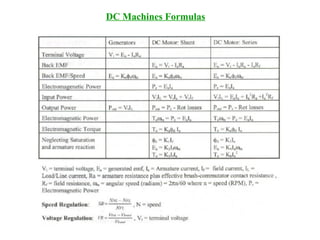
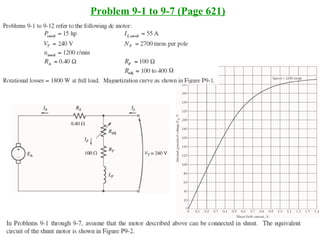
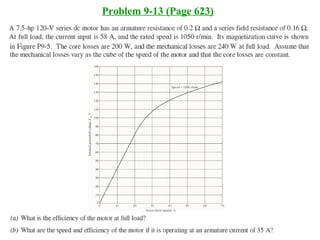
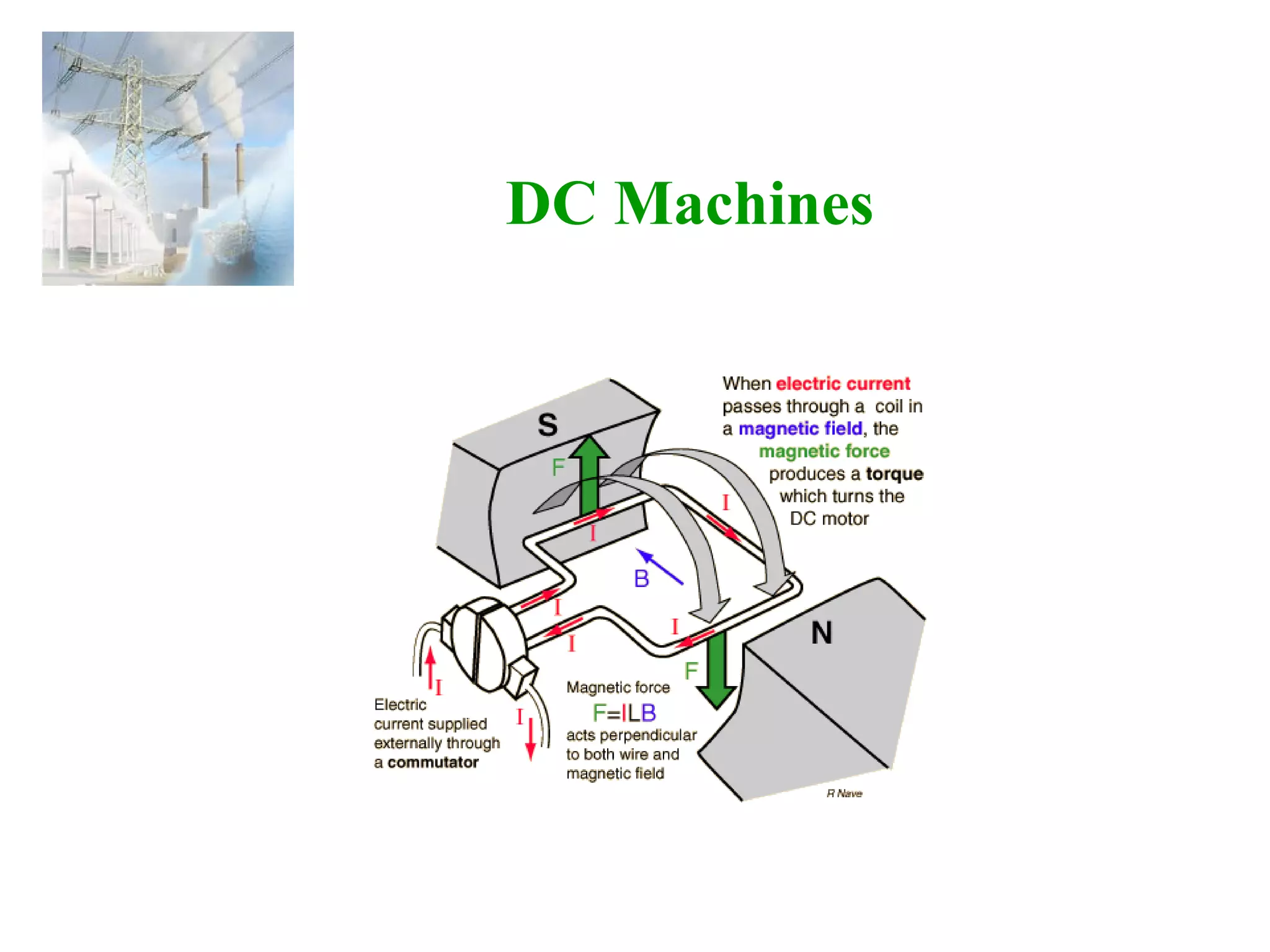
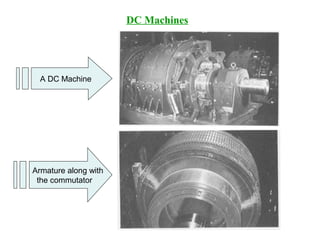
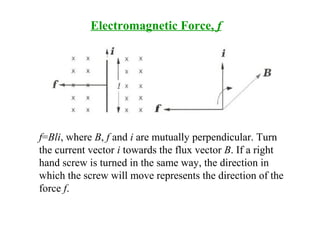
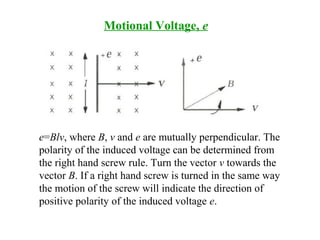
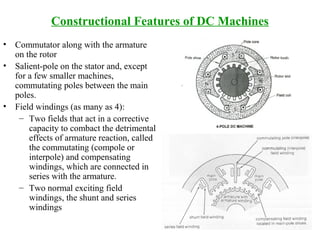
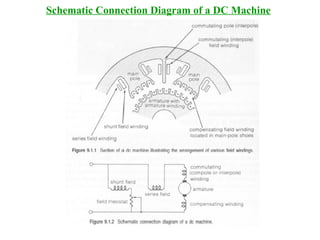
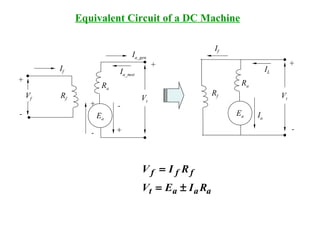
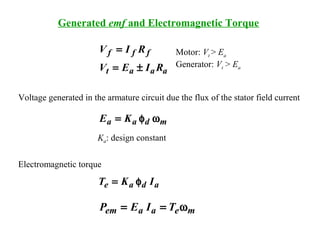
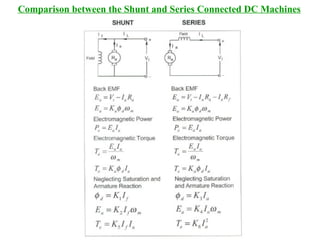
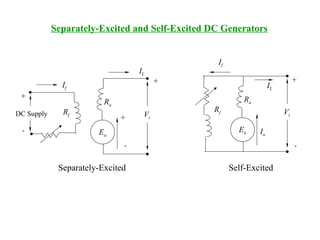
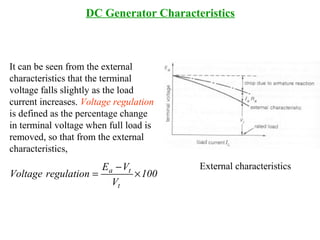
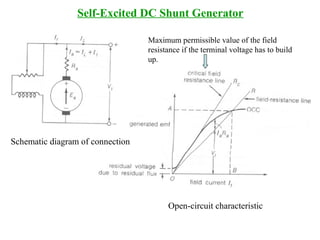
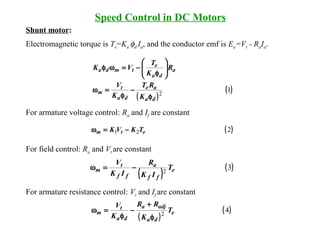
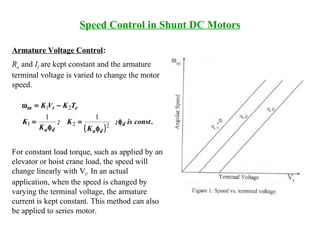
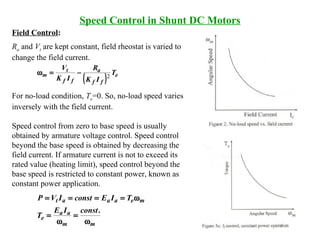
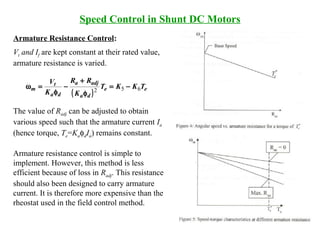
DC machines operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction and force. They have commutators, field windings, and armature windings. DC machines can operate as motors or generators depending on the direction of power flow. Speed in DC motors can be controlled through methods like armature voltage control, field control, and armature resistance control. DC generators have open-circuit, load, and