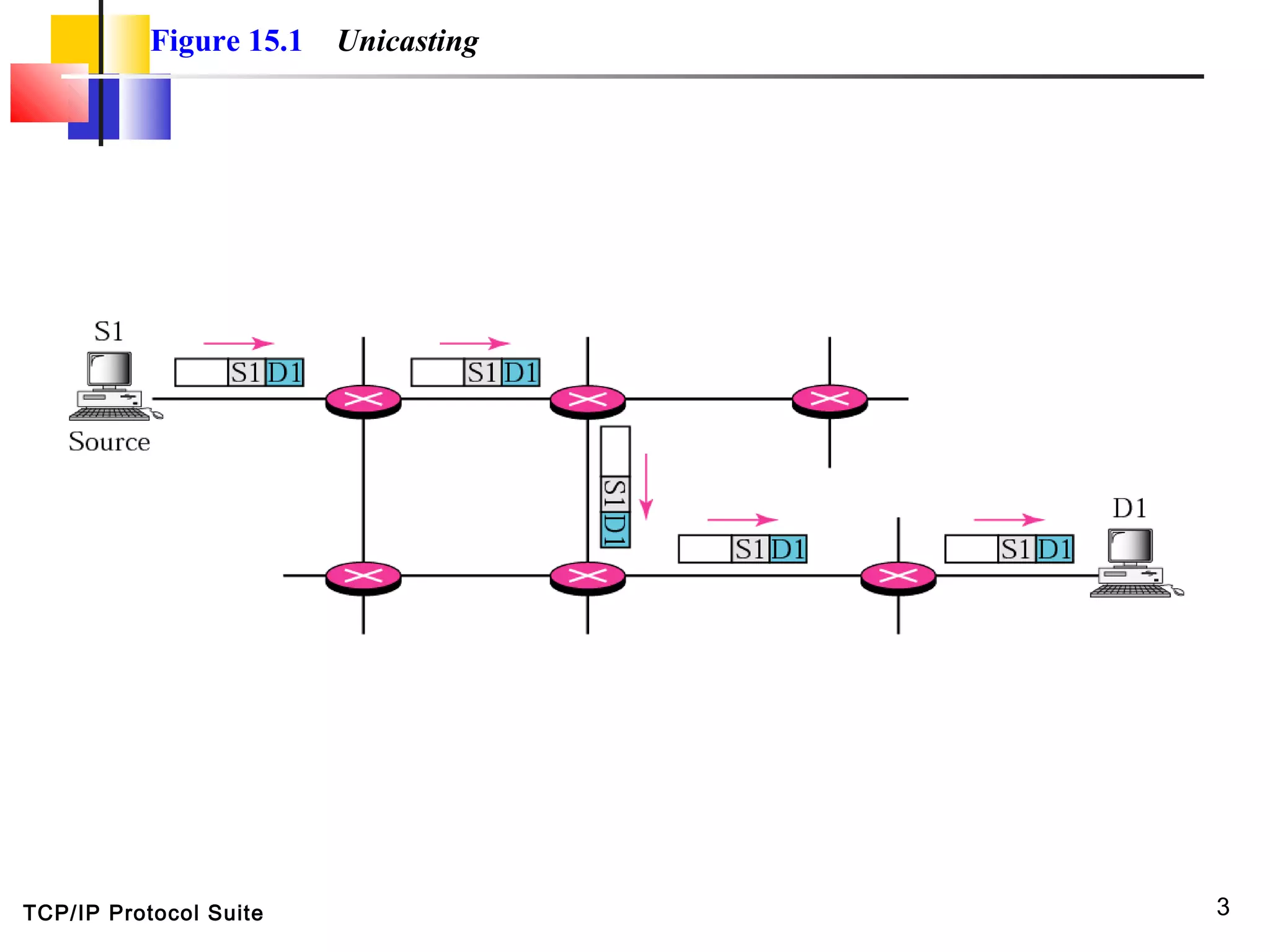
