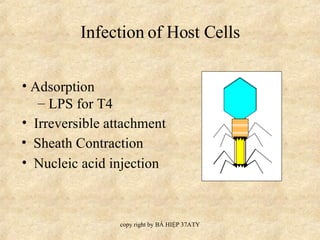
Bacteriophage, or phages, are viruses that infect bacteria. They have potential medical applications as alternatives to antibiotics. Some companies are studying phages to treat infections caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella. Phages can either undergo a lytic cycle, where they multiply within the host and cause it to lyse, or a lysogenic cycle where they integrate into the host genome and remain dormant. The lysogenic cycle provides a model for how some animal viruses cause transformation of cells.