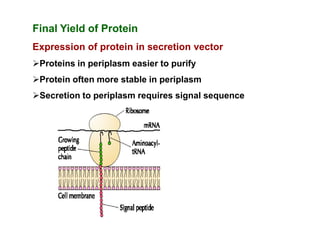
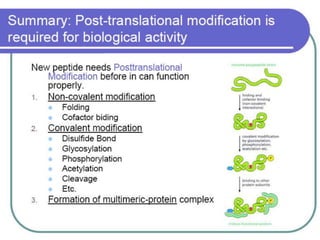
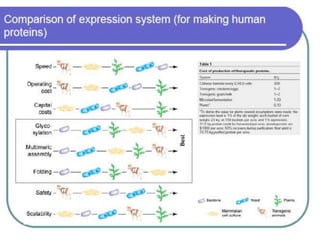
Commercial production of gene products requires high levels of gene expression. Several factors can be manipulated to increase protein production, including the vector, host chromosome location, gene dosage, transcription elements like promoters and terminators, translation elements like ribosome binding sites, and codon optimization. Final localization of the protein, such as secretion extracellularly, and preventing degradation through fusion proteins or other means can also improve yields. However, expression in E. coli has limitations like the inability to perform post-translational modifications and potential endotoxin contamination.