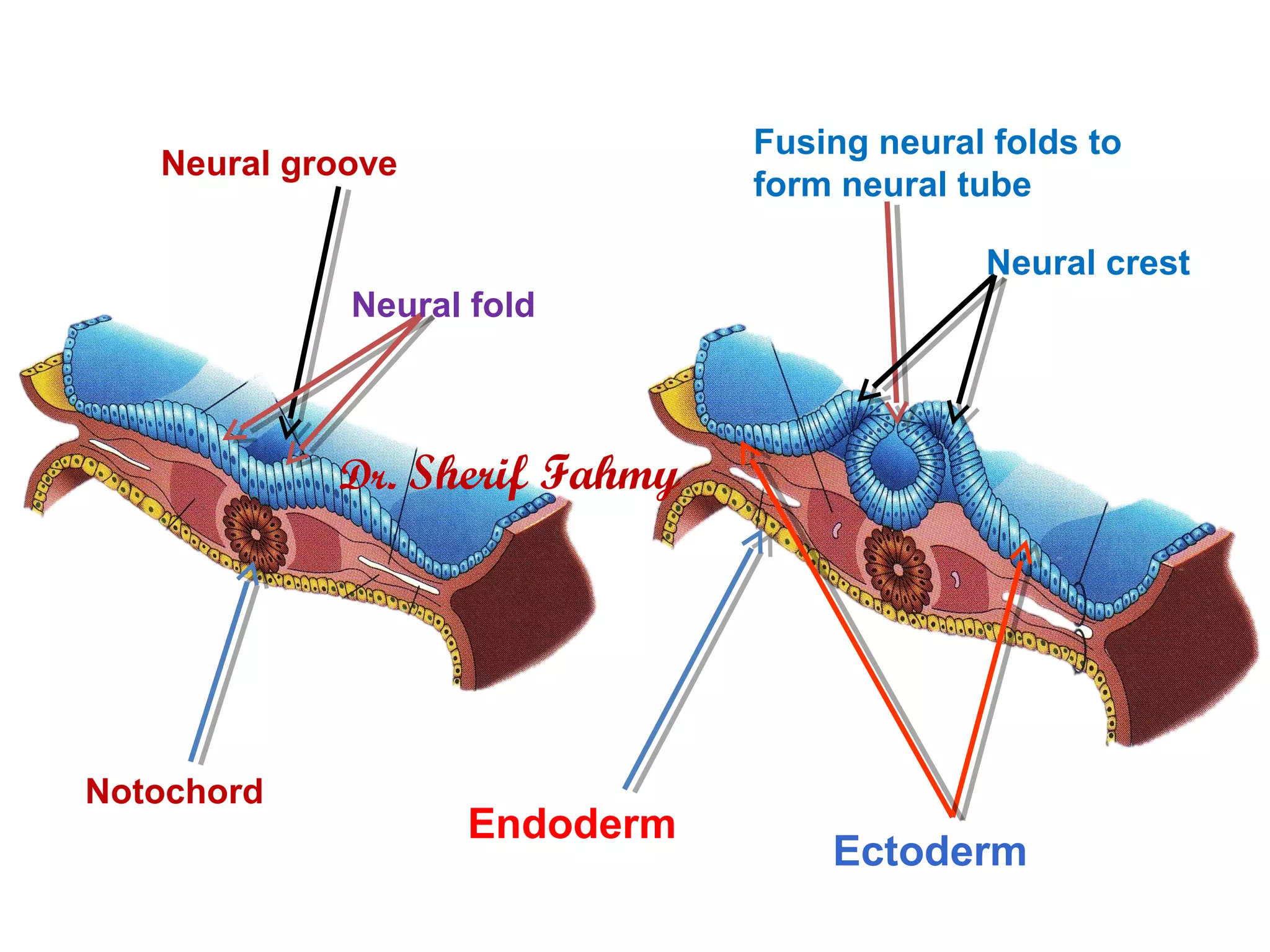
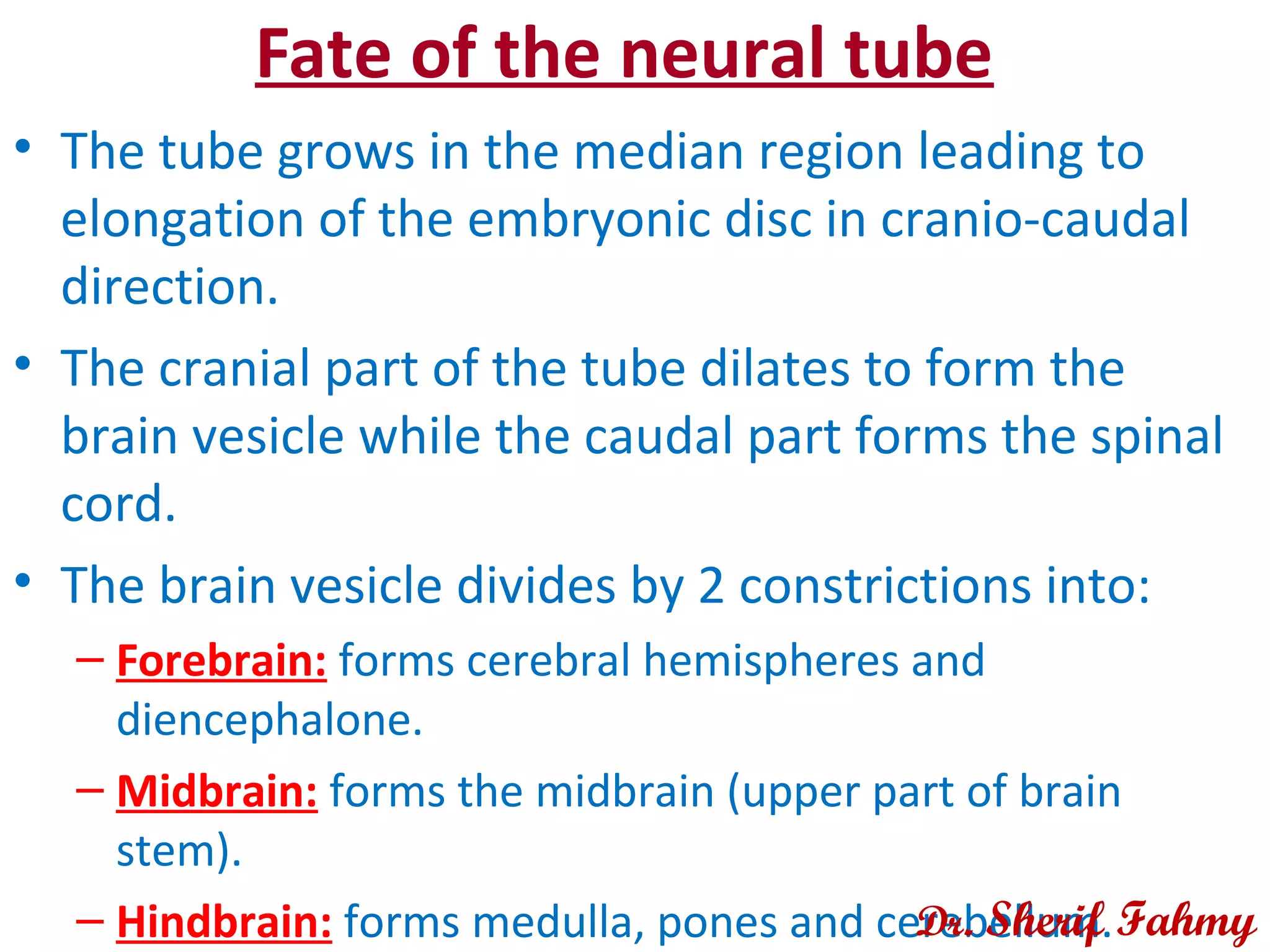
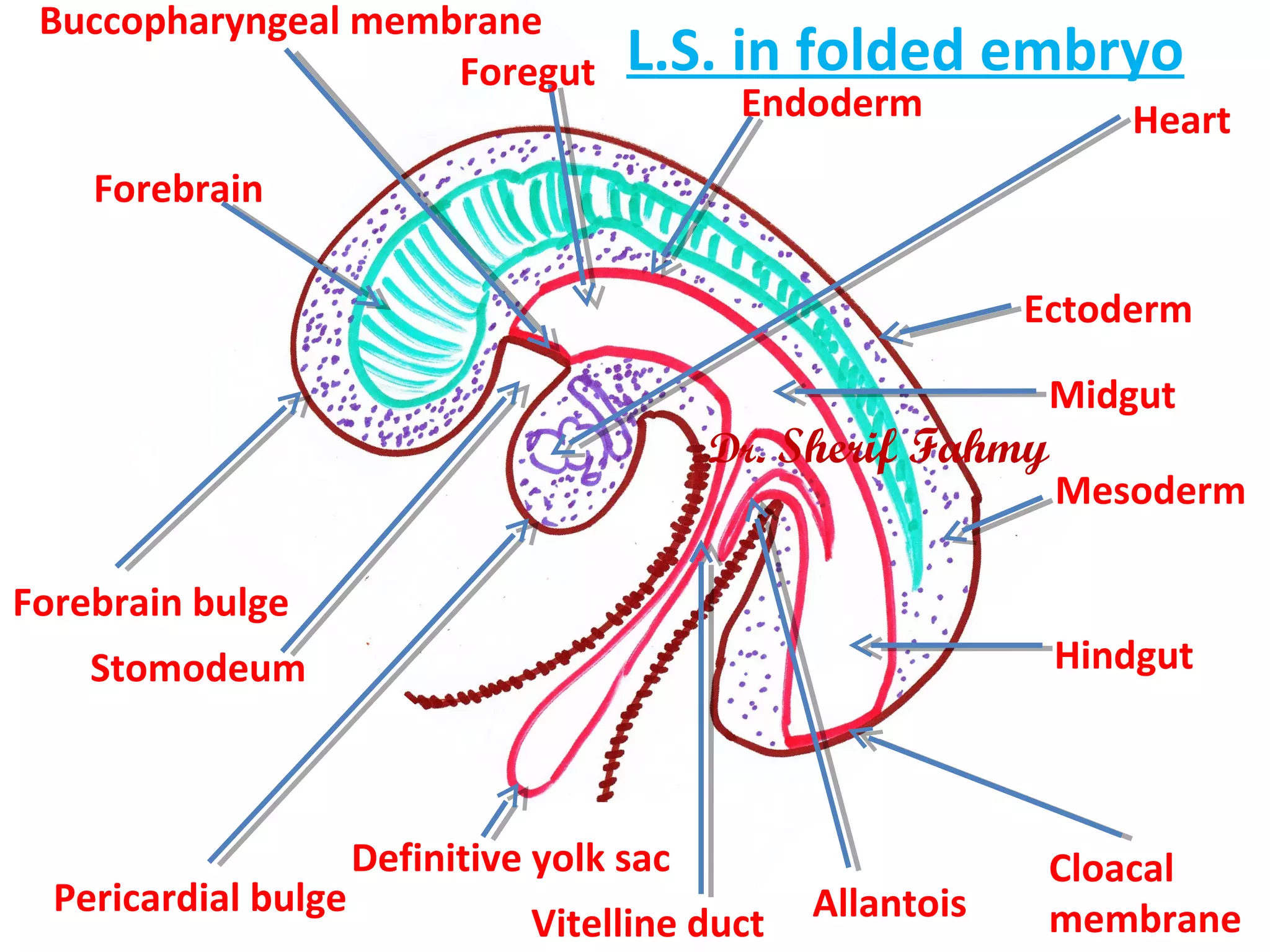
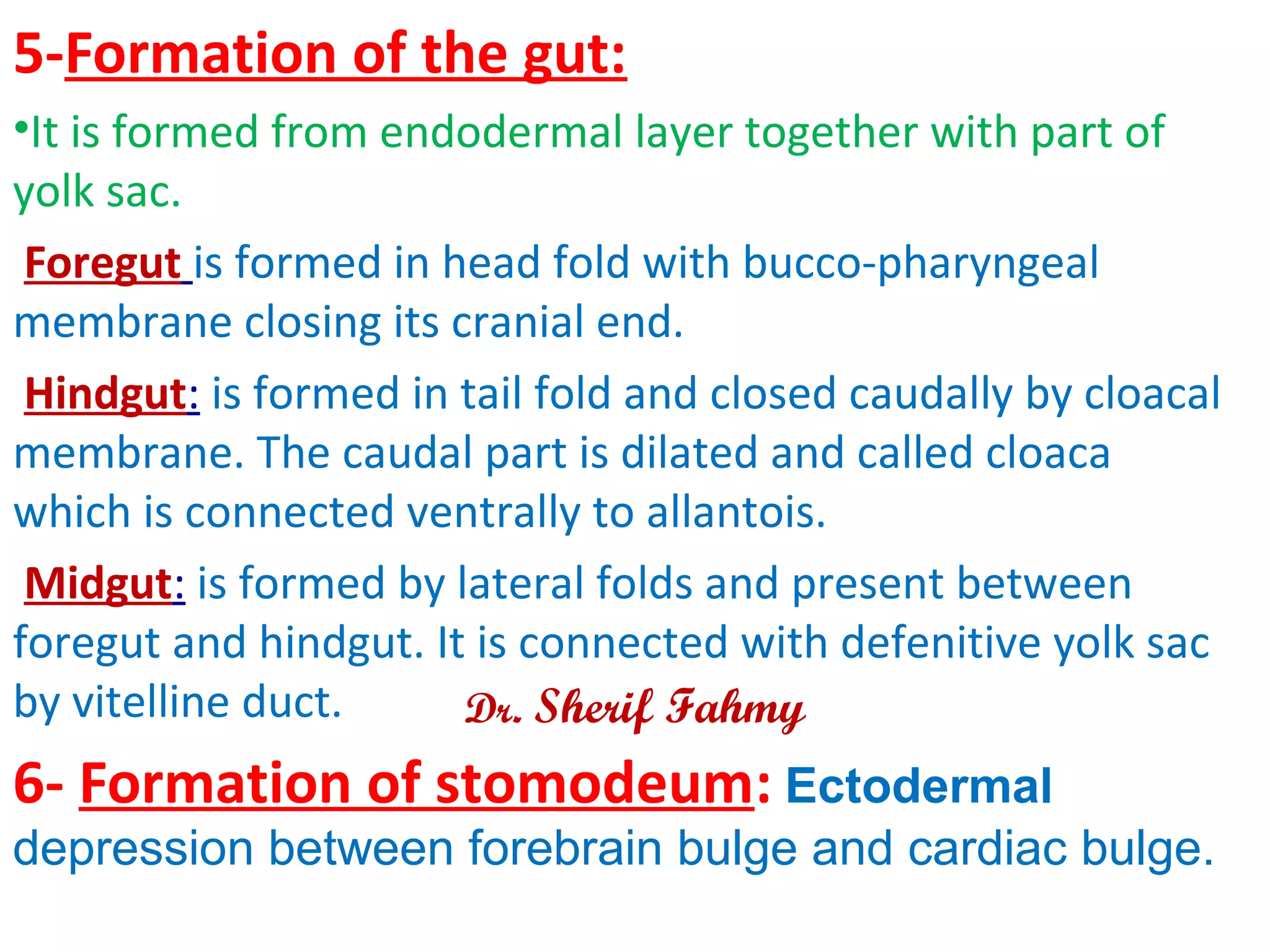
