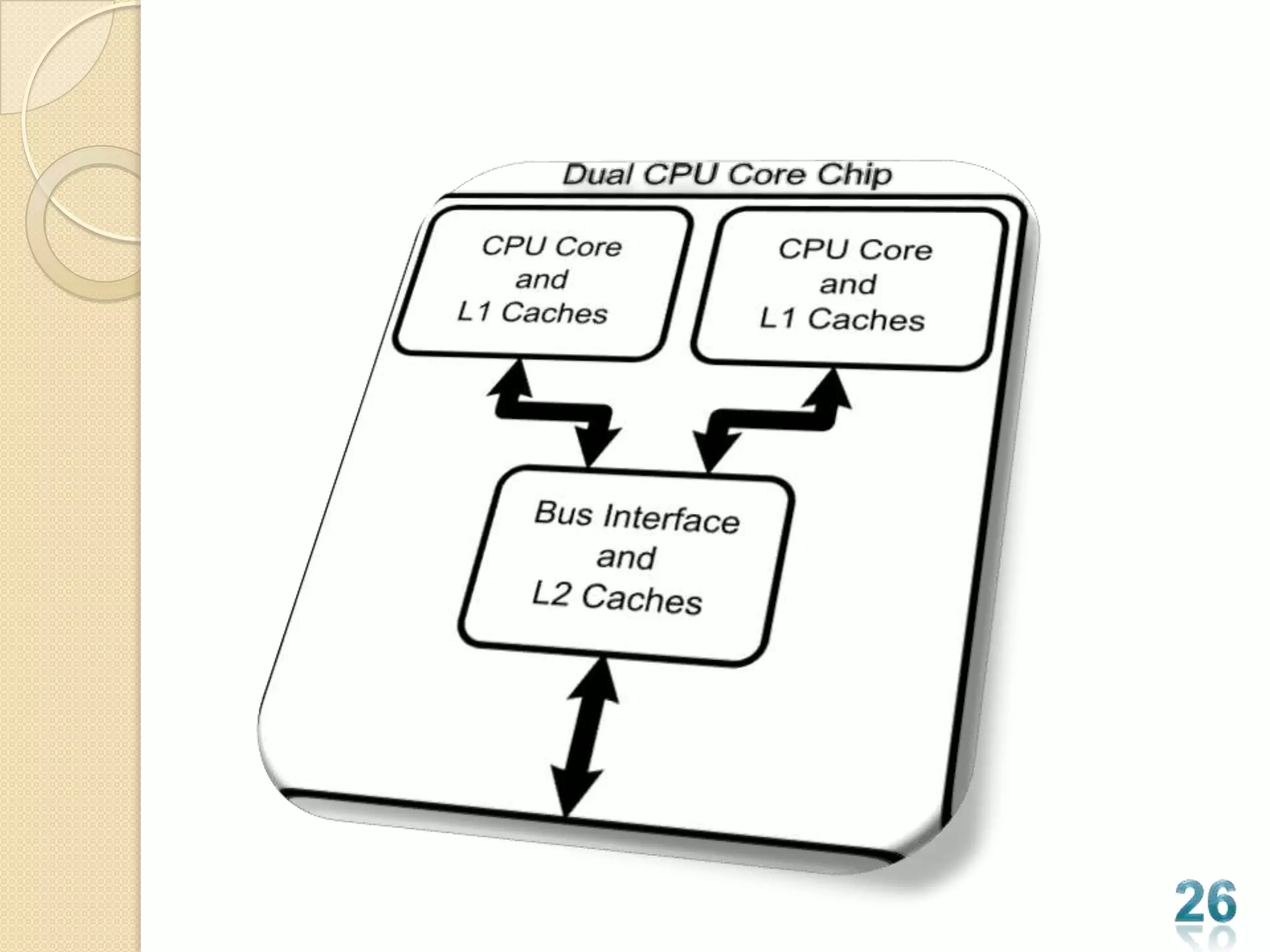
This document is a student's report on the history of microprocessors from 4-bit to 64-bit models. It outlines the major microprocessor models released by Intel from the 4004 in 1971 to the current multi-core 64-bit Core i7 models. For each generation of processors, details are given on specifications like clock speed, transistor count, cache memory and capabilities. The report provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of microprocessor technology and performance over decades.