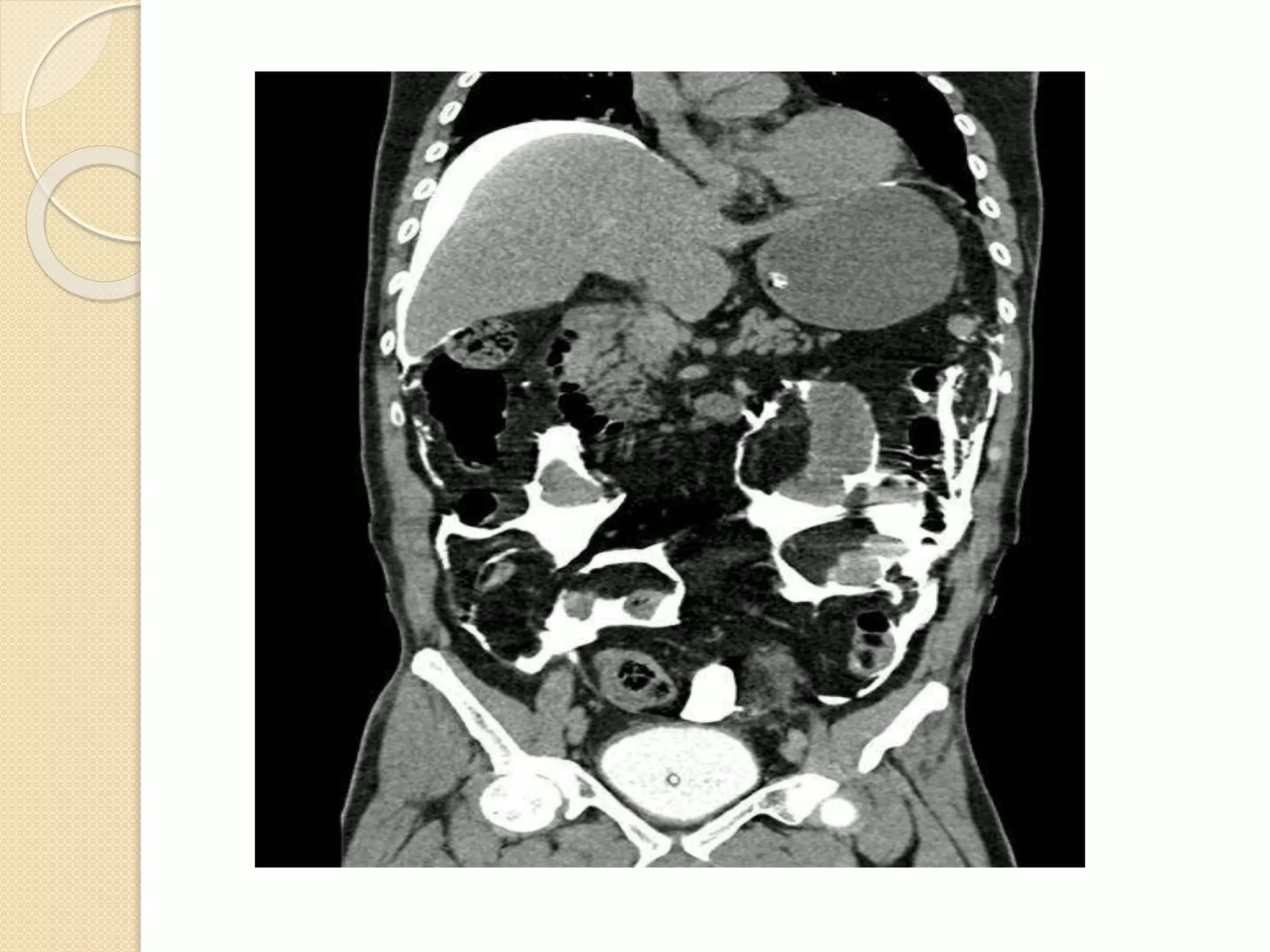
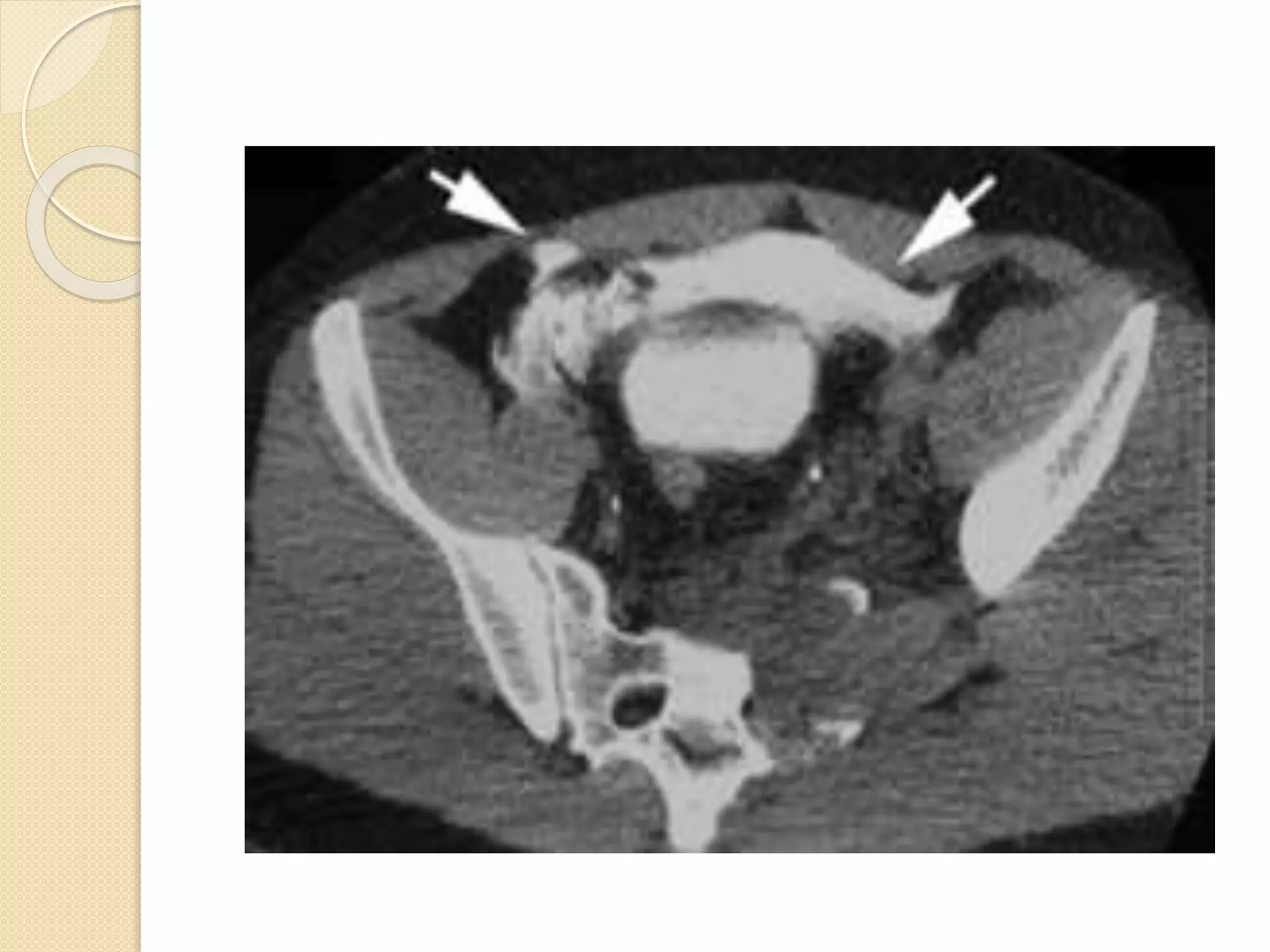
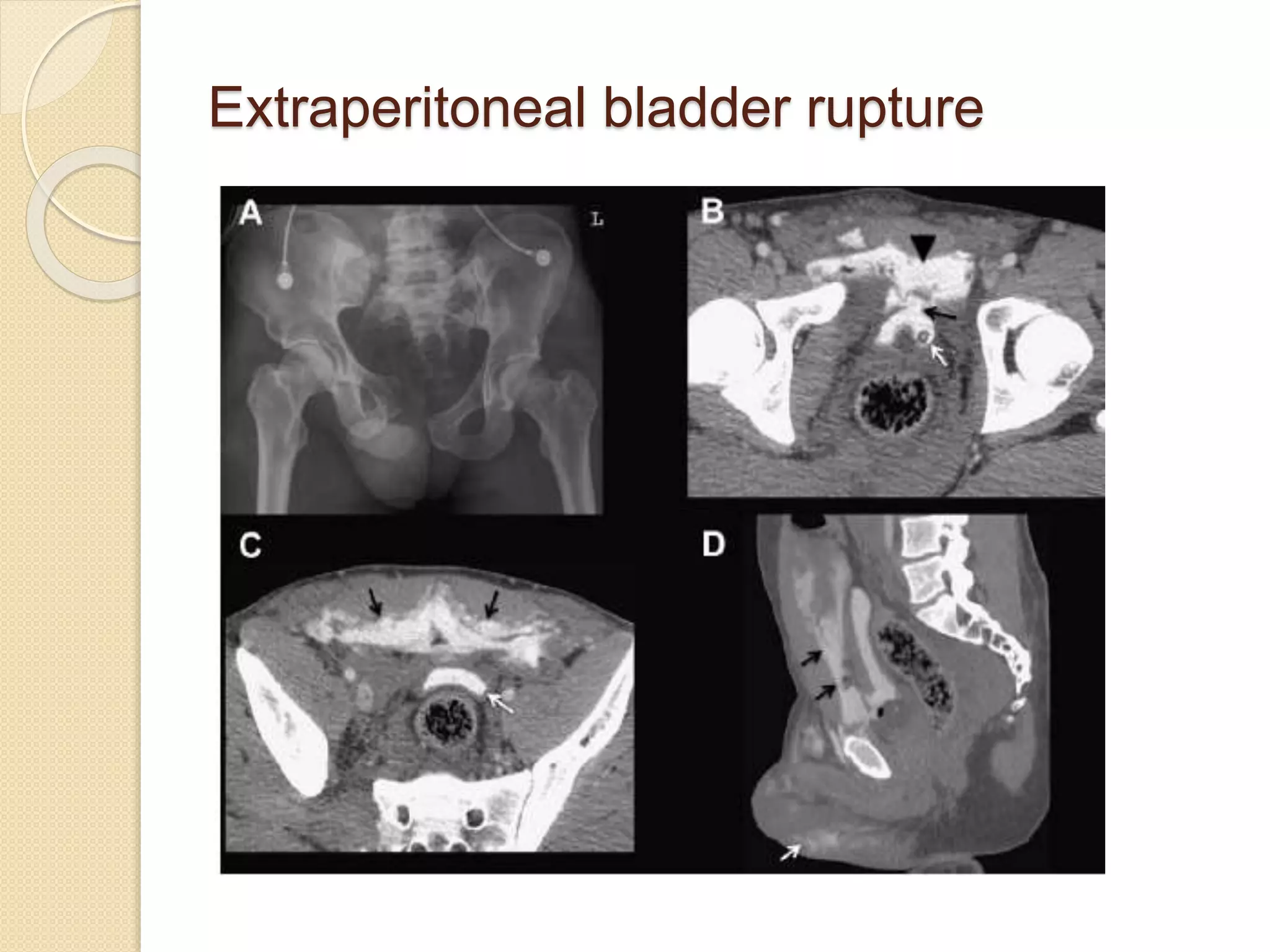
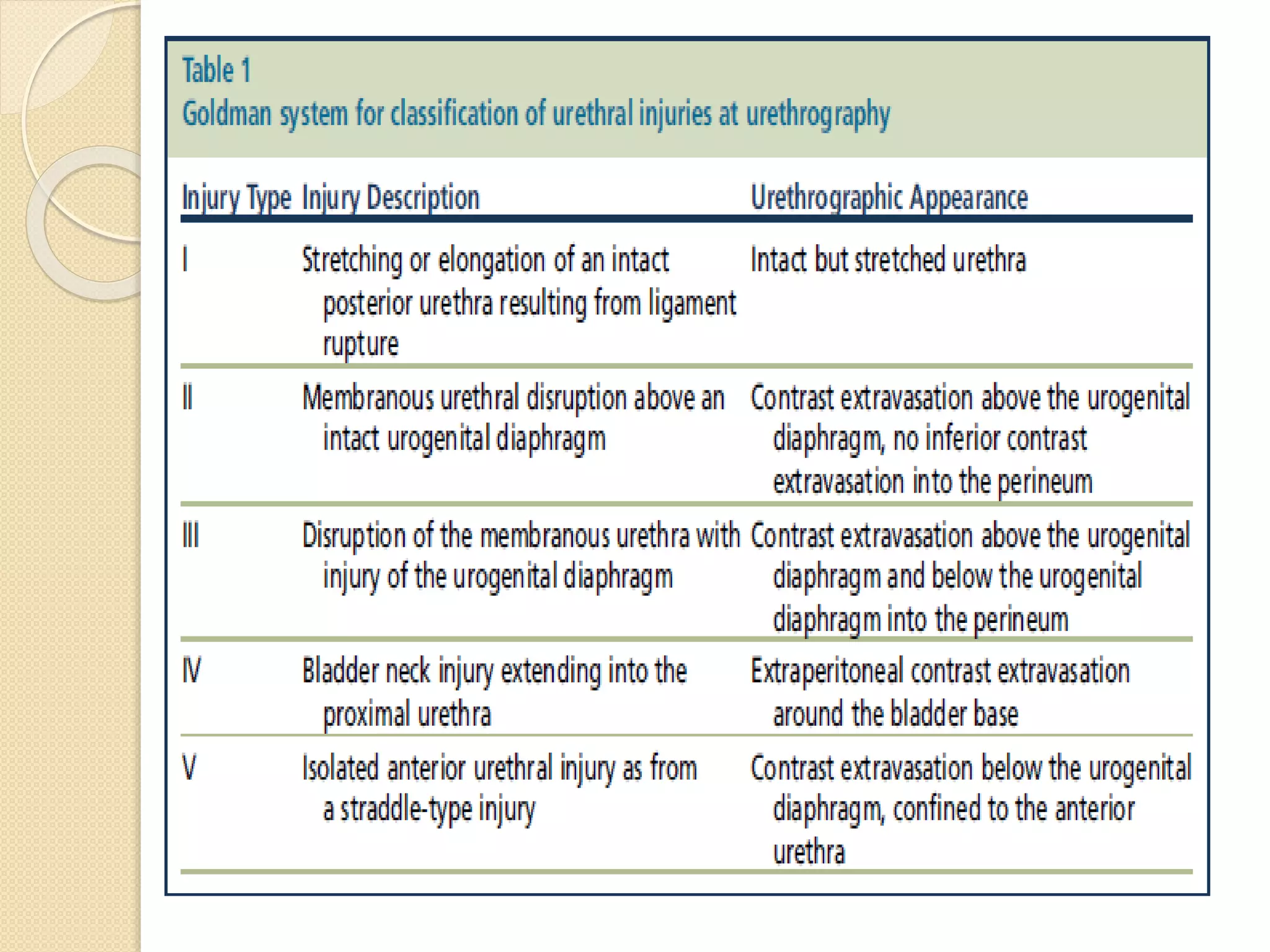
This document discusses injuries to the bladder and urethra, providing details on diagnosis and management. It notes that bladder injuries occur in 1.6% of blunt trauma victims and are usually associated with pelvic fractures. Gross hematuria is present in most bladder injury cases. Urethral injuries in males are divided into those affecting the posterior urethra associated with pelvic fractures, and anterior injuries from blunt or penetrating trauma. Diagnosis is via retrograde cystography or urethrography. Most extraperitoneal bladder ruptures are now managed non-operatively with catheter drainage, while intraperitoneal ruptures require surgical repair. Urethral injuries may be treated with immediate surgical closure, catheter drainage