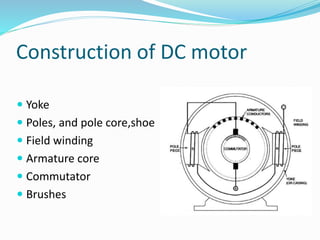
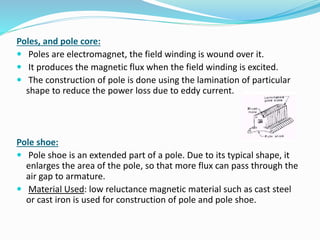
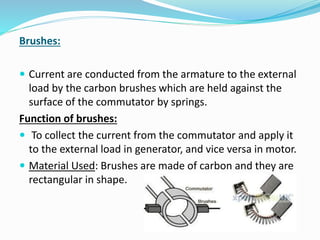
A DC motor operates by generating a force on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. It consists of a yoke, poles, pole cores, field winding, armature core, commutator, and brushes. The field winding is energized to create alternating north and south poles. The armature winding inside the armature core cuts this magnetic field to generate an EMF which is converted to DC by the commutator and supplied to an external load through the brushes, causing the motor to rotate.