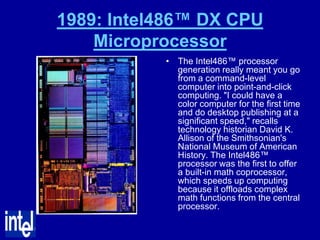
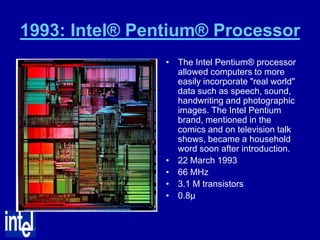
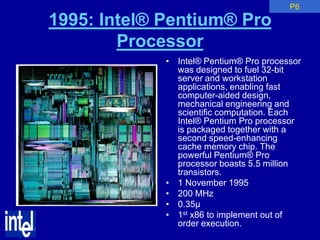
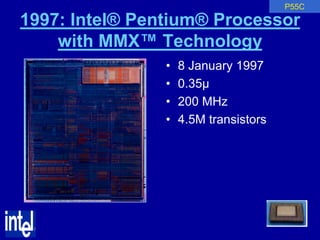
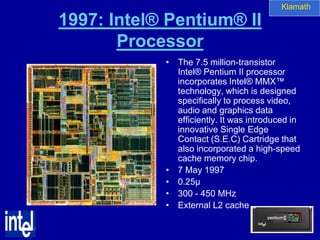
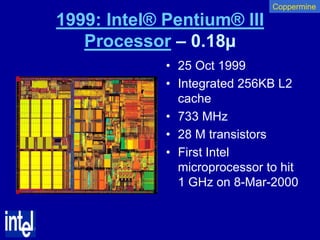
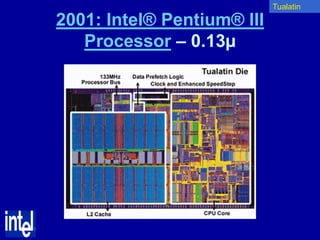
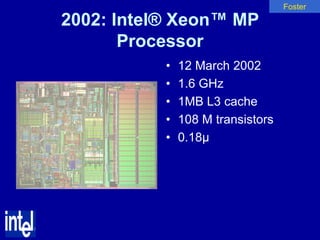
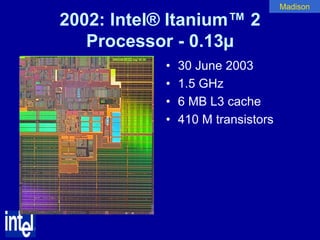
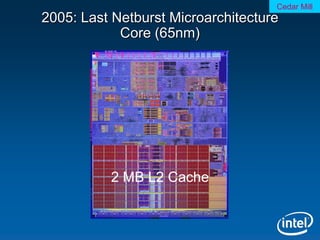
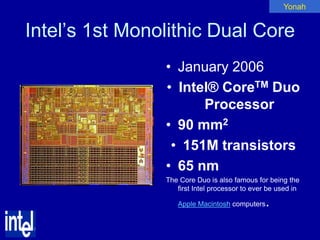
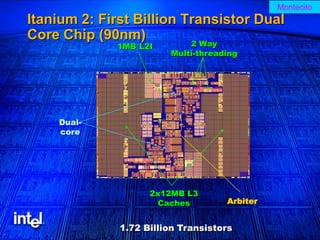
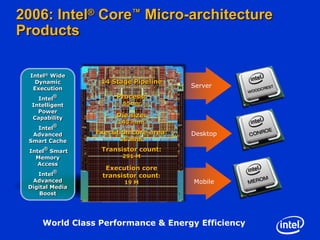
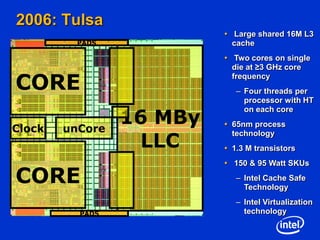
The document summarizes the evolution of Intel microprocessors from 1971 to 1999. It describes key microprocessors including the 4004, 8008, 8080, 8088, 286, 386, 486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium II, Pentium III, and Celeron. With each generation, transistors increased and features improved to enable more powerful personal computing. The Intel microprocessors established Intel as the dominant force in the PC market and fueled the growth of the personal computer industry.