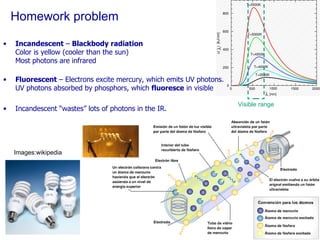
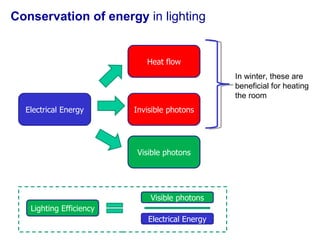
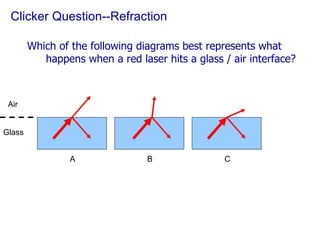
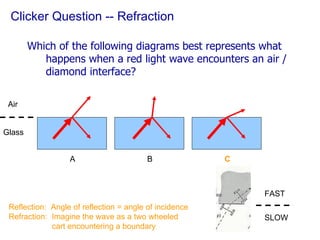
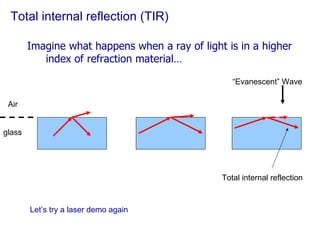
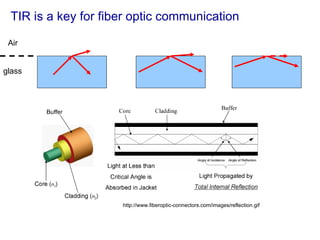
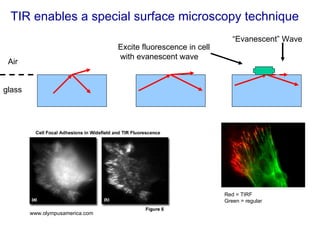
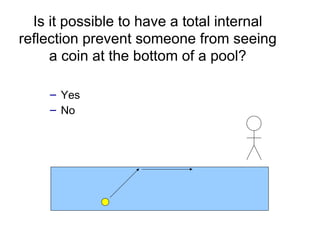
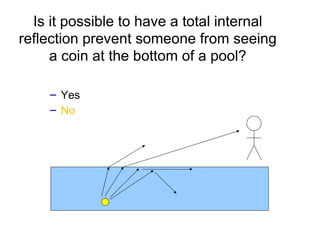
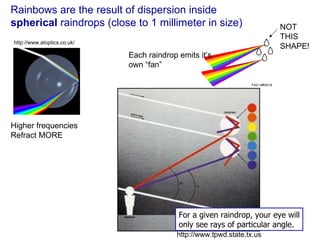
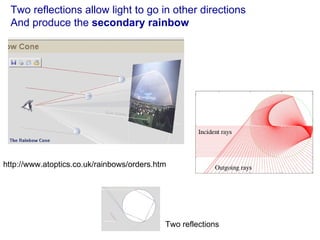
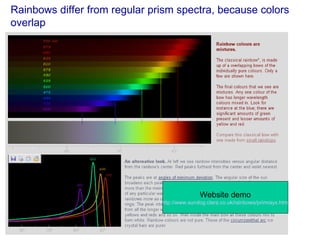
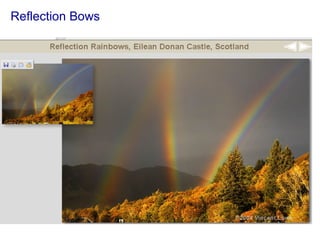
The document covers concepts related to light behavior, including total internal reflection, refraction, and dispersion. It discusses the formation of rainbows through these phenomena and includes various classroom activities and visual aids. Additionally, connections are made to lighting efficiency and fiber optic communication.