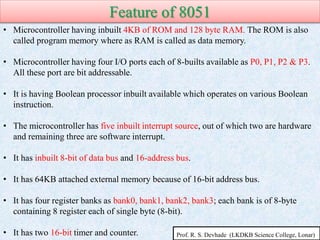
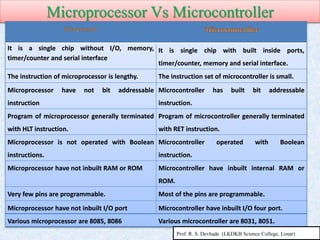
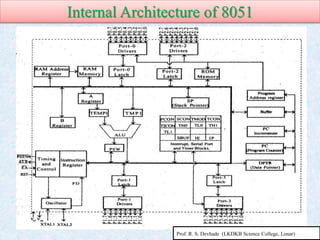
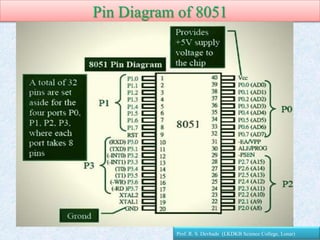
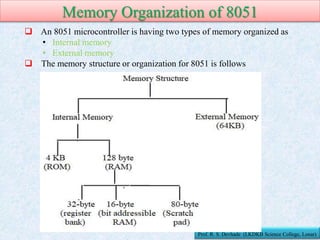
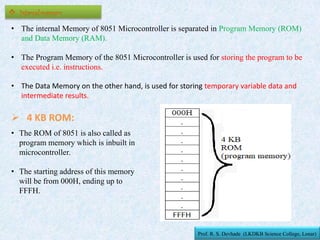
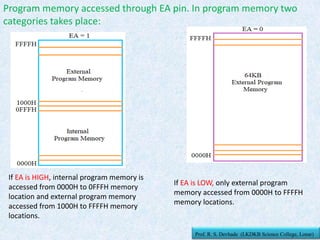
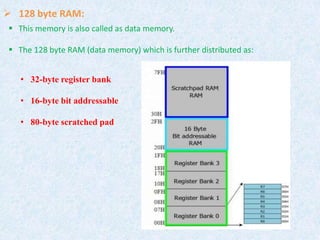
The document provides information about the 8051 microcontroller. It discusses the internal architecture and features of the 8051 microcontroller. The 8051 has 4KB of ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, four I/O ports, two timers, interrupts and more built into a single chip. It also compares microprocessors and microcontrollers, explaining that microcontrollers have internal memory and I/O ports built-in, while microprocessors do not. Additionally, it outlines the memory organization of the 8051, including its internal and external memory layout.