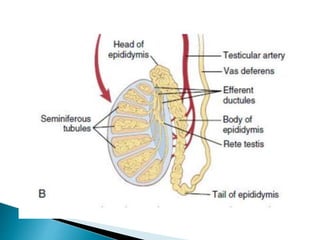
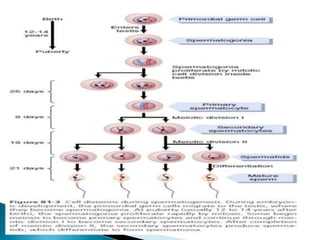
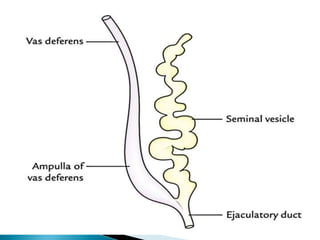
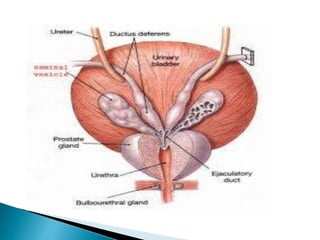
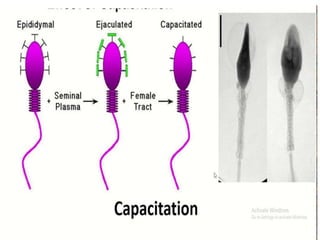
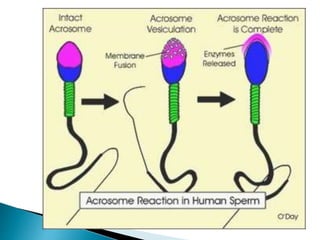
This document discusses the process of sperm maturation and capacitation. It explains that hormones stimulate spermatogenesis in the testes. Sperm then mature in the epididymis over 18-24 hours, gaining motility. During capacitation in the female reproductive tract, cholesterol is removed from sperm membranes over 1-10 hours, making them more permeable and able to undergo the acrosome reaction for fertilization. This involves releasing enzymes to penetrate the egg's protective layers.