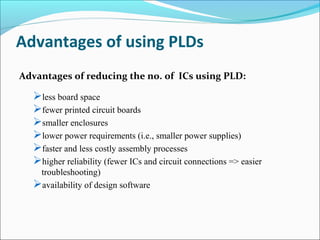
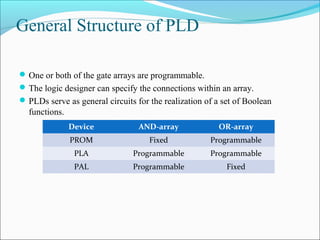
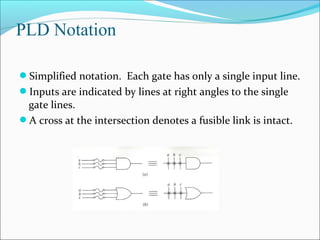
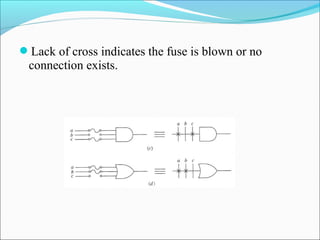
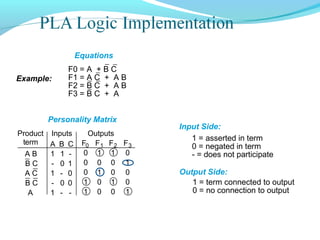
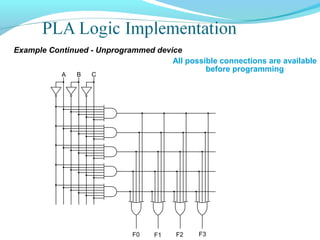
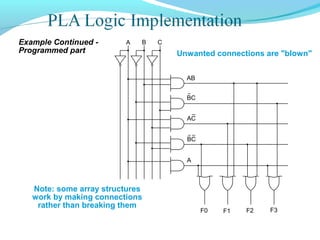
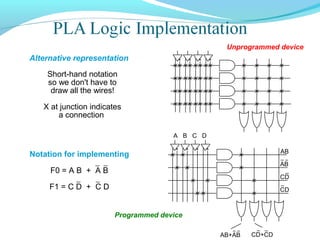
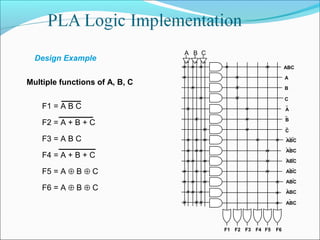
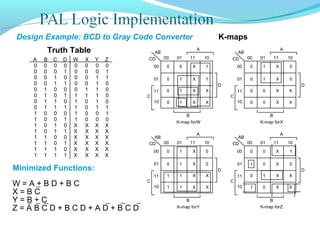
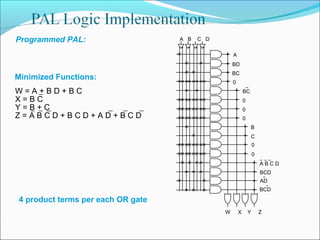
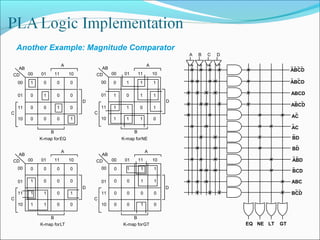
This document discusses programmable logic devices (PLDs), including their structure, programming, advantages, and examples. PLDs contain programmable logic elements like gates and flip-flops that can be configured by the user to implement different logic functions. This reduces components compared to using separate ICs, lowering costs and improving reliability. The document examines the structures of programmable array logic (PAL) and programmable logic arrays (PLA), how they are programmed, and provides examples of implementing logic functions with each. It also discusses more complex PLDs and field programmable gate arrays, which provide even more programmable logic resources.