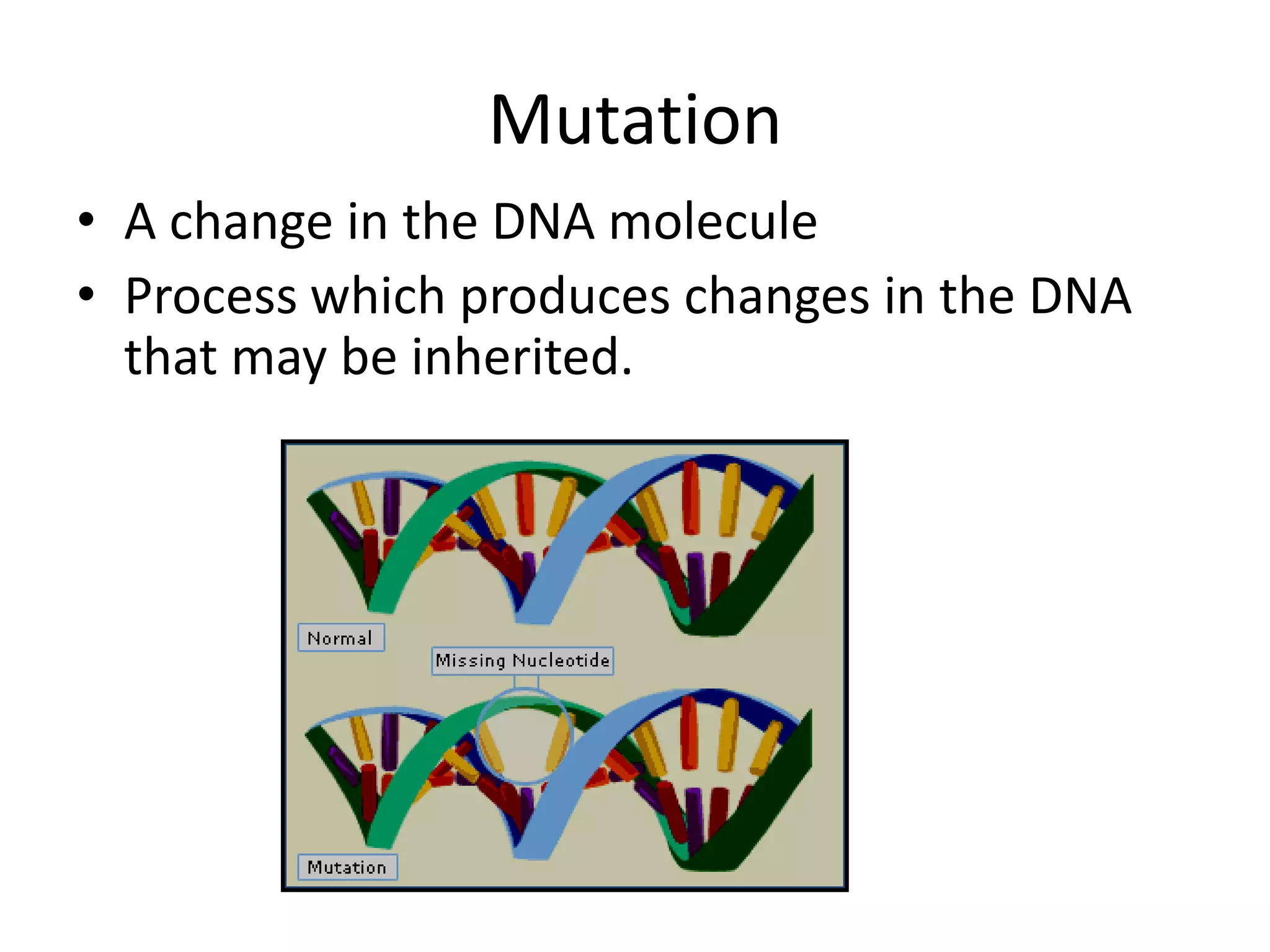
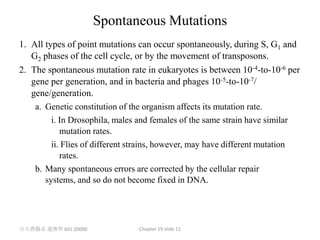
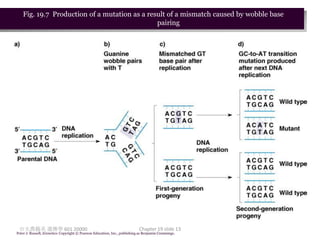
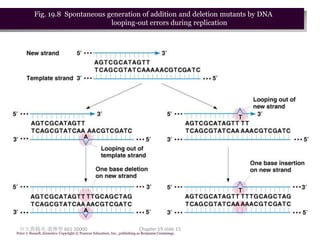
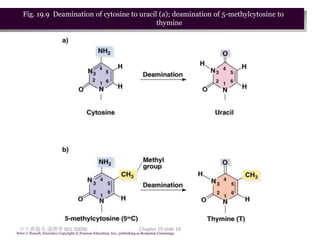
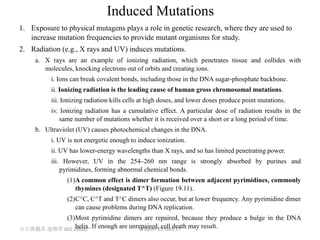
1. Mutation refers to changes in DNA that may be inherited. Mutations can occur spontaneously during DNA replication or due to exposure to mutagens.
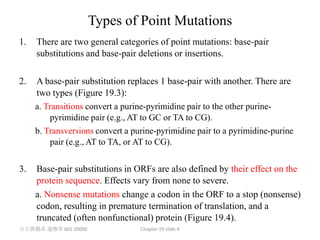
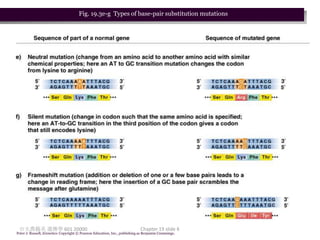
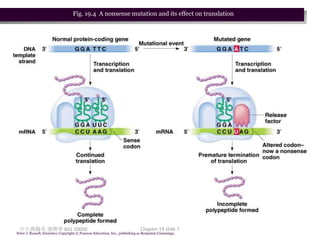
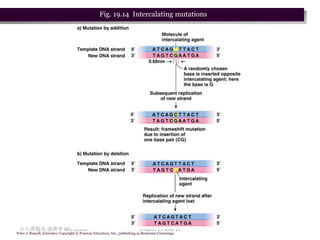
