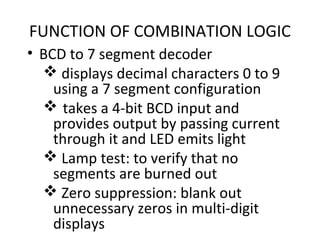
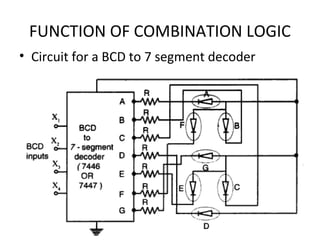
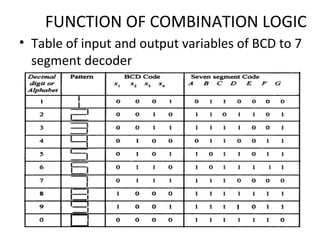
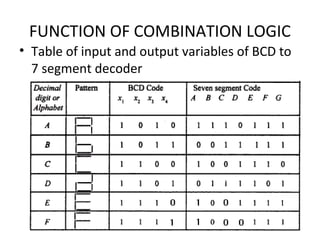
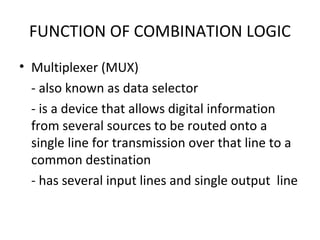
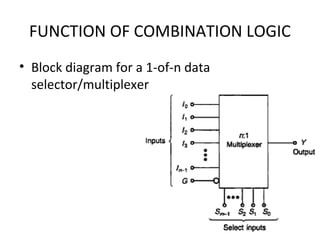
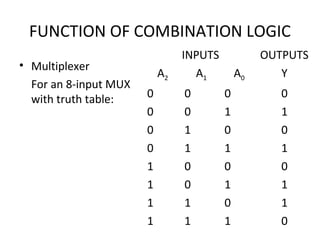
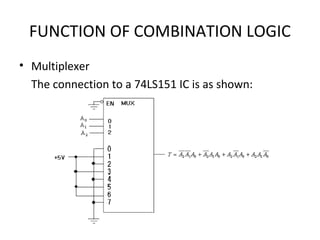
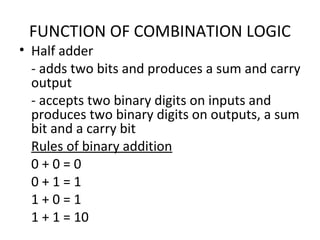
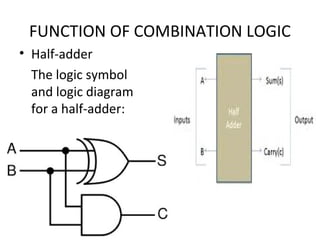
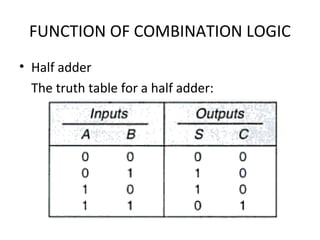
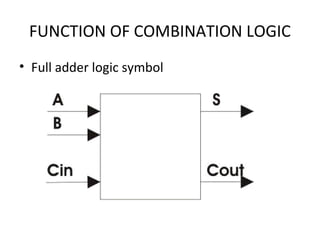
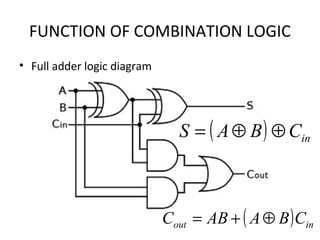
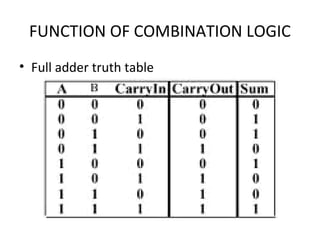
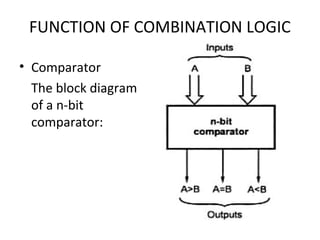
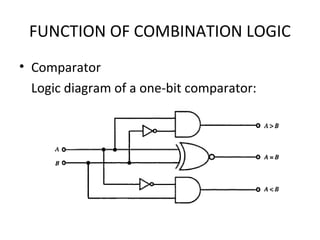
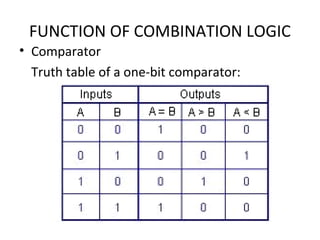
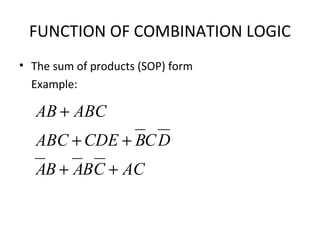
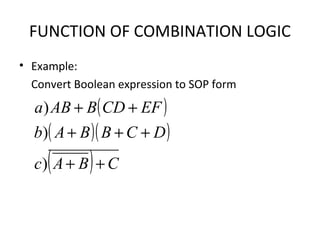
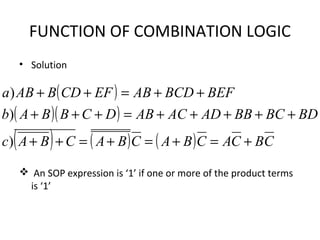
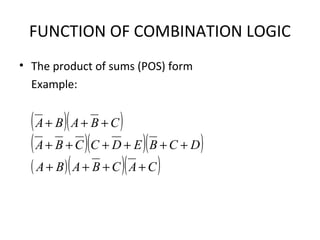
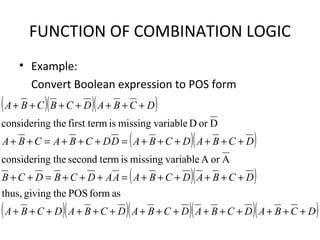
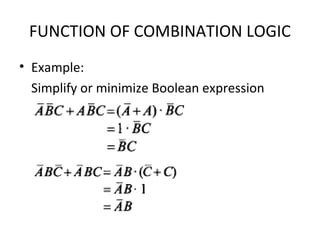
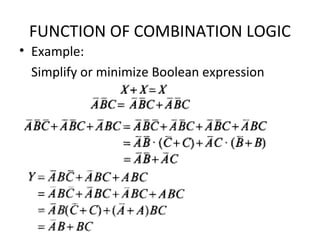
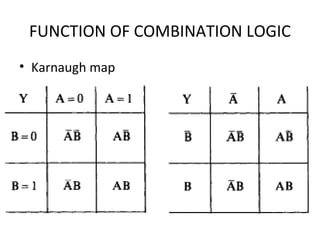
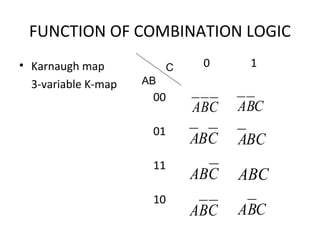
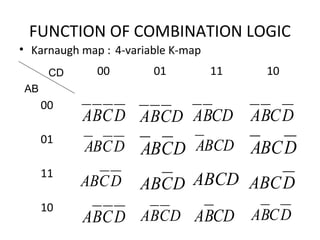
