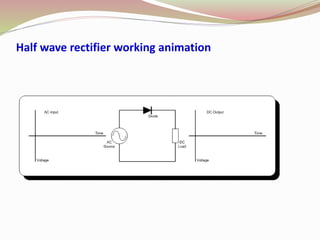
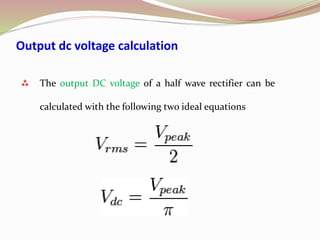
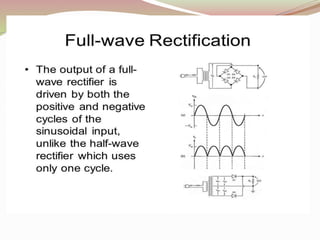
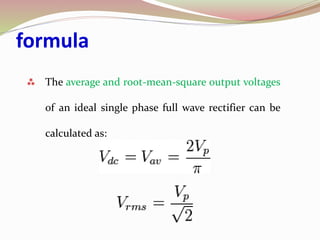
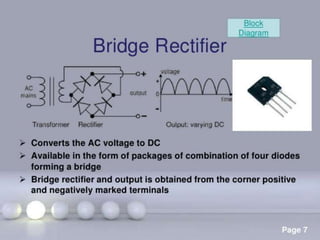
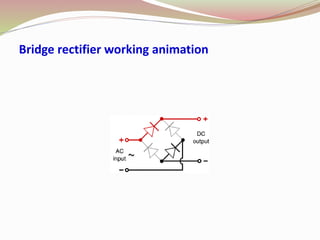
Rectifier types were presented including half wave, full wave, and bridge rectifiers. Half wave rectifiers only pass one half of the AC wave while full wave rectifiers pass both halves using either two diodes in a center-tapped transformer or four diodes. Bridge rectifiers use four diodes in a bridge configuration to achieve full-wave rectification and have the advantage of requiring no transformer.