2. There are two main types of point mutations: base substitutions which replace one base with another, and deletions/insertions which remove or add DNA bases. These mutations can have varying effects on protein function.
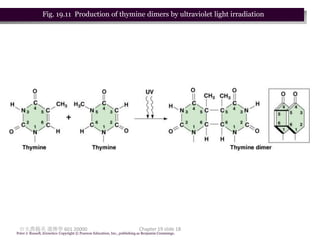
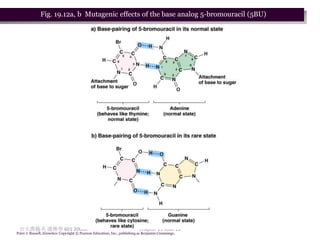
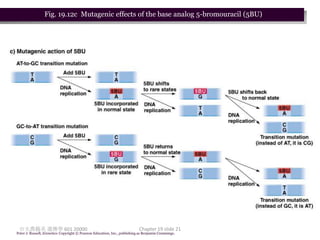
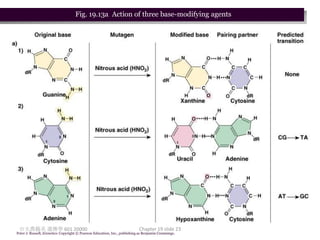
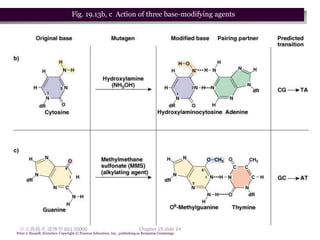
3. Mutagens like radiation and UV light can induce mutations by damaging DNA and interfering with its replication. Ionizing radiation breaks DNA bonds while UV causes pyrimidine dimers that introduce mutations.