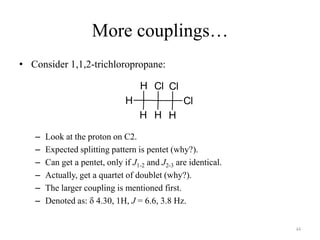
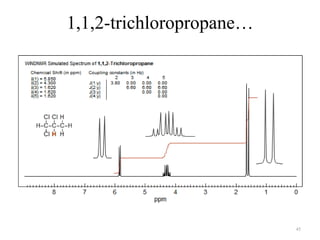
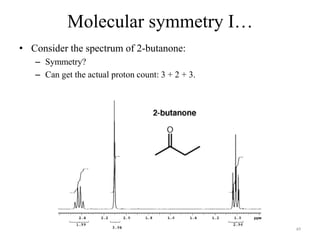
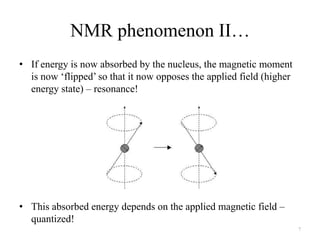
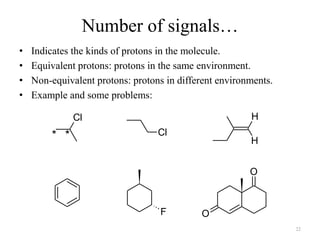
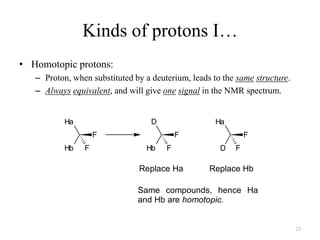
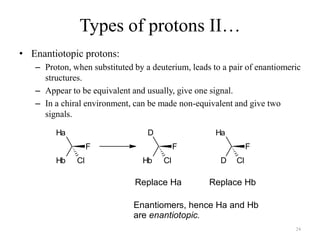
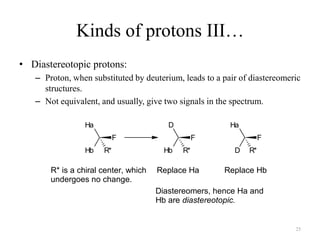
1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy utilizes the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine the structure of organic molecules.
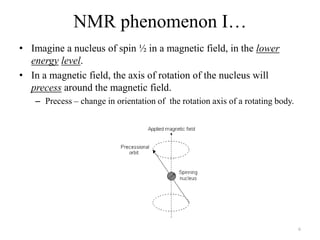
2. NMR works by applying a strong magnetic field which causes the nuclei of atoms like 1H, 13C, and 19F to align and absorb electromagnetic radiation at characteristic frequencies.
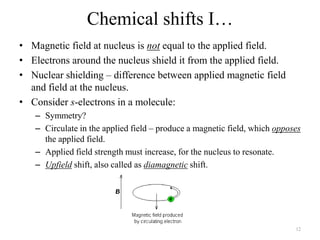
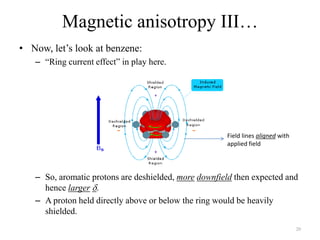
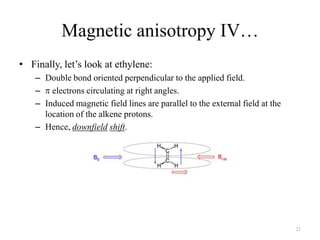
3. The frequency of absorption, known as the chemical shift, depends on the magnetic field strength and the electron density around the nucleus, providing information about the molecular structure.

















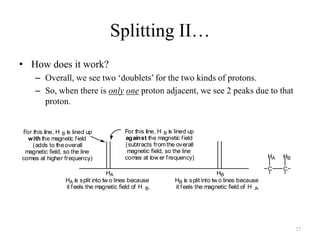

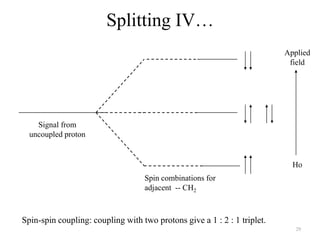

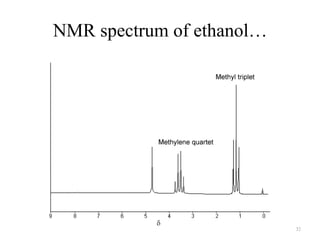
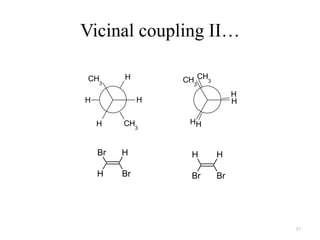
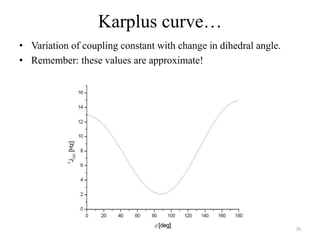

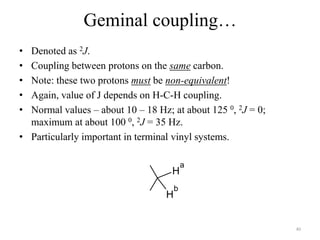


!['W' coupling…
a
H H
a
H a
H
b
b
O H H
H b
H
4J
ab (meta) = 1 – 3 Hz 4J
ab = 0 – 2 Hz Bicyclo[2.2.1]hexane
4J = 7 Hz
ab
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearmagneticresonance-partiallecturenotes-120401050220-phpapp02/85/Nuclear-magnetic-resonance-partial-lecture-notes-43-320.jpg)