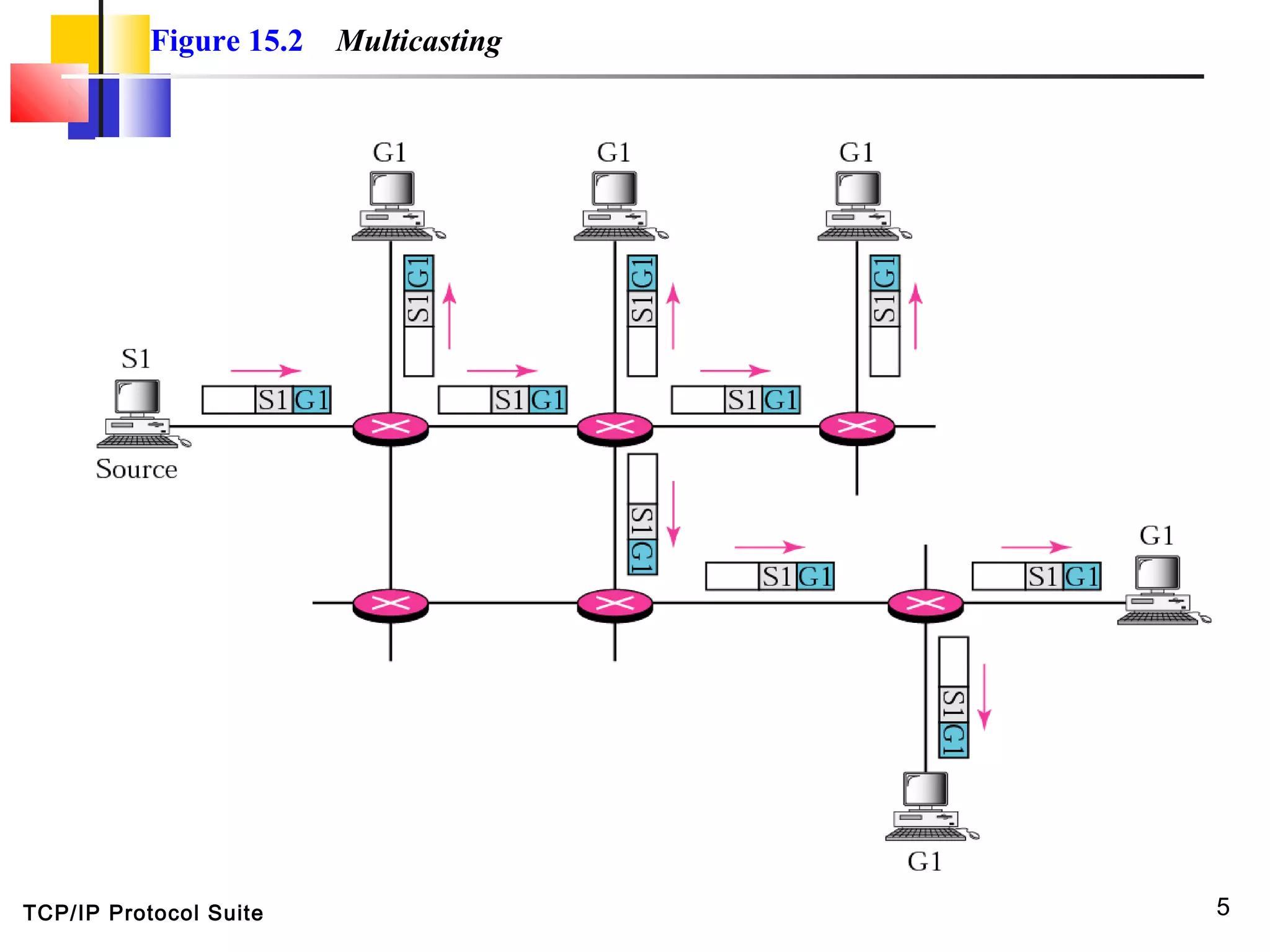
