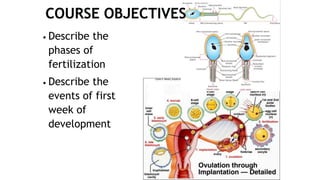
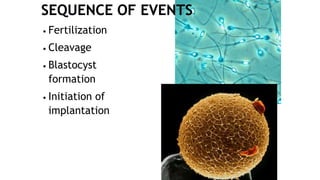
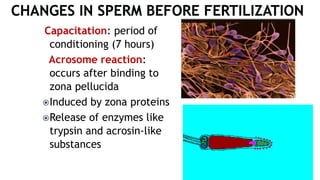
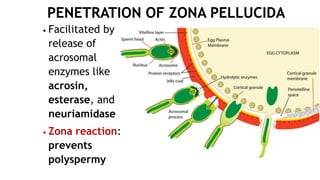
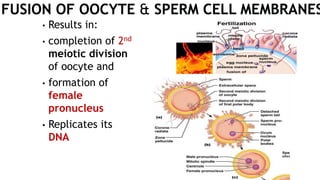
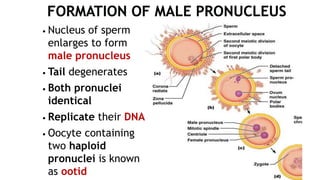
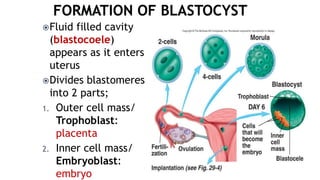
1. Fertilization involves the fusion of an egg and sperm, forming a zygote with a full set of chromosomes. The zygote then undergoes cleavage, forming a morula by day 3 and a blastocyst by day 5 as it travels down the fallopian tube.
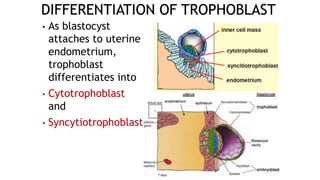
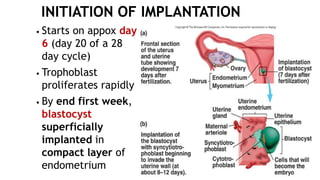
2. The blastocyst implants in the uterine wall around 1 week after fertilization. The trophoblast cells of the blastocyst initiate implantation and will later form the placenta, while the inner cell mass gives rise to the embryo.
3. During the first week, the zygote develops from a single cell through cleavage, compaction, blastulation and begins implantation in the uterus.