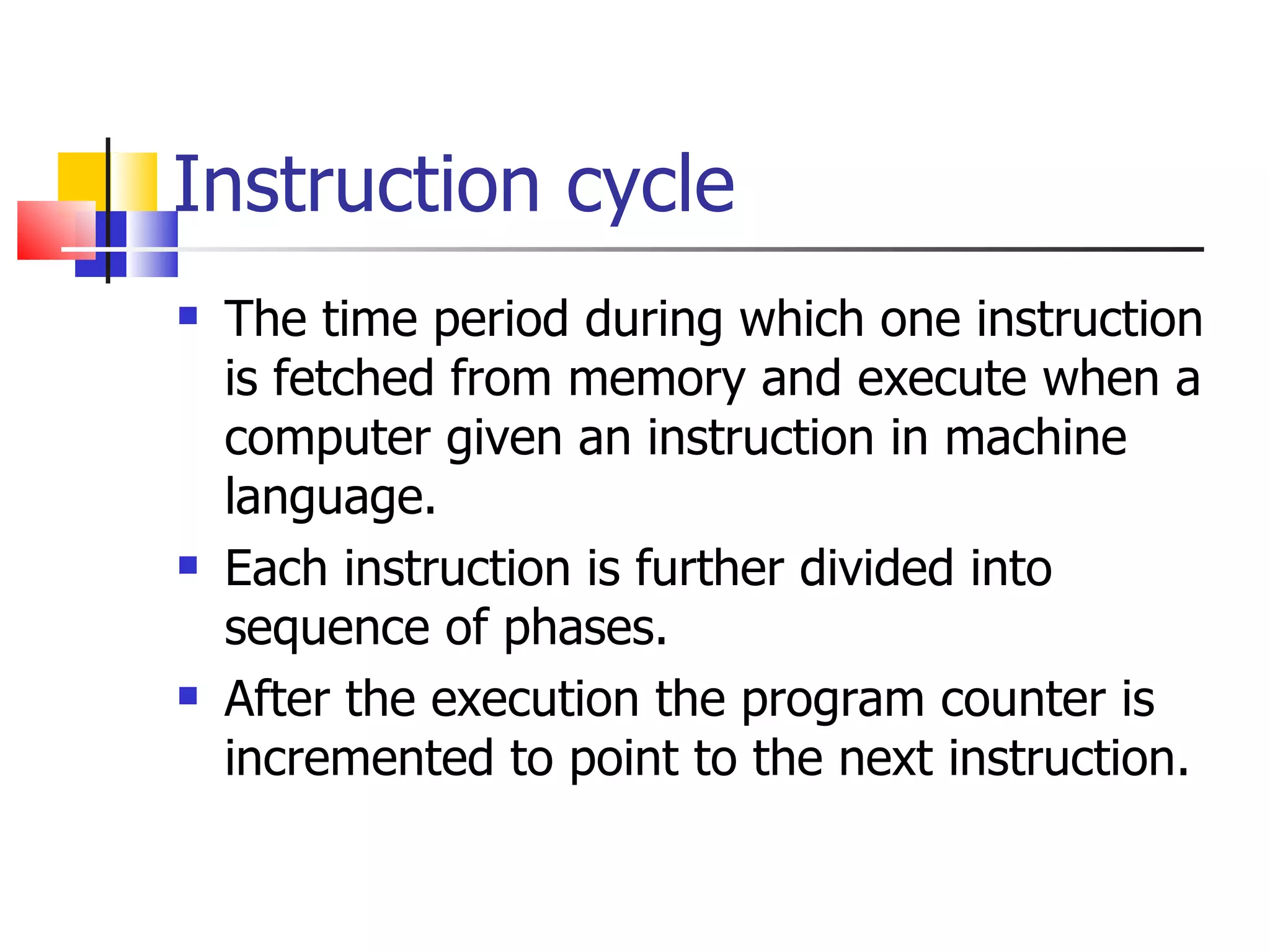
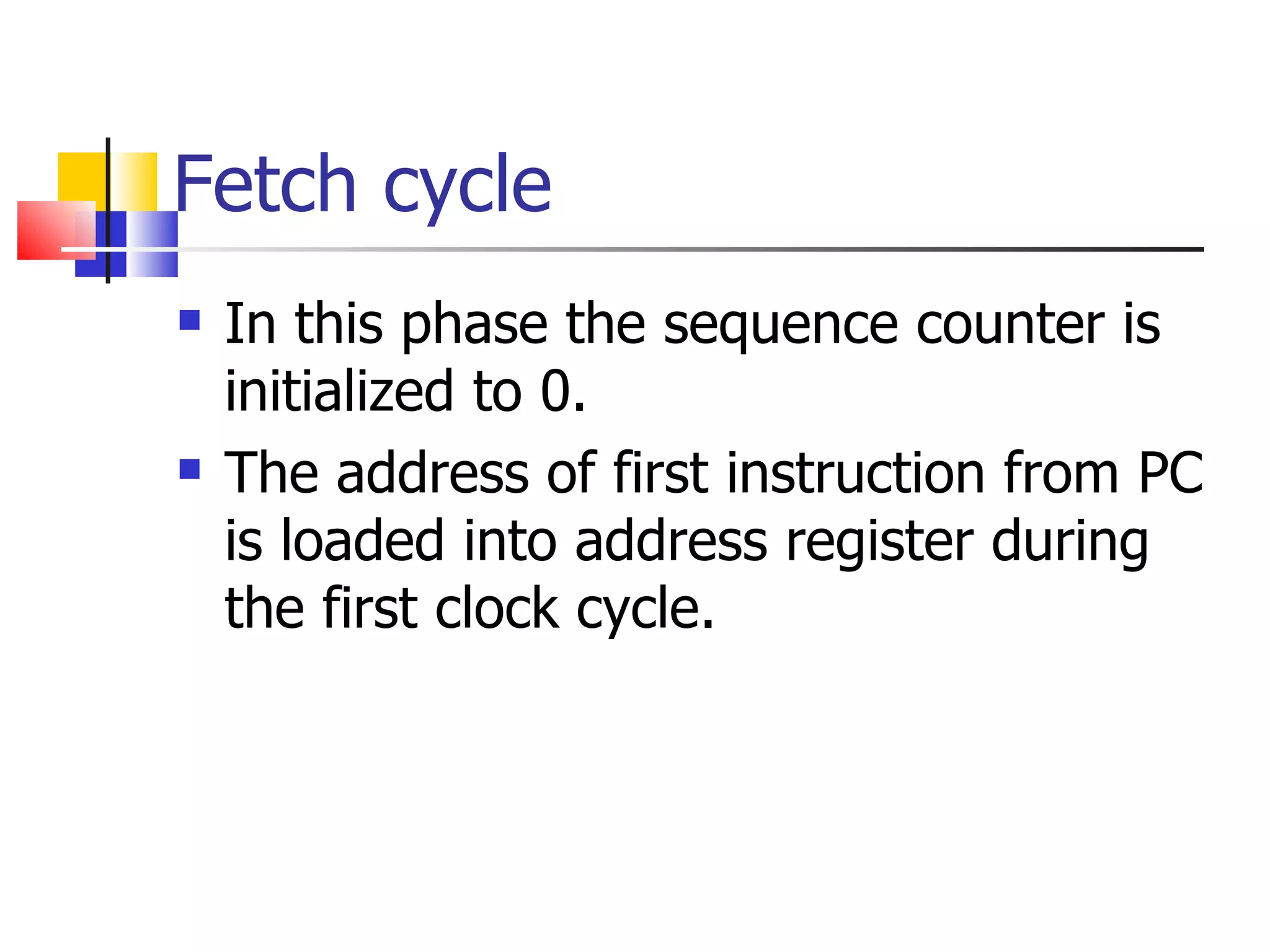
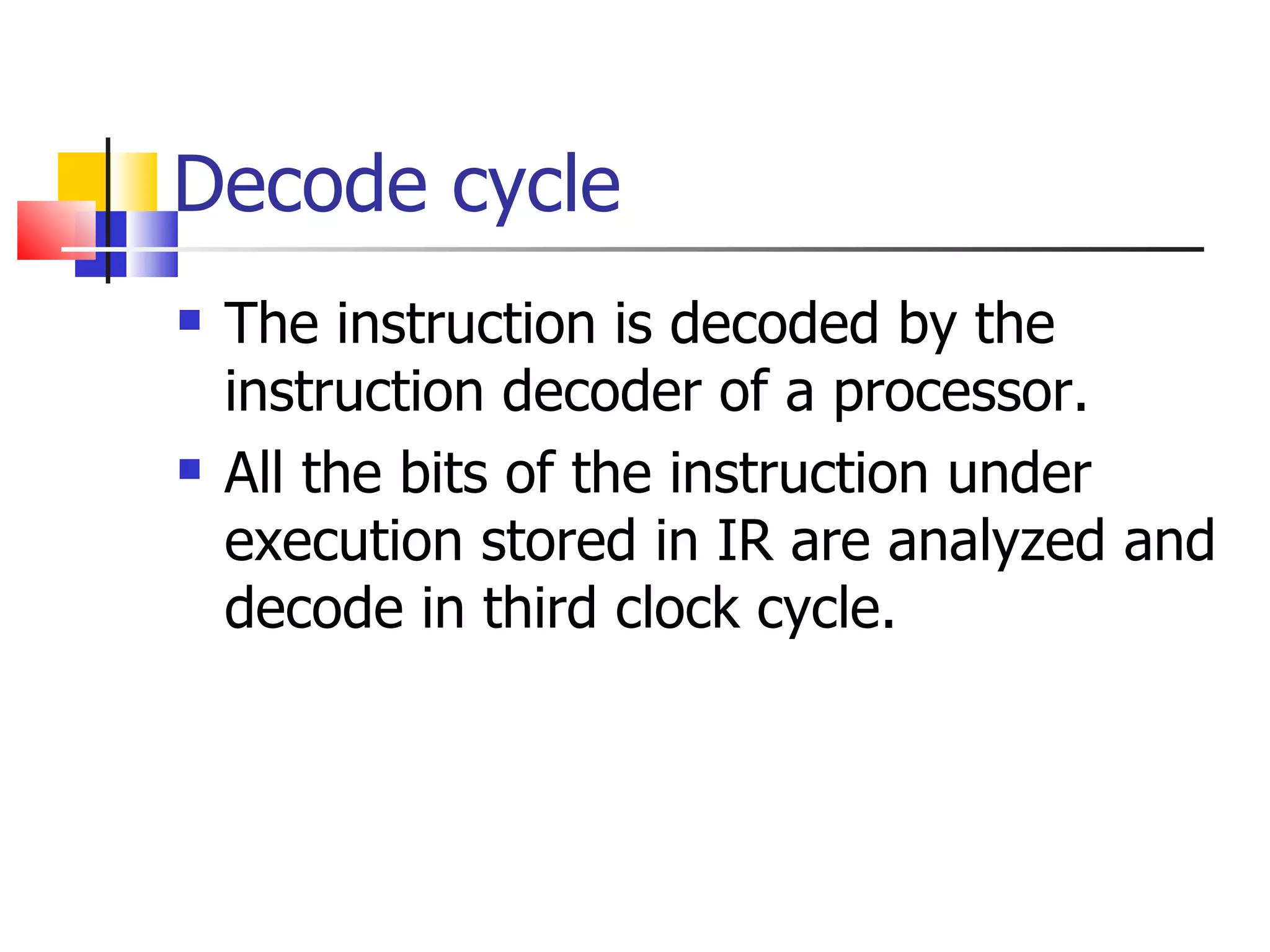
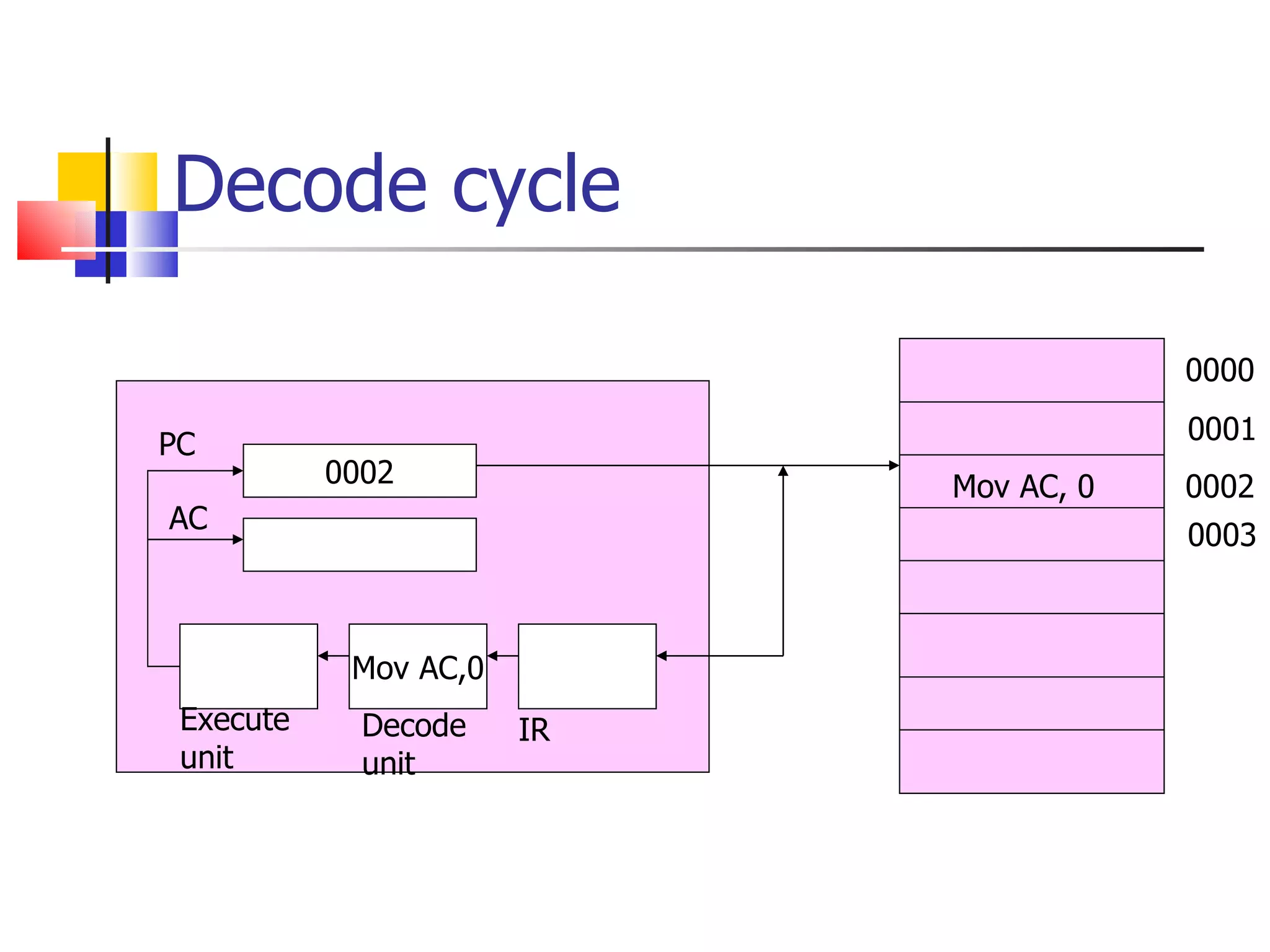
