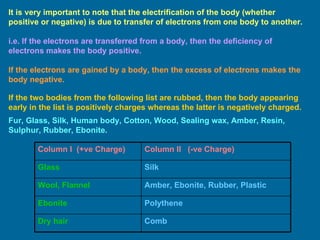
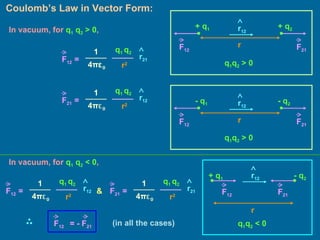
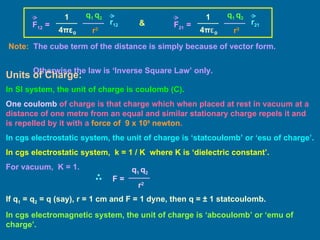
This document discusses various topics related to electrostatics including frictional electricity, properties of electric charges, Coulomb's law, units of charge, relative permittivity, and continuous charge distribution. It defines frictional electricity as the transfer of electrons from one body to another when two suitable bodies are rubbed together. It also describes Coulomb's law, which states that the electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Finally, it discusses different types of continuous charge distributions including linear, surface, and volume charge densities.