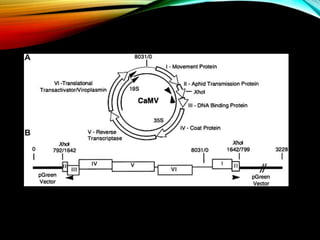
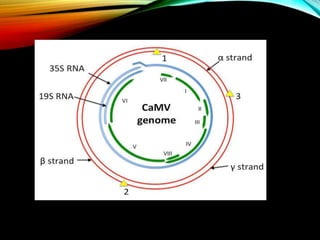
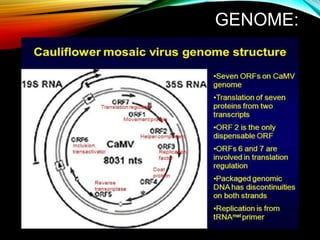
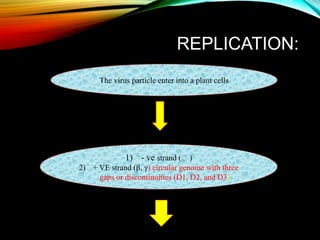
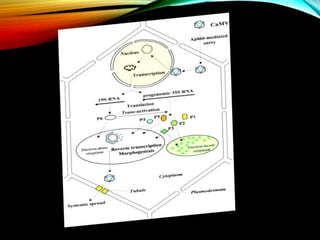
The document discusses the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV), the first plant virus with a DNA genome that primarily affects the Brassicaceae family and is transmitted by aphids. It highlights the virus's significance in plant virology and genetic engineering, particularly through its strong 35S promoter, which is widely utilized in genetically modified organisms. The document also outlines the virus's structure, replication process, and the risks associated with using its promoter in transgenic crops.