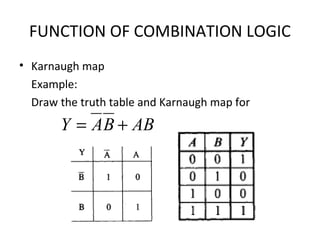
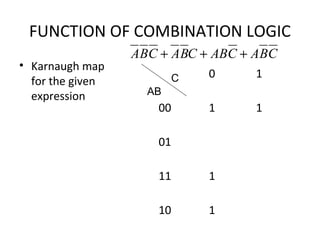
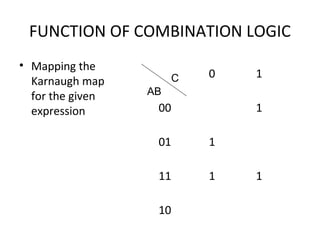
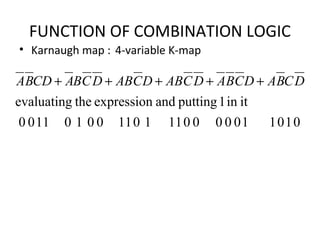
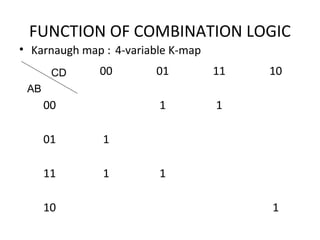
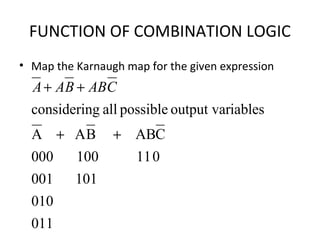
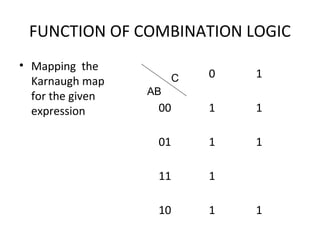
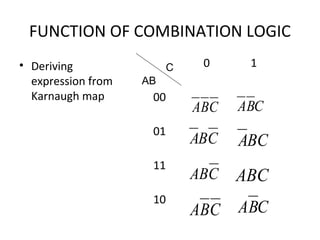
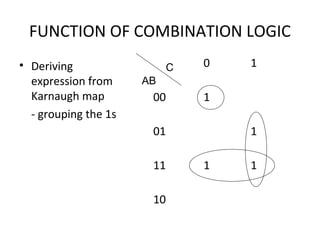
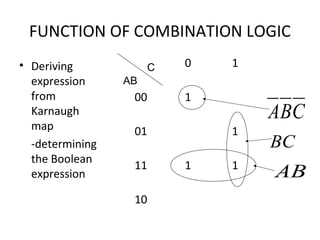
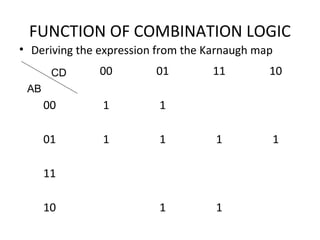
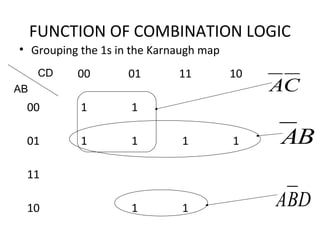
This document discusses various functions of combination logic. It describes BCD to 7-segment decoders, multiplexers, tri-state logic, fan-out, addresses, half adders, full adders, comparators, logic minimization using Karnaugh maps. BCD to 7-segment decoders convert 4-bit codes to activate the correct LED segments. Multiplexers allow selecting one of several inputs to transmit on a single output line. Tri-state logic adds a high impedance state to prevent bus conflicts. Karnaugh maps provide a systematic way to simplify Boolean logic expressions by grouping adjacent ones.