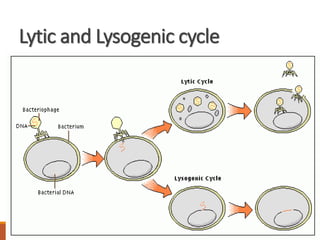
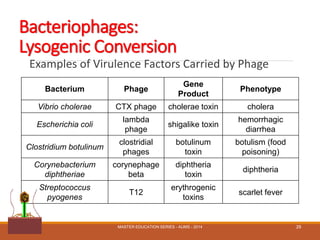
Bacteriophages are viruses that specifically infect and destroy bacteria, with significant medical applications, including phage therapy for bacterial infections. They can either undergo a lytic cycle, leading to host cell destruction, or a lysogenic cycle, where their genetic material integrates into the host's DNA, potentially enhancing the virulence of bacteria. Over 5000 bacteriophages have been classified into 13 families based on their structure and characteristics.