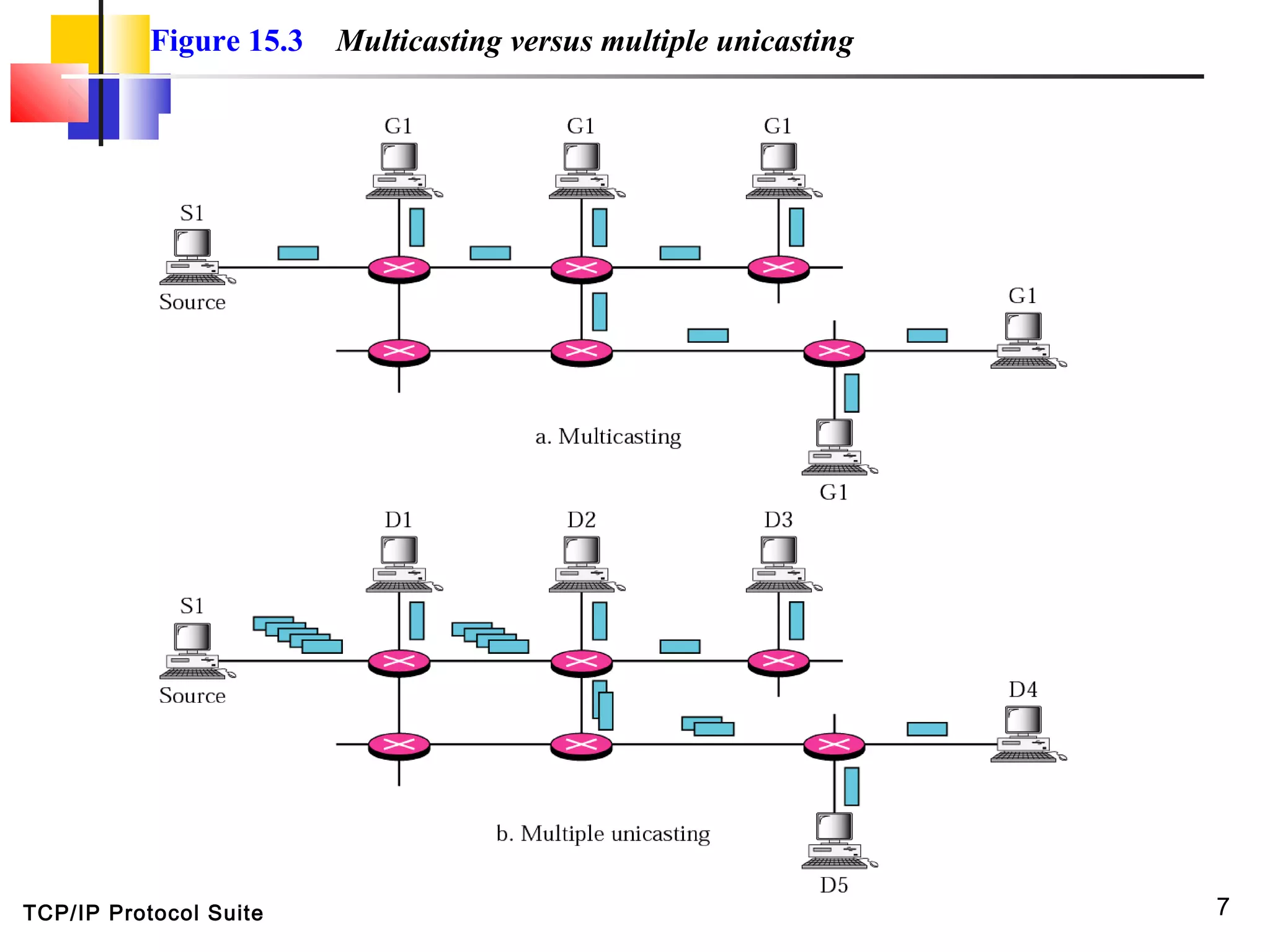
