Embed presentation
Downloaded 216 times



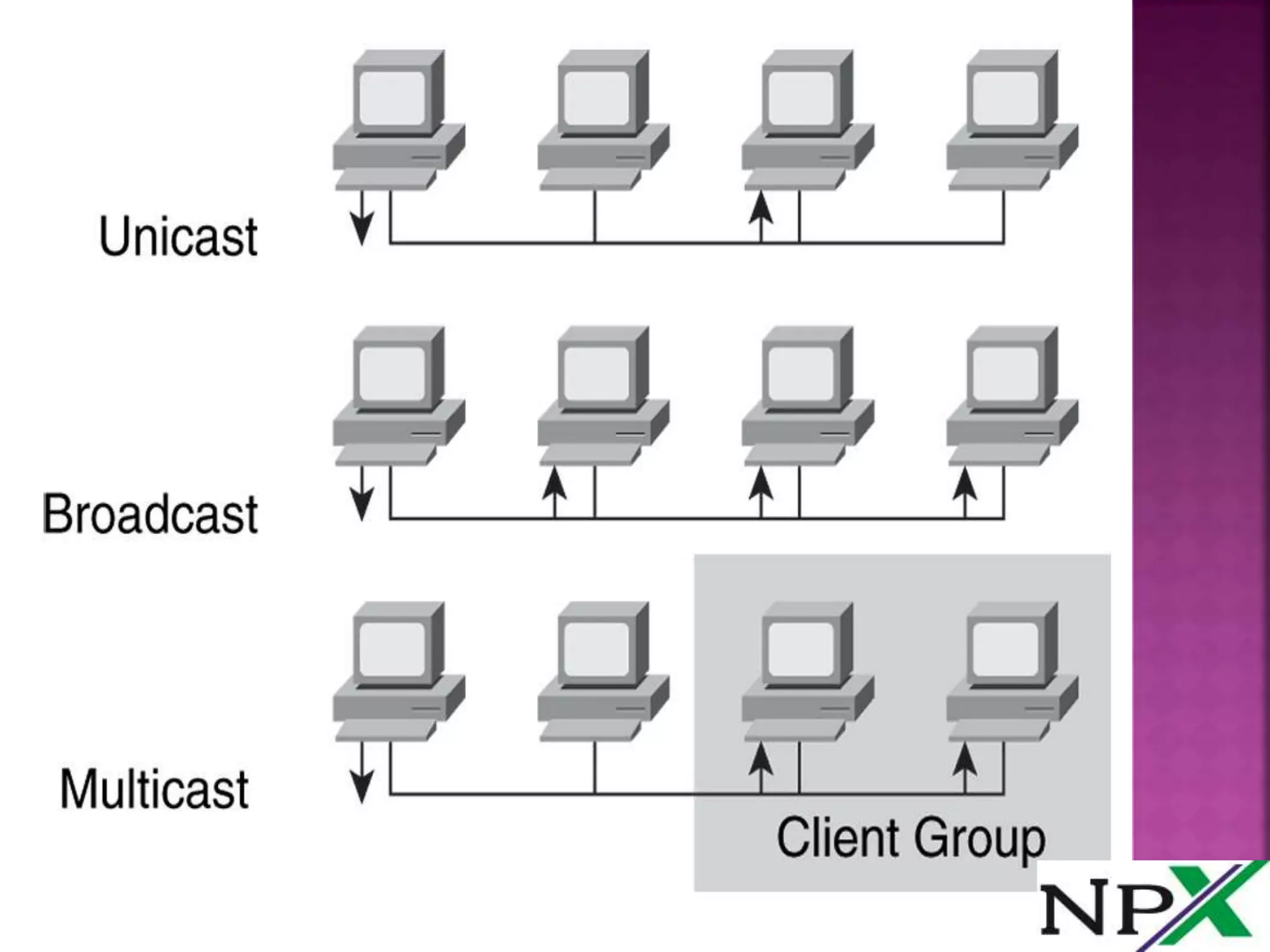

Unicast involves sending data from one computer to another, with one sender and one receiver. Multicast sends data to a group of devices that have joined the multicast group, with one sender but multiple potential receivers. Broadcast sends data from one computer that is then forwarded to all connected devices, with one sender and all devices receiving the broadcast traffic.