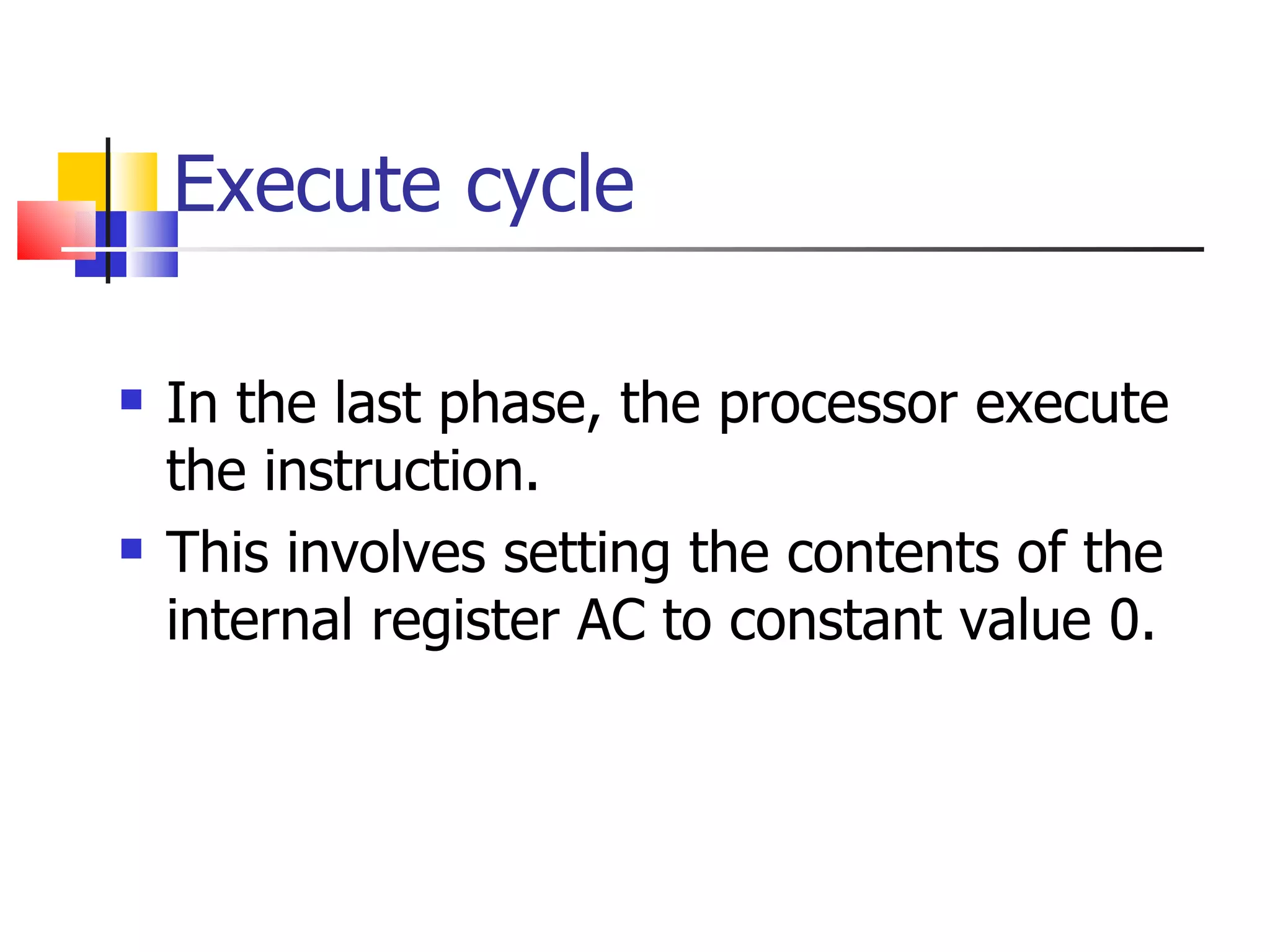
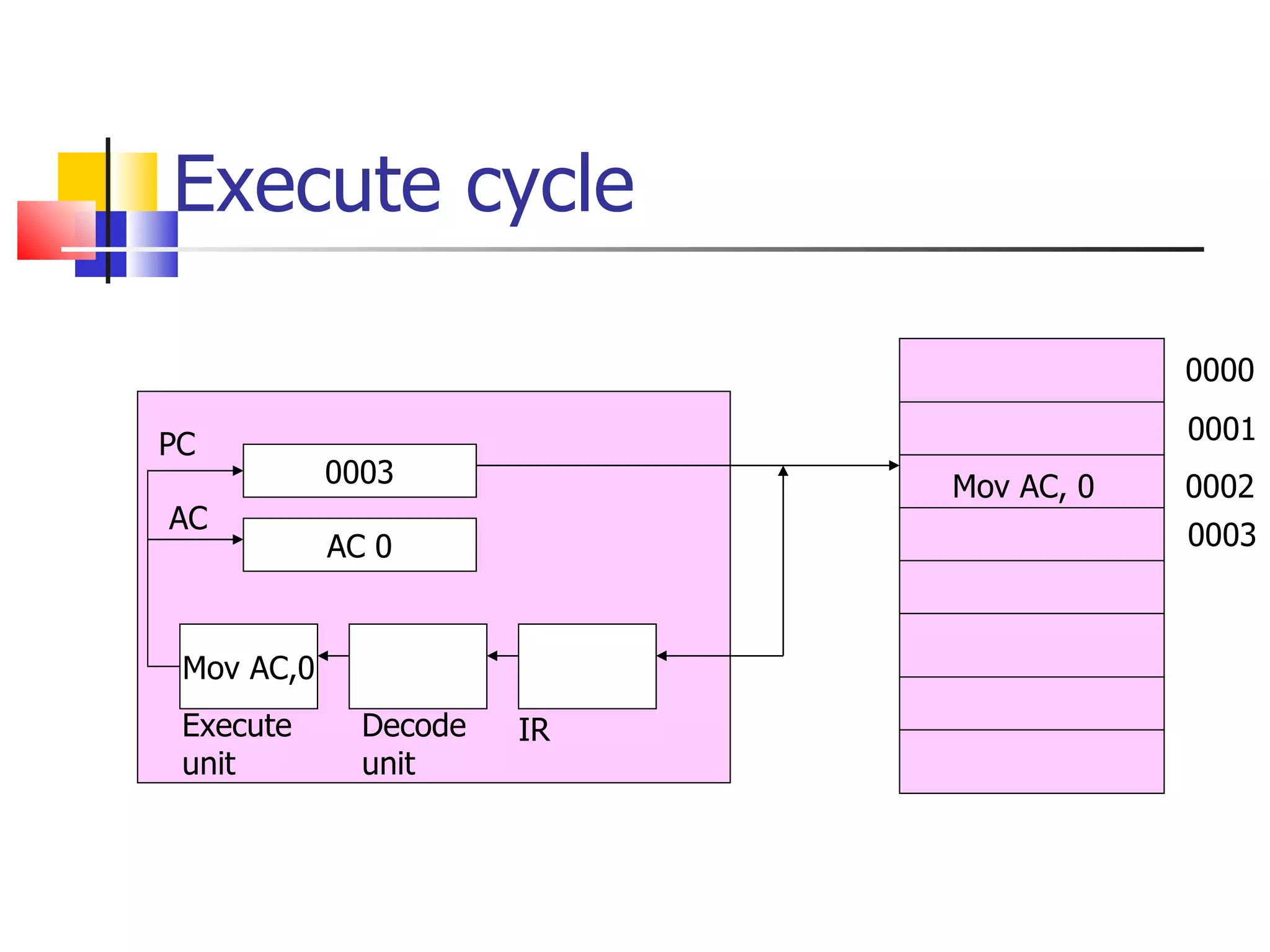
The instruction cycle describes the process a computer follows to execute each machine language instruction. It involves 4 phases: 1) Fetch - the instruction is fetched from memory and placed in the instruction register. 2) Decode - the instruction is analyzed and decoded. 3) Execute - the processor executes the instruction by performing the specified operation. 4) The program counter is then incremented to point to the next instruction, and the cycle repeats. Each phase involves transferring data between the program counter, instruction register, memory, and other components via a common bus under the control of a timing unit. The instruction specifies the operation to be performed, such as a memory reference, register operation, or I/O access.