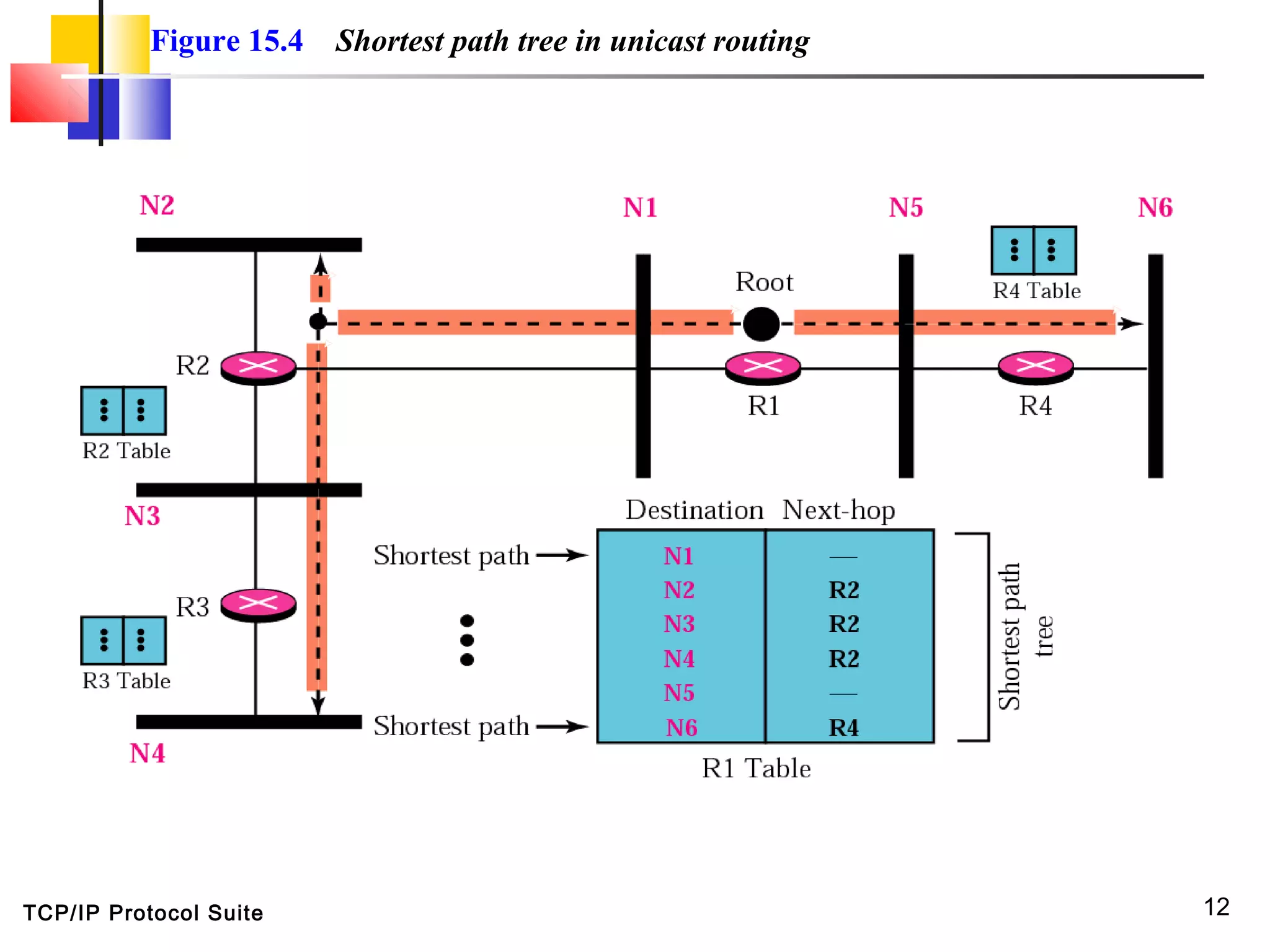
