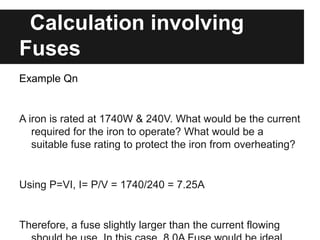
This document provides information about electrical energy and dangers of electricity. It discusses types of dangers like overheating cables, damp environments, and damaged insulation. It then describes various safety features used at home like circuit breakers, fuses, switches, earthing, three-pin plugs, and double insulation. Circuit breakers and fuses prevent excessive current flow by tripping or blowing. Switches should be connected to live wires. Earthing provides a path for stray currents. Three-pin plugs contain a fuse. Double insulation insulates internal components from external casing. An example calculation for a suitable fuse rating to protect an iron is also provided.