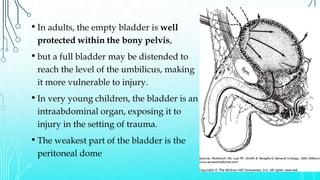
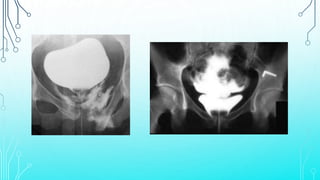
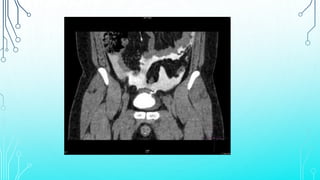
Bladder injuries can occur from trauma or medical procedures and range from extraperitoneal to intraperitoneal. Extraperitoneal injuries make up 70% of cases and are often associated with pelvic fractures, while intraperitoneal injuries expose the bladder more directly. Clinical signs include hematuria, pelvic pain, and inability to catheterize. Diagnosis involves cystography to detect contrast leakage. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the injury, with uncomplicated extraperitoneal injuries often managed conservatively with catheter drainage and complicated or intraperitoneal injuries typically requiring surgical repair.