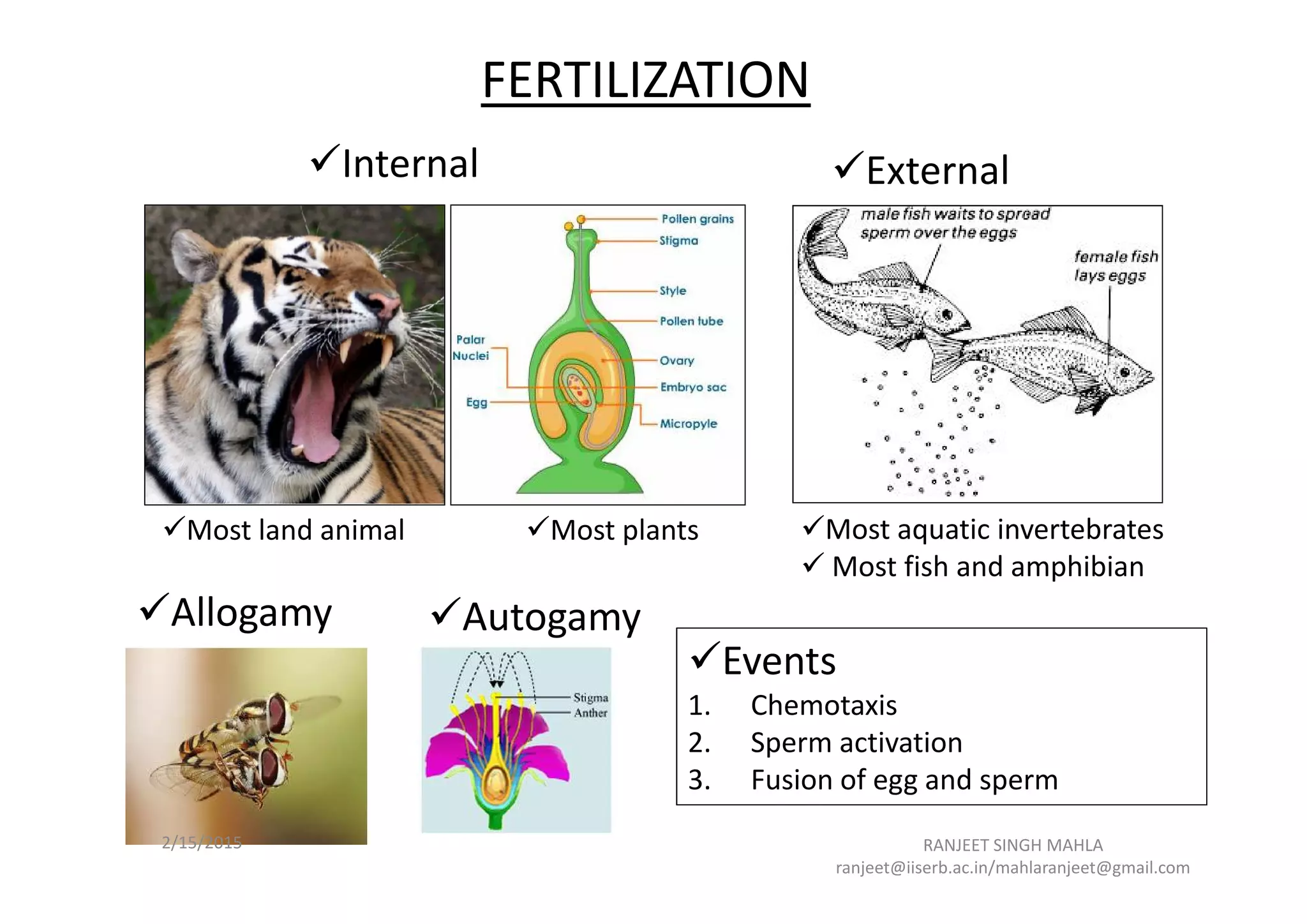
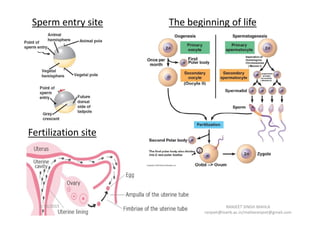
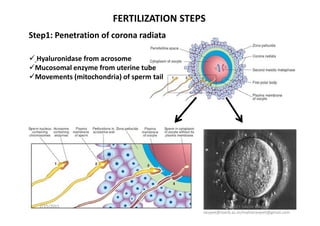
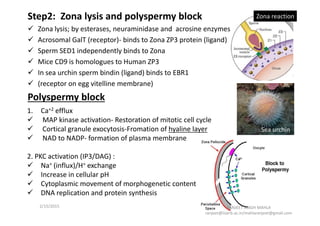
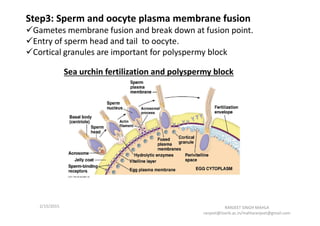
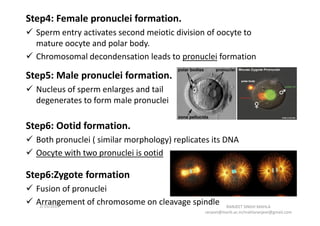
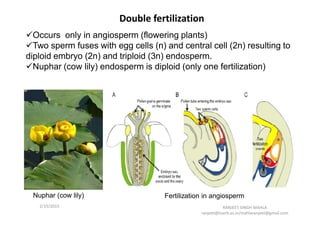
The document discusses the process of fertilization in various organisms, emphasizing internal and external fertilization mechanisms, particularly in aquatic invertebrates, fish, amphibians, and plants. It details the steps involved in fertilization, including the penetration of the oocyte, fusion of gametes, and the formation of pronuclei, as well as the process of double fertilization in angiosperms. Key biochemical events such as enzyme activities, calcium efflux, and membrane fusion are highlighted as essential to the fertilization process.