external characteristics that define their performance based on variables like terminal voltage, field current, and load current. Efficiency is impacted by losses such as copper losses and mechanical losses.






![DC Generator Characteristics
Open-circuit and load characteristics
The terminal voltage of a dc
generator is given by
( )[ ]
aa
mf
aaat
RI
dropreactionArmatureIf
RIEV
−
−=
−=
ω,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturedcmachines-130708132230-phpapp02/85/Lecture-dc-machines-18-320.jpg)

![Armature Voltage Control:
A variable dc voltage can be applied to a series motor
to control its speed. A variable dc voltage can be
obtained from a power electronic converter.
Torque in a series motor can be expressed as
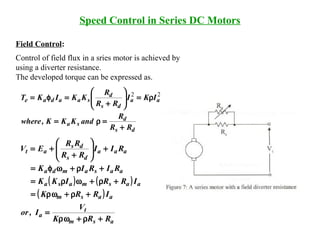
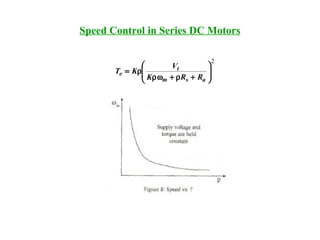
Speed Control in Series DC Motors
( )[ ]
sae
t
sa
sa
sae
t
m
samsa
tsa
asaadae
KKT
V
KK
RR
KKT
V
,or
RRKK
VKK
IKKIKT
≈
+
−=ω
++ω
=
=φ=
2
2
2
( )
( )
( ) ( )
samsa
t
a
saamasa
saamda
saaat
asd
RRKK
V
I
RRIIKK
RRIK
RRIEV
IK
++ω
=
++ω=
++ωφ=
++=
=φ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturedcmachines-130708132230-phpapp02/85/Lecture-dc-machines-26-320.jpg)