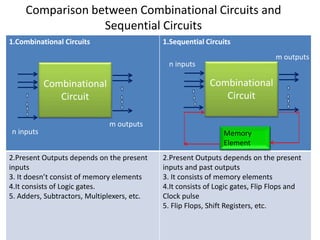
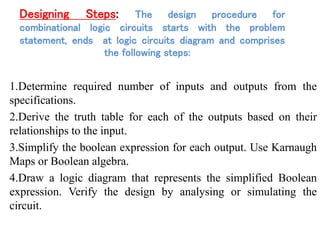
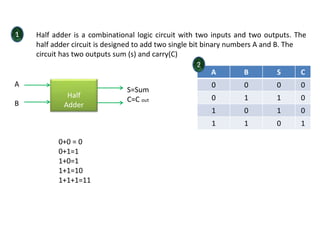
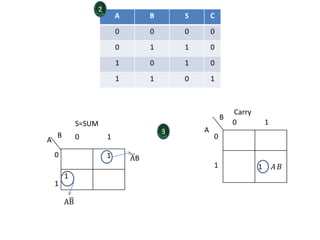
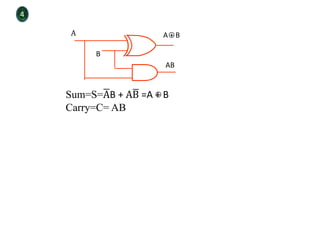
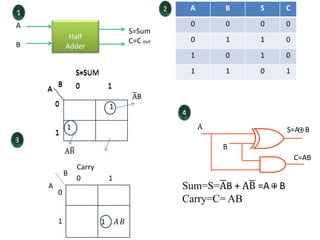
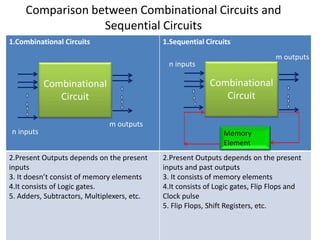
Combinational logic circuits have outputs that depend only on present inputs. They do not have memory elements and consist only of logic gates. A half adder is a simple combinational logic circuit with two inputs - A and B. It has two outputs - the sum (S) and carry (C). It is designed to add two single bit binary numbers and its truth table and logic diagram are presented as an example.