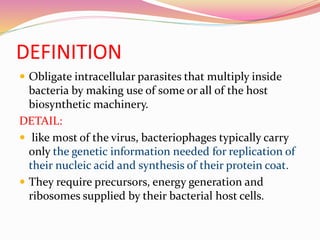
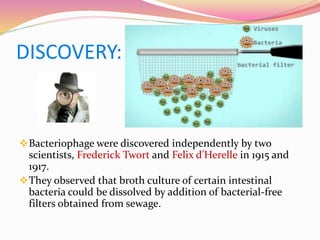
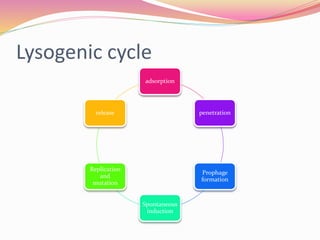
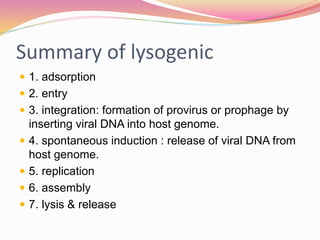
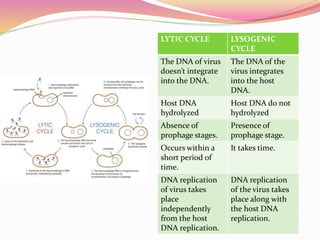
Bacteriophages are viruses that specifically infect bacteria, using the host's cellular machinery for replication and reproduction. They have complex structures, exist in lytic and lysogenic life cycles, and can be transmitted between bacteria via transduction. While they offer advantages as potential antibiotics against resistant bacteria, their use is limited by specificity and a lack of extensive efficacy studies.



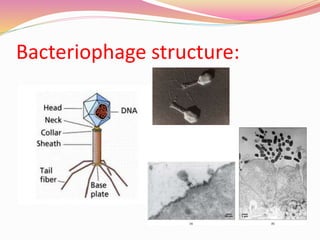
![MORPHOLOGY:
Phages have a complex structure.
They have tadpole shaped, with hexagonal head and a
cylinderical tail.
The head consists of a tightly packed core of nucleic acid
[DNA].
It surrounded by a protein coat or capsid.
size of the head vary in different phages; from 28nm to 100nm.
Tail is composed of a tightly packed core and the tail fiber is
attached.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriophage2020-200907135658/85/Bacteriophage-6-320.jpg)

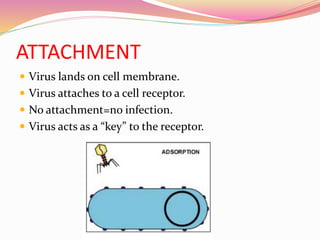
![PENETRATION
Virus enzyme weakens cell membrane.
Genetic material [DNA/RNA] enters host cell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriophage2020-200907135658/85/Bacteriophage-12-320.jpg)




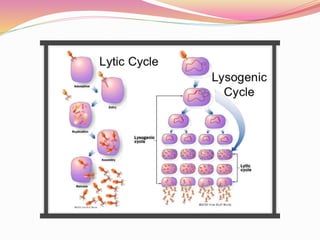

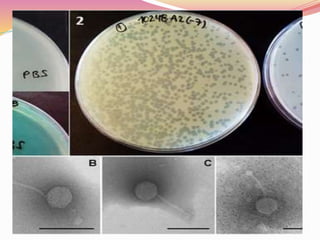
![PHAGE ASSAY
Lysis of the bacteriophage is indicated by theformation of a
zone of clearing or plaque within the lawnof bacteria.
The number of plaques that develop and the appropriate
dilution factors can be used to calculate the number of
bacteriophages.
i.e. Plaque forming units[PFU] in a sample.
PURPOSE;
This can be used to purify a clonal population of virus or
determine viral titer as pfu/ml. So that known amount of
virus can be used to infect cells during subsequent work.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriophage2020-200907135658/85/Bacteriophage-23-320.jpg)