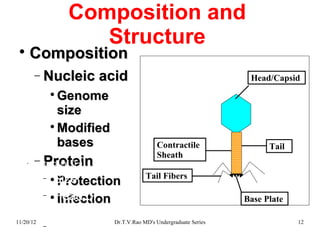
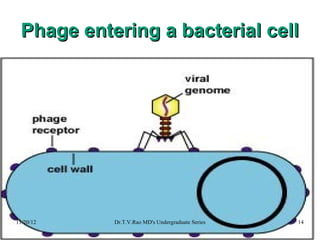
Bacteriophages, or phages, are viruses that specifically infect and destroy bacteria, initially observed in the early 20th century. They can replicate within bacteria using the host's machinery and exhibit various life cycles, including lytic and lysogenic, with implications for gene transfer and medical applications. Bacteriophages also play a role in enhancing bacterial virulence through lysogenic conversion, carrying genes that can produce toxins and other harmful factors.