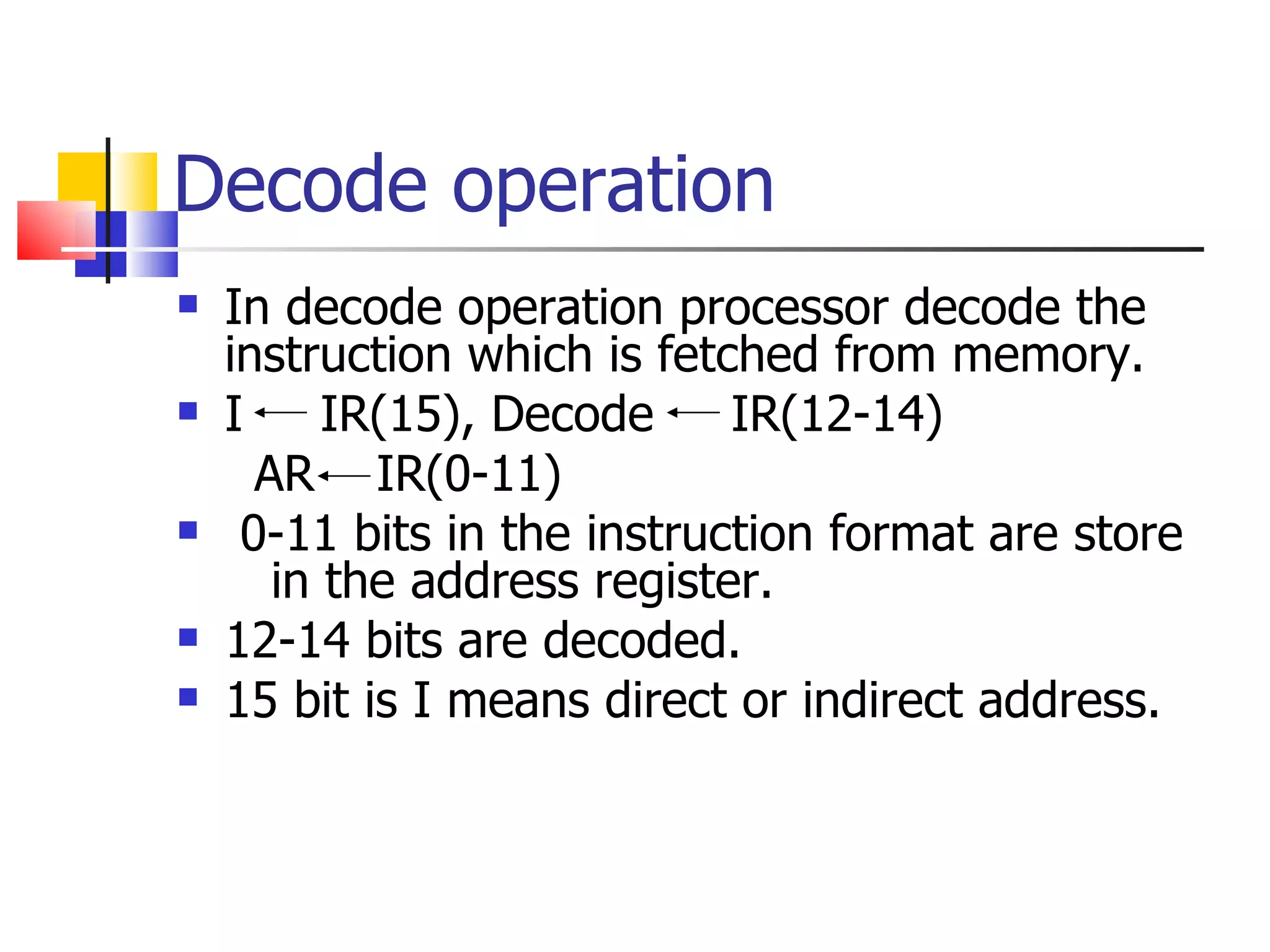
![SC 0 AR PC IR M[AR], PC PC+1 Decode IR(12-14) IR(15), AR IR(0-11) D I I Execute reg. reference Execute I/O reference Execute memory reference Execute memory reference Nothing AR M[AR] =0 Memory reference I/O or reg. reference 1= =1 0= =1 0= I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-111228101635-phpapp01/75/Instruction-cycle-11-2048.jpg)
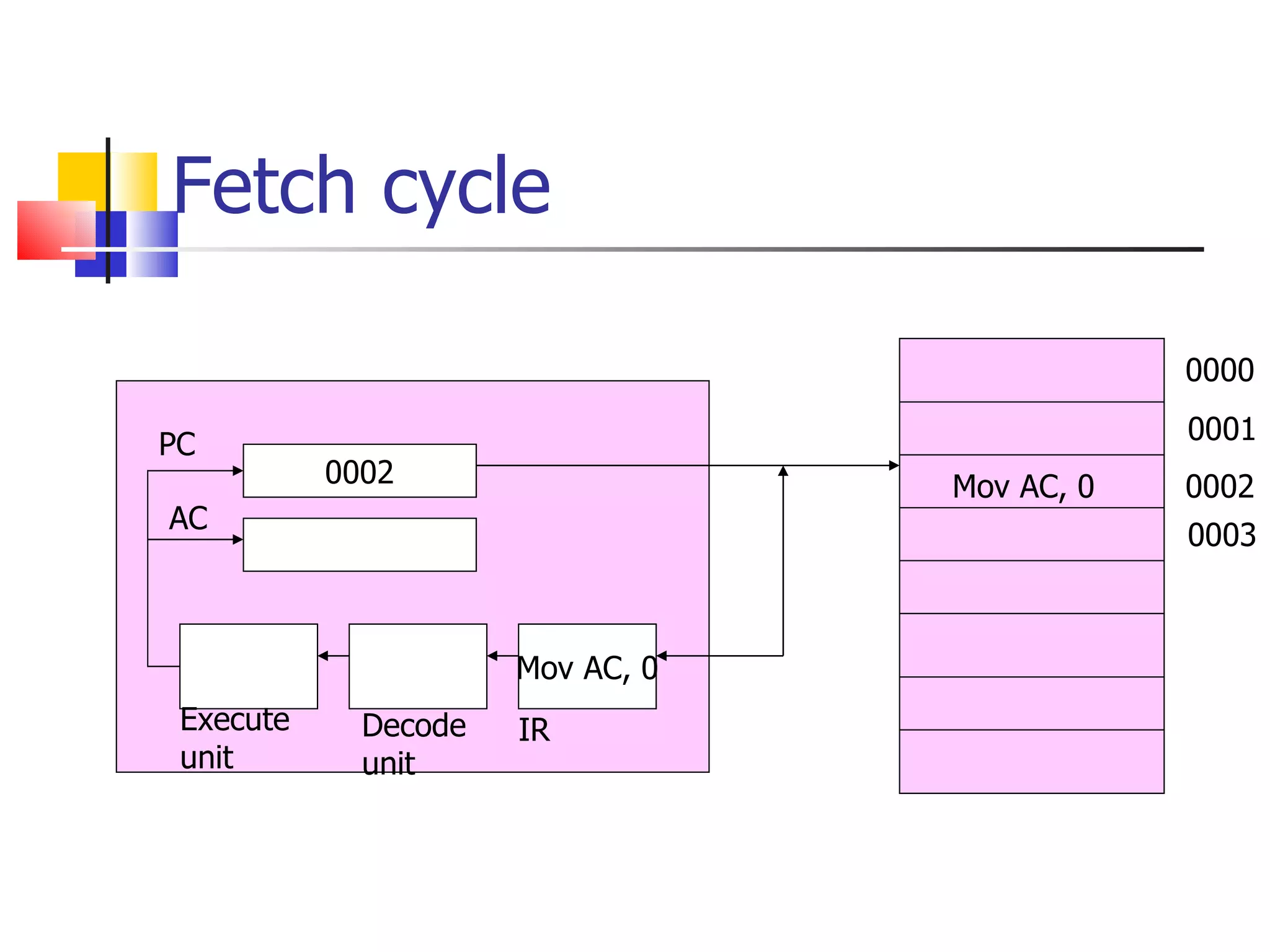
![Fetch operation The circuit comprises of various registers, memory unit I/O devices, control and timing unit ALU and a common bus. AR PC IR M[AR], PC PC+1 The instruction read from memory is then placed in the instruction register.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-111228101635-phpapp01/75/Instruction-cycle-12-2048.jpg)

![Execution Operation If D=0 and IR(15)=0, that means memory reference instruction is direct address instruction. If D=0 and IR(15)=1, that means memory reference instruction is indirect address instruction. AR M[AR], AR holds the address part of the instruction After the instruction is executed, SC is cleared to 0 and control returns to the fetch phase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instructioncycle-111228101635-phpapp01/75/Instruction-cycle-15-2048.jpg)