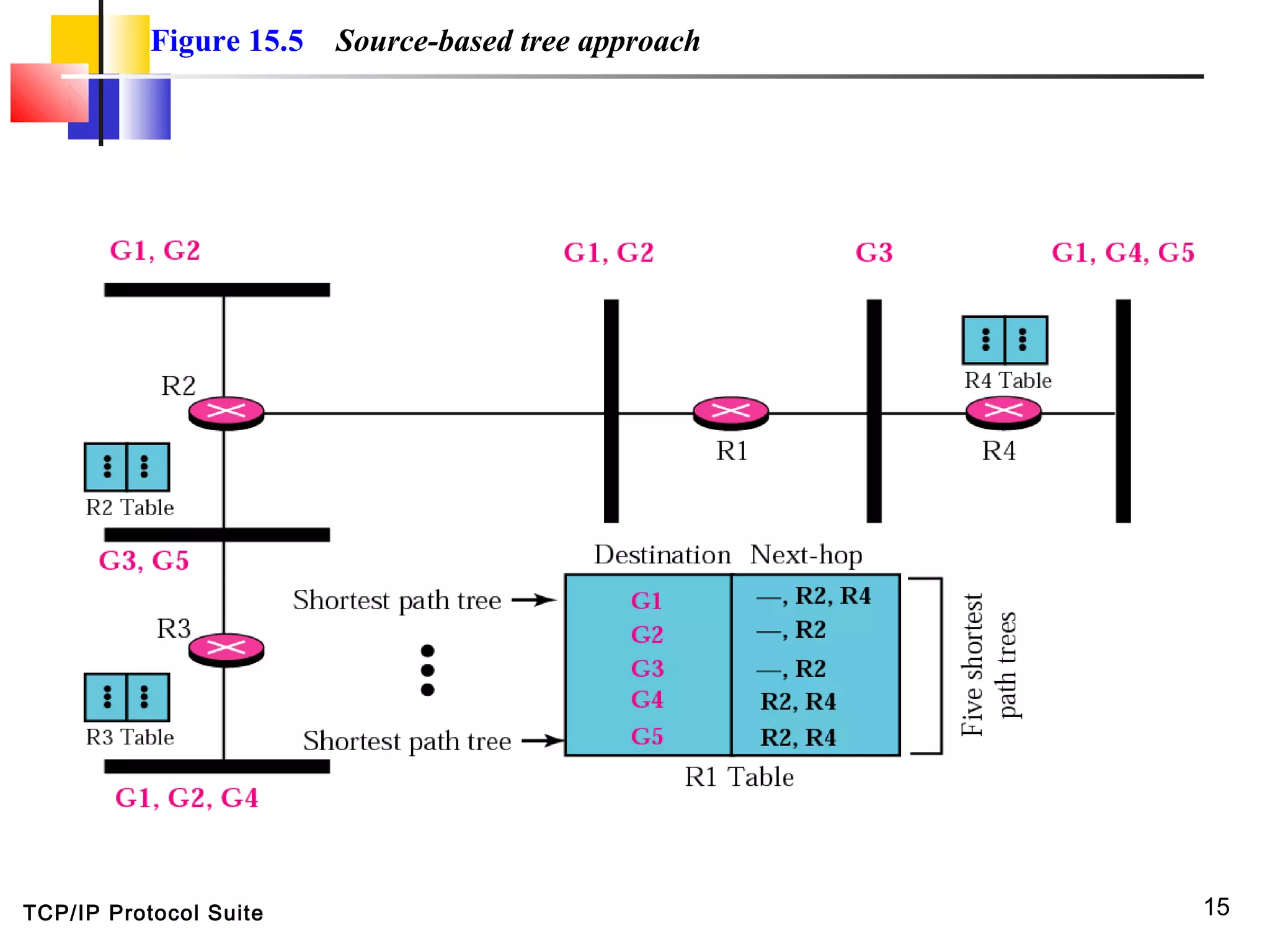
