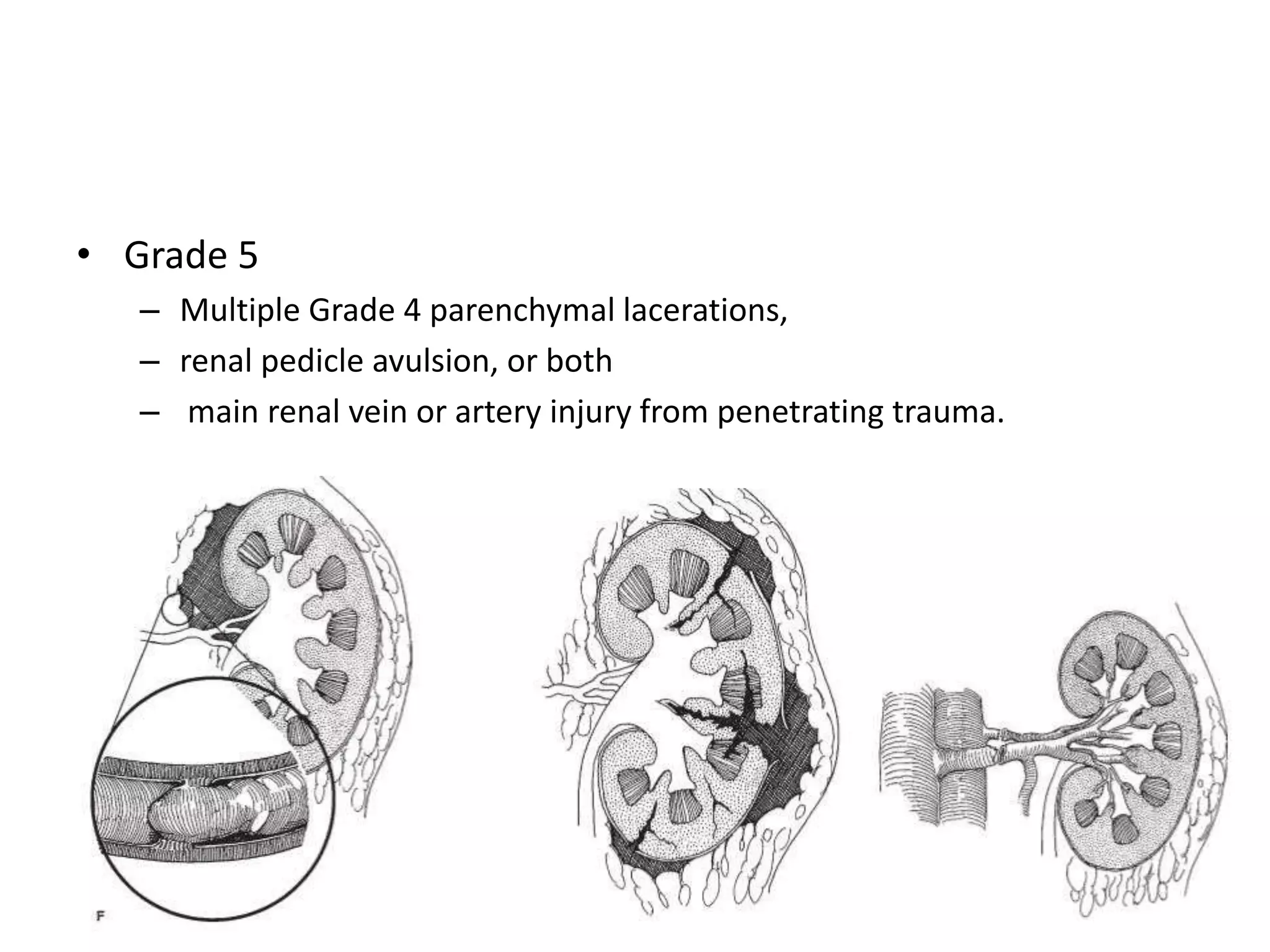
Renal trauma can be caused by either penetrating or blunt injuries. Blunt trauma accounts for 90-95% of renal injuries and is often caused by motor vehicle accidents or falls. The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) classification system grades renal injuries from 1 to 5 based on CT or surgical findings, with higher grades indicating more severe parenchymal lacerations or vascular injuries. Computed tomography (CT) with contrast is the gold standard for evaluating stable patients with renal trauma as it can detect lacerations, extravasation, and vascular injuries.










![Etiology
• Penetrating
- gunshot wounds
- stab wounds
• Blunt
- Rapid deceleration (eg, motor vehicle
crash
- fall from heights)
- direct blow to the flank (eg, physical
assault, sports injury)
Iatrogenic
- endourologic procedures
- extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy
- renal biopsy,
- percutaneous renal procedures
- Intraoperative
Other
- renal transplant rejection
- Childbirth [may cause spontaneous renal
lacerations]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renaltrauma-180209183957/75/Renal-trauma-11-2048.jpg)