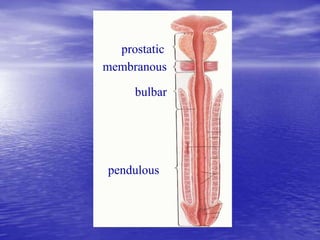
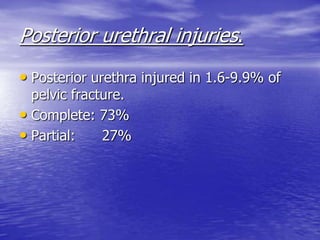
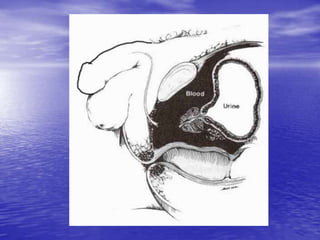
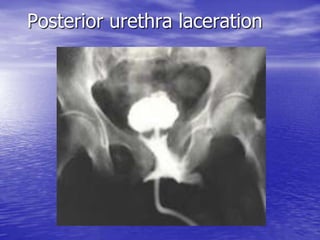
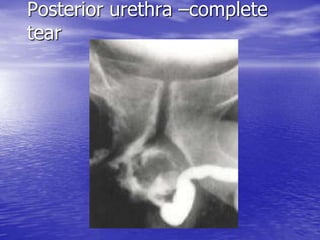
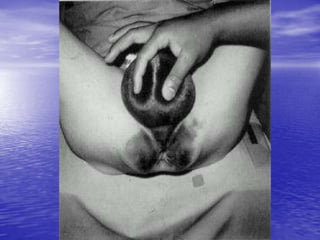
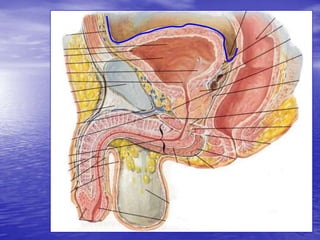
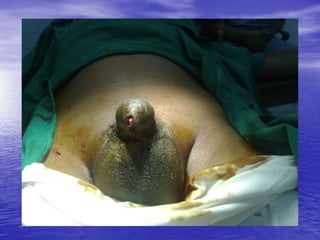
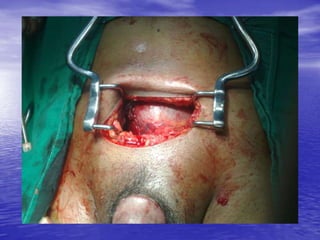
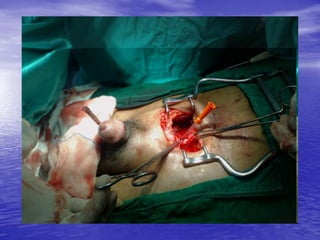
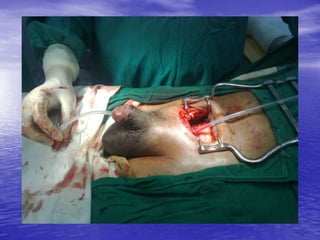
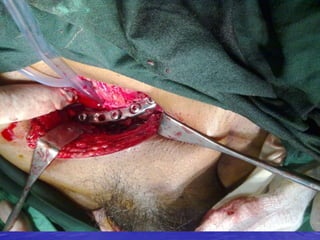
Urethral and bladder injuries can occur from pelvic fractures or direct trauma. Posterior urethral injuries commonly occur from shearing forces in pelvic fractures and require initial suprapubic cystostomy with delayed repair to avoid complications. Anterior urethral injuries from straddle injuries may be contusions or lacerations, treated with catheterization or cystostomy depending on severity. Bladder injuries are often extraperitoneal from pelvic fractures and present as hematuria, diagnosed by cystography or CT cystography and treated with catheter drainage. Intraperitoneal bladder injuries require surgery.