This document discusses the process of fertilization in three parts:
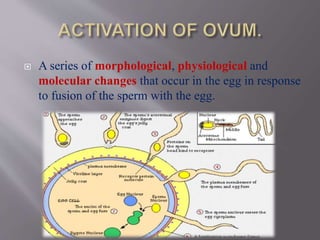
1) It describes the steps of fertilization, including capacitation, contact, acrosome reaction, fusion of sperm and egg, and activation of the ovum.
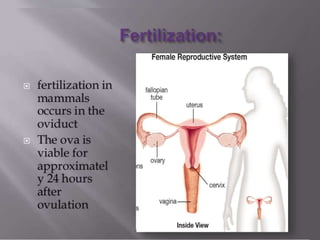
2) It explains the differences between external fertilization, which occurs outside the body, and internal fertilization, which occurs inside the body.
3) It outlines the process after sperm enters the female reproductive tract, including the pronuclei fusing to form a zygote within 20 hours of fertilization.