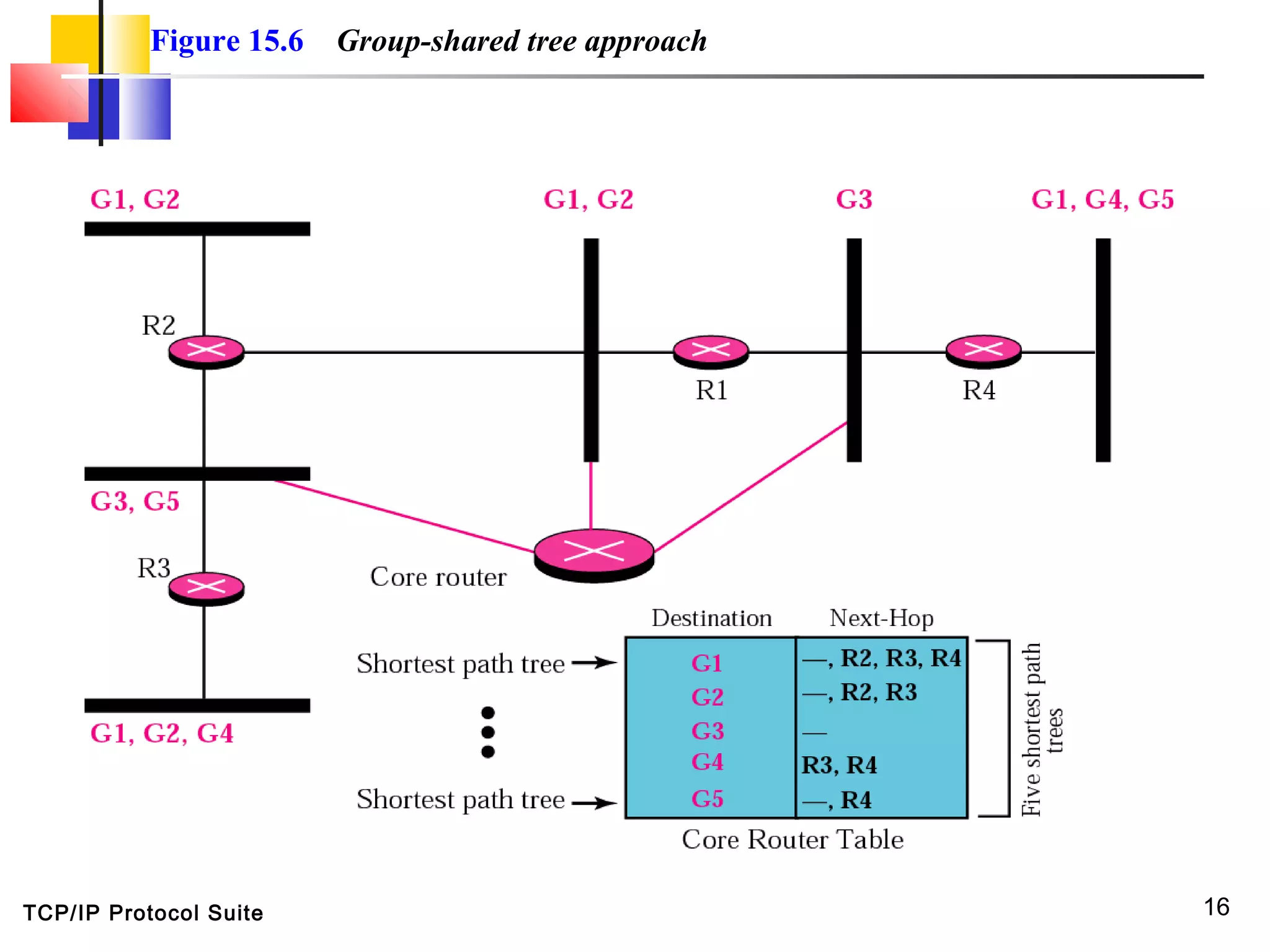
