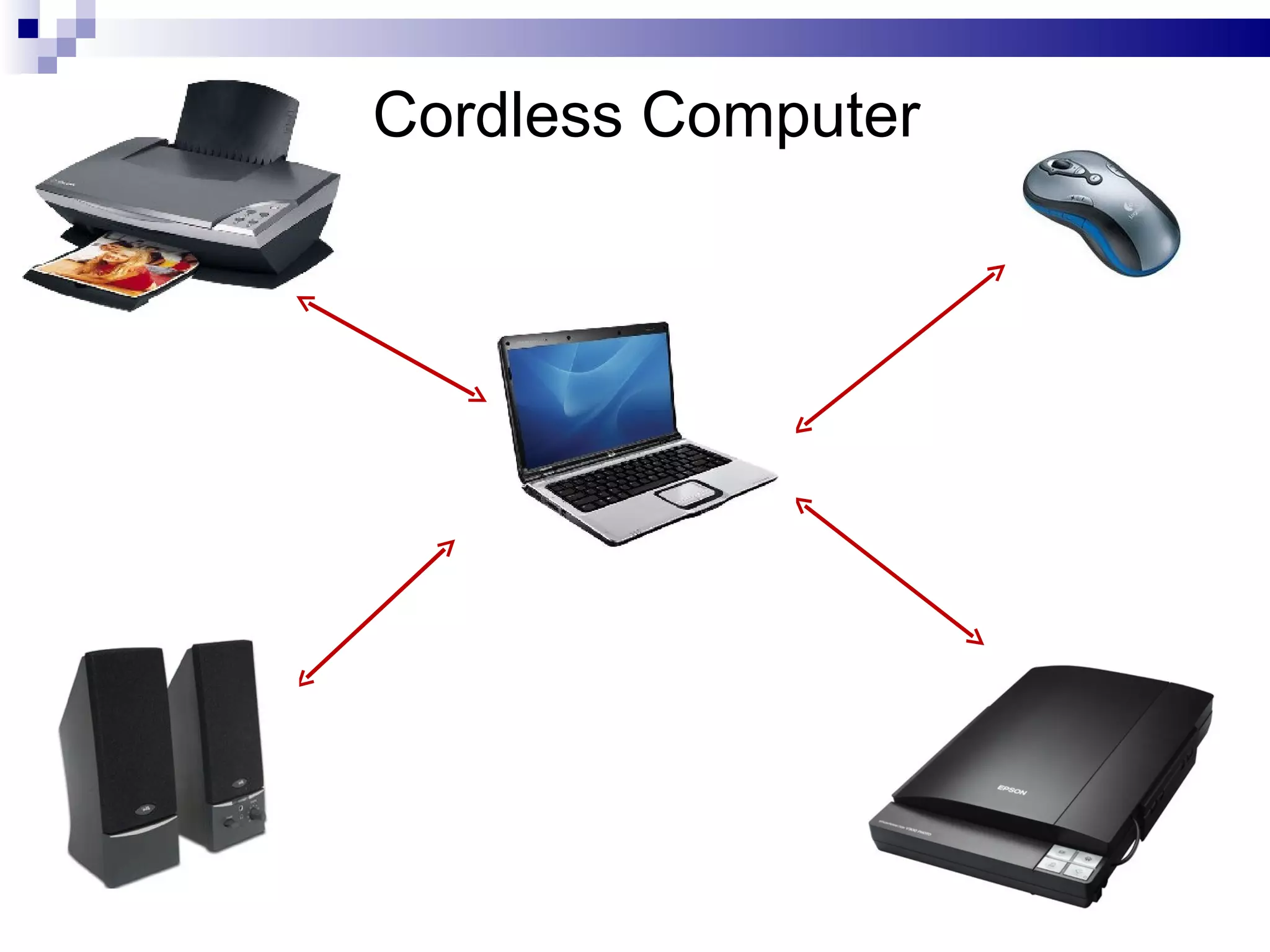
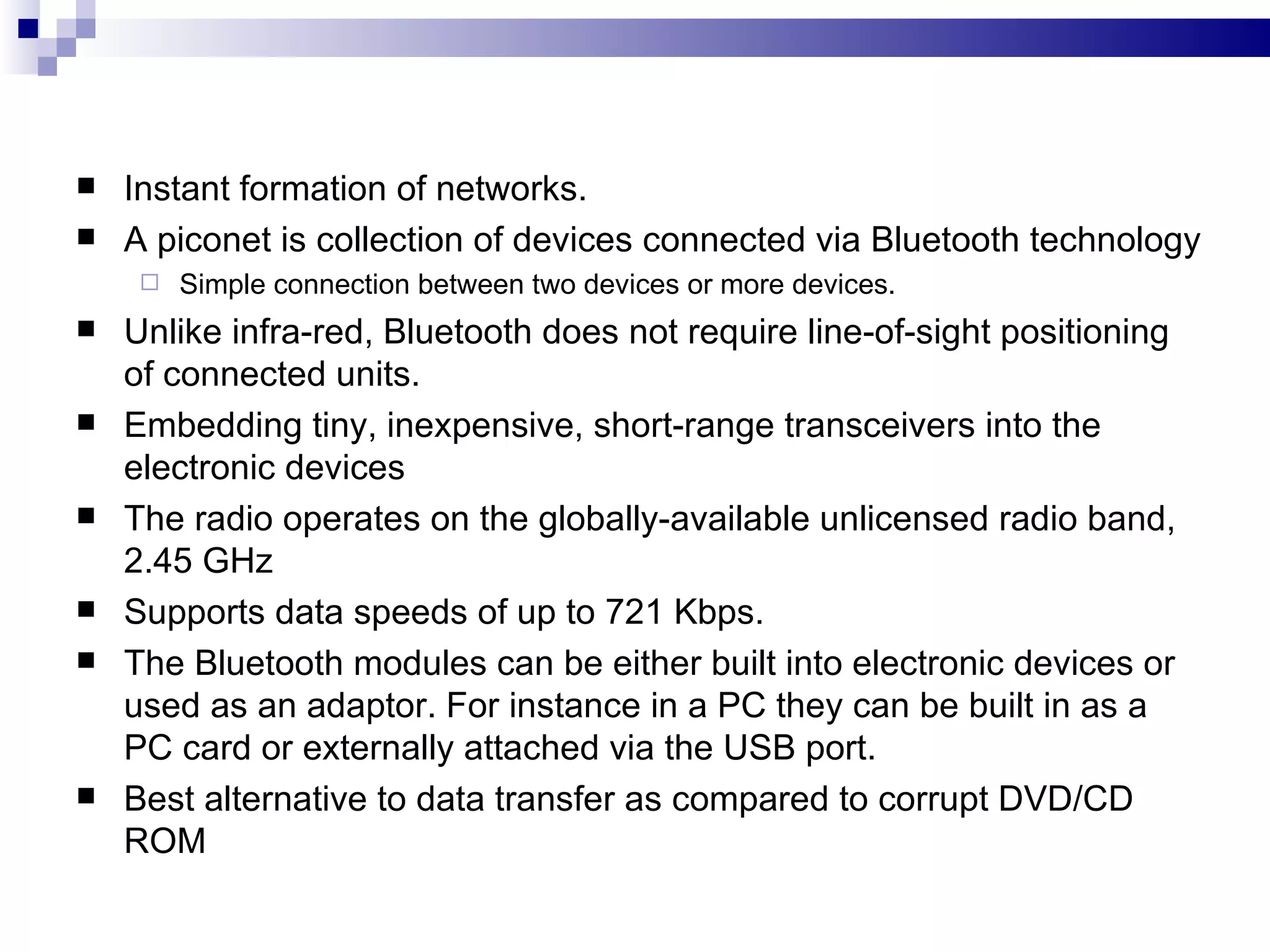
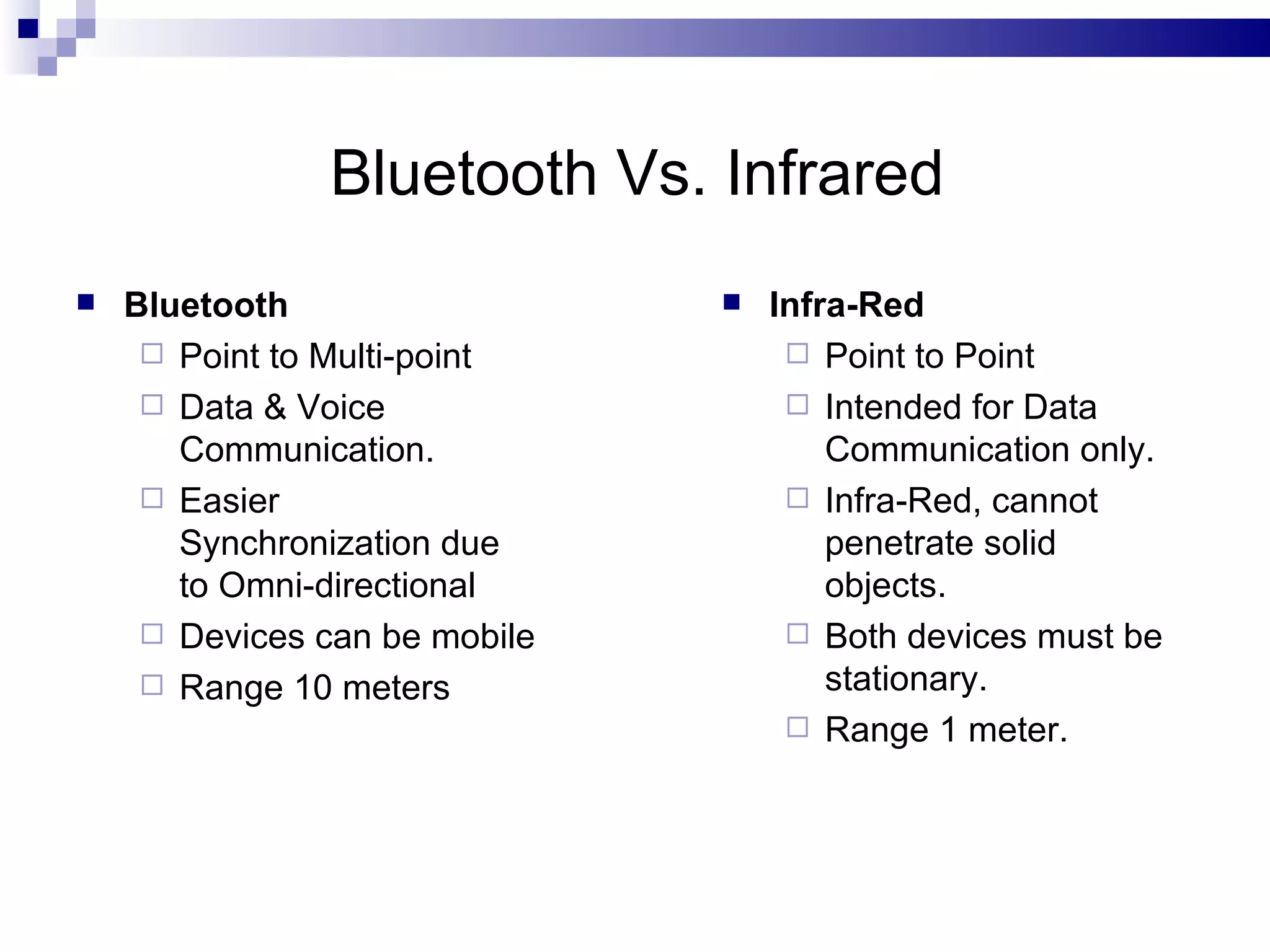
The document provides information on Bluetooth and CDMA technologies. For Bluetooth, it describes its origins, how it works by forming instant networks between devices, advantages like freedom from cables and standardized protocol, and limitations around compatibility and security. For CDMA, it gives an introduction to code division multiple access used for data and voice, its key elements using spreading codes, and advantages like improved capacity and security for 3G networks. Applications of Bluetooth include wireless peripherals, printers, and connecting devices like phones and computers, while CDMA is used widely in cellular networks.