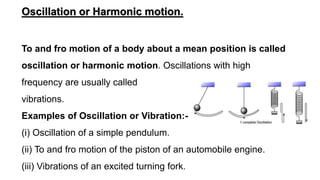
Periodic motion repeats at regular time intervals. Examples include planetary orbits and clock hands. Oscillation involves to-and-fro motion about a mean position, like a pendulum swing. It is always periodic but periodic motion need not involve oscillation. The time for one full cycle is the period (T). Frequency (ν) is the number of cycles per second. Angular frequency (ω) relates frequency and period. Displacement variables describe the changing quantity in oscillations, like position or angle. Simple harmonic motion involves a restoring force proportional to displacement towards the equilibrium point, like a spring. It can be modeled by sine and cosine functions and includes oscillations of springs and pendulums.