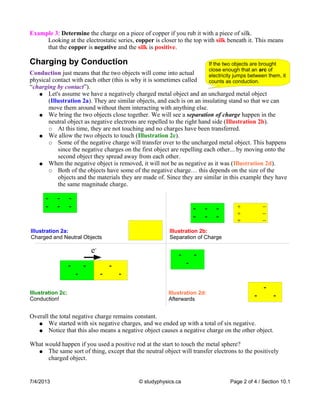
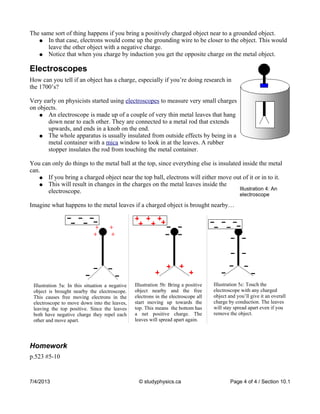
Charging by friction occurs when two materials are rubbed together, causing electrons to be transferred from one material to the other based on their positions in the electrostatic series. Charging by conduction involves direct contact between two objects, causing charge to be shared between them. Charging by induction does not require contact—bringing a charged object near an object connected to ground by a wire causes its charge to increase by attracting or repelling the object's electrons through the wire. An electroscope is used to detect charge by causing its metal leaves to spread apart in the presence of a charged object due to induction and the redistribution of its internal electrons.