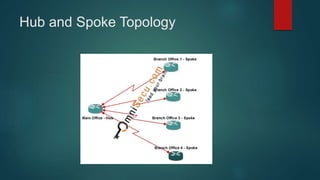
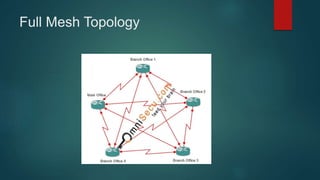
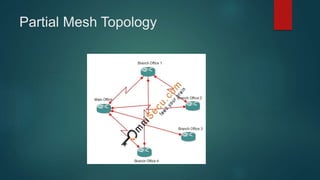
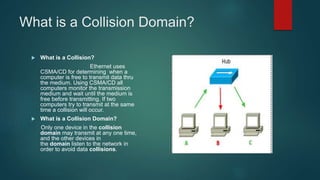
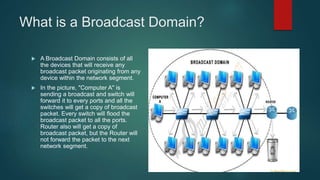
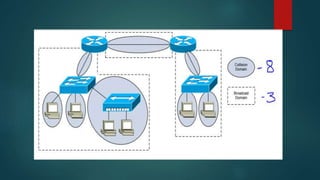
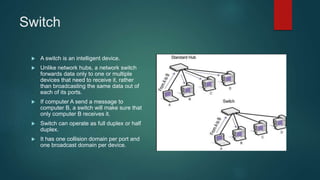
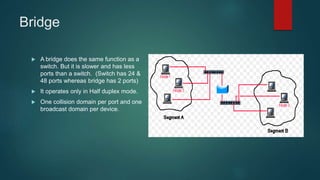
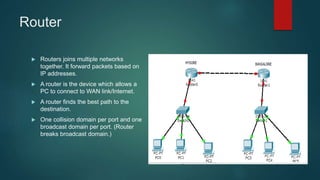
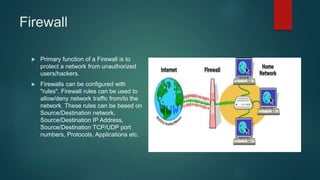
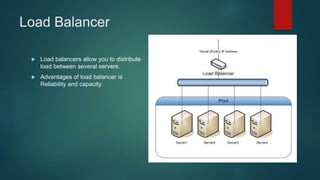
This document provides an overview of computer networking fundamentals. It defines a computer network as a set of connected computers that share information and resources. Local area networks (LANs) operate within a small area, while wide area networks (WANs) interconnect multiple LANs across a larger area. Networking devices like switches, routers, and firewalls help share information and hardware resources on a network, while ensuring security and reliability. The document also discusses topics like collision and broadcast domains, and common network topologies.