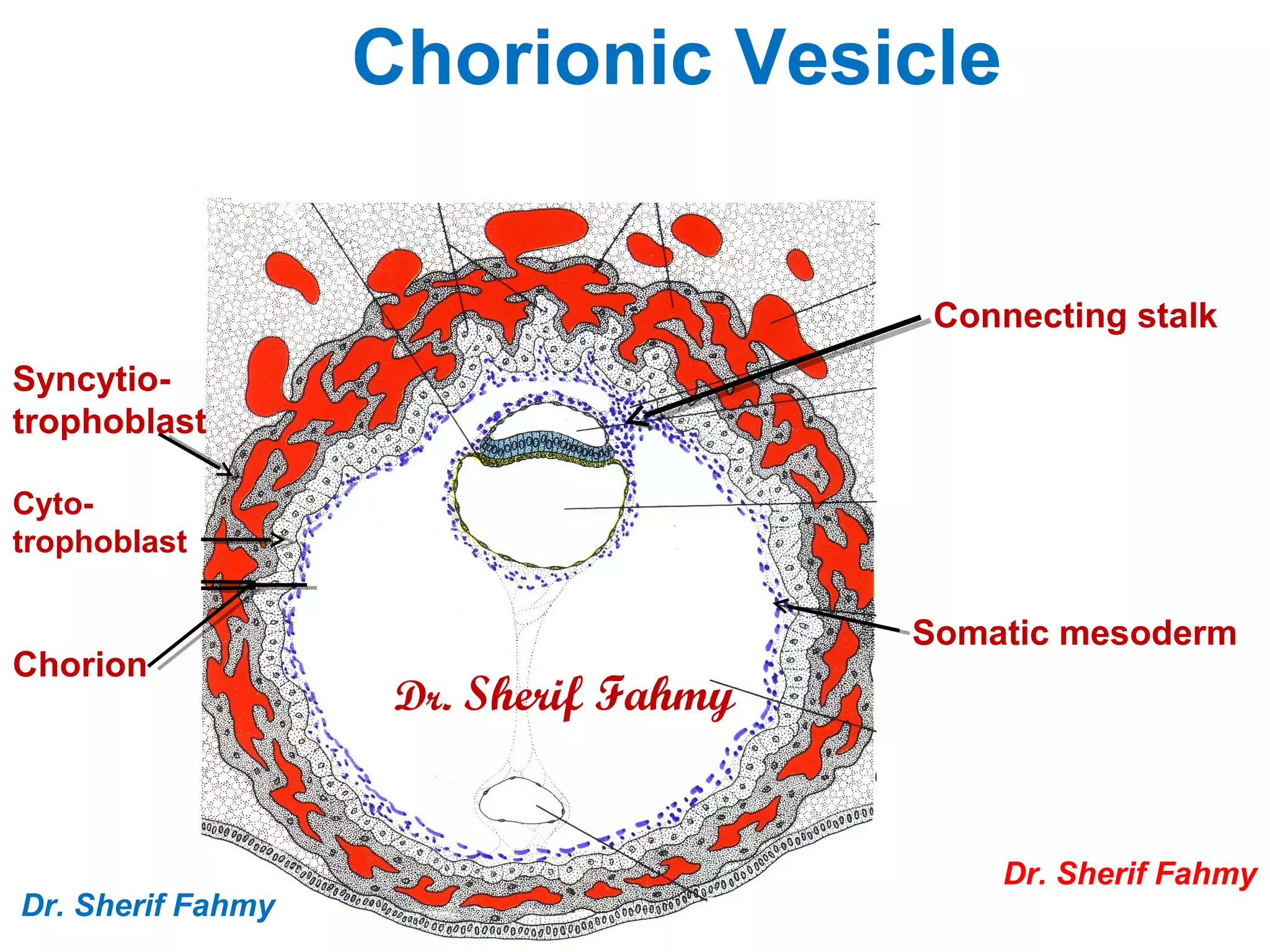
The document discusses embryonic development from the 4th to 8th week. It describes how the neural tube forms from the neural plate and folds, and how it eventually develops into the brain and spinal cord. It also discusses the fate of the neural crest in forming various structures. The ectoderm gives rise to other structures like the skin, ears and eyes. As the embryo folds and bends upon itself, its shape changes from a flat disc to a cylinder. This folding results in the gut and membranes that will aid in nutrient exchange for the growing embryo.