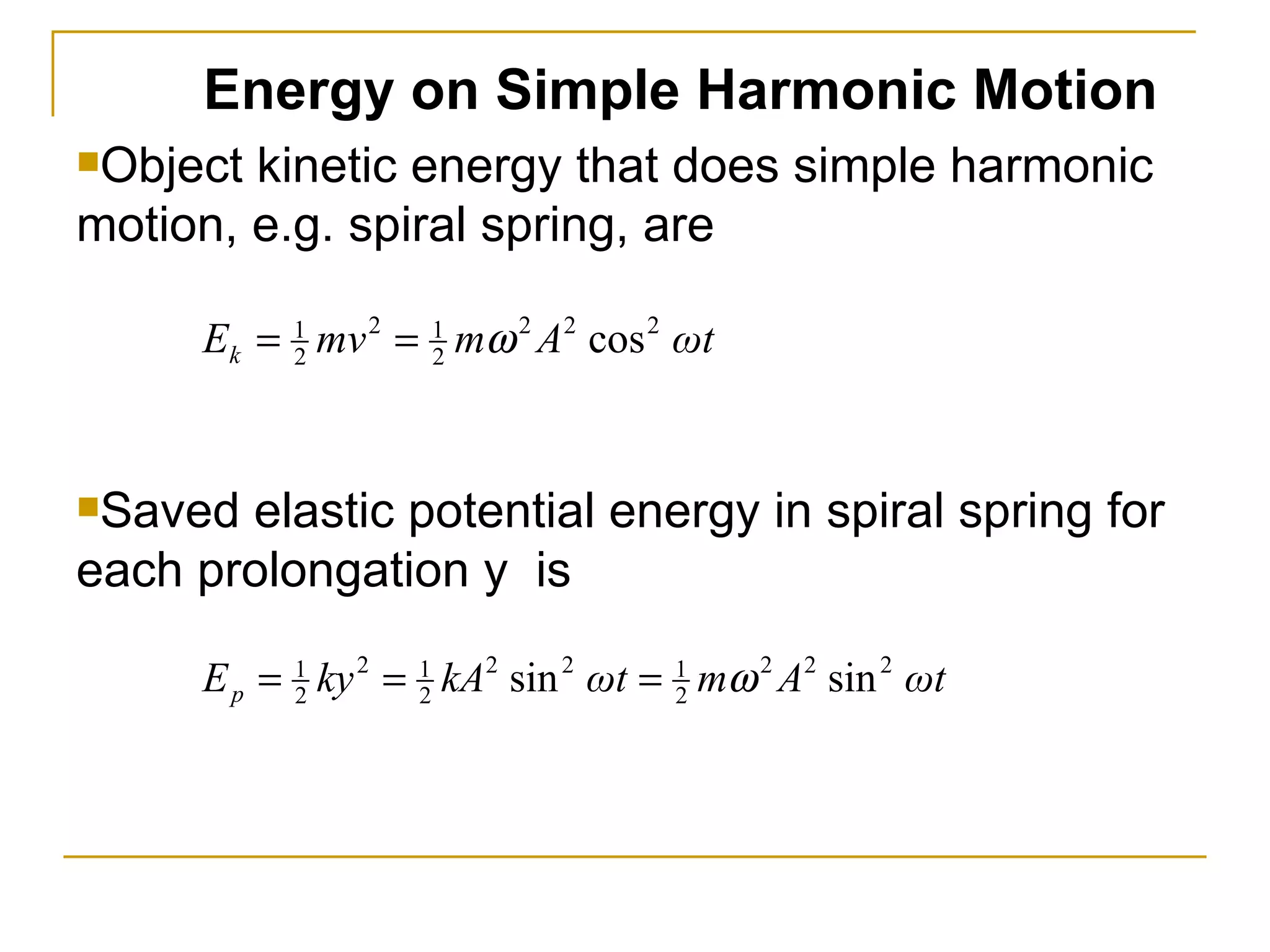
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) refers to the periodic oscillatory motion of an object where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from its equilibrium position. There are two types of SHM: linear SHM such as oscillations of a spring or pendulum, and angular SHM such as a torsional pendulum. The period of SHM is the time required for one complete oscillation, while the frequency is the number of oscillations that occur per second. For a spring with spring constant k and mass m, the period is 2π√(m/k). For a simple pendulum of length l, the period is 2π√(l/g). SHM can be described by equations