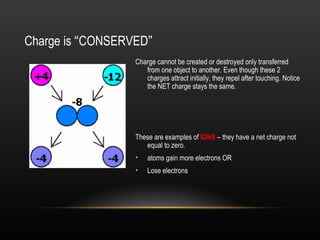
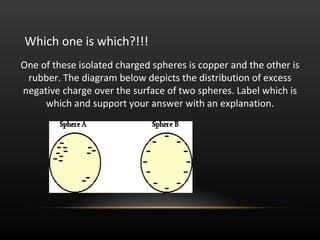
This document discusses electricity and electric charge. It defines the basic properties of electric charge including that there are two types - positive and negative. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract. Charge is conserved and cannot be created or destroyed. The key particles - proton, electron, and neutron - and their charges are identified. Conductors allow charge to move through them while insulators restrict charge movement. Triboelectric series shows how charge transfers during friction. Induction can charge objects without contact by redistributing protons and electrons. Devices like electroscopes and Van de Graaff generators are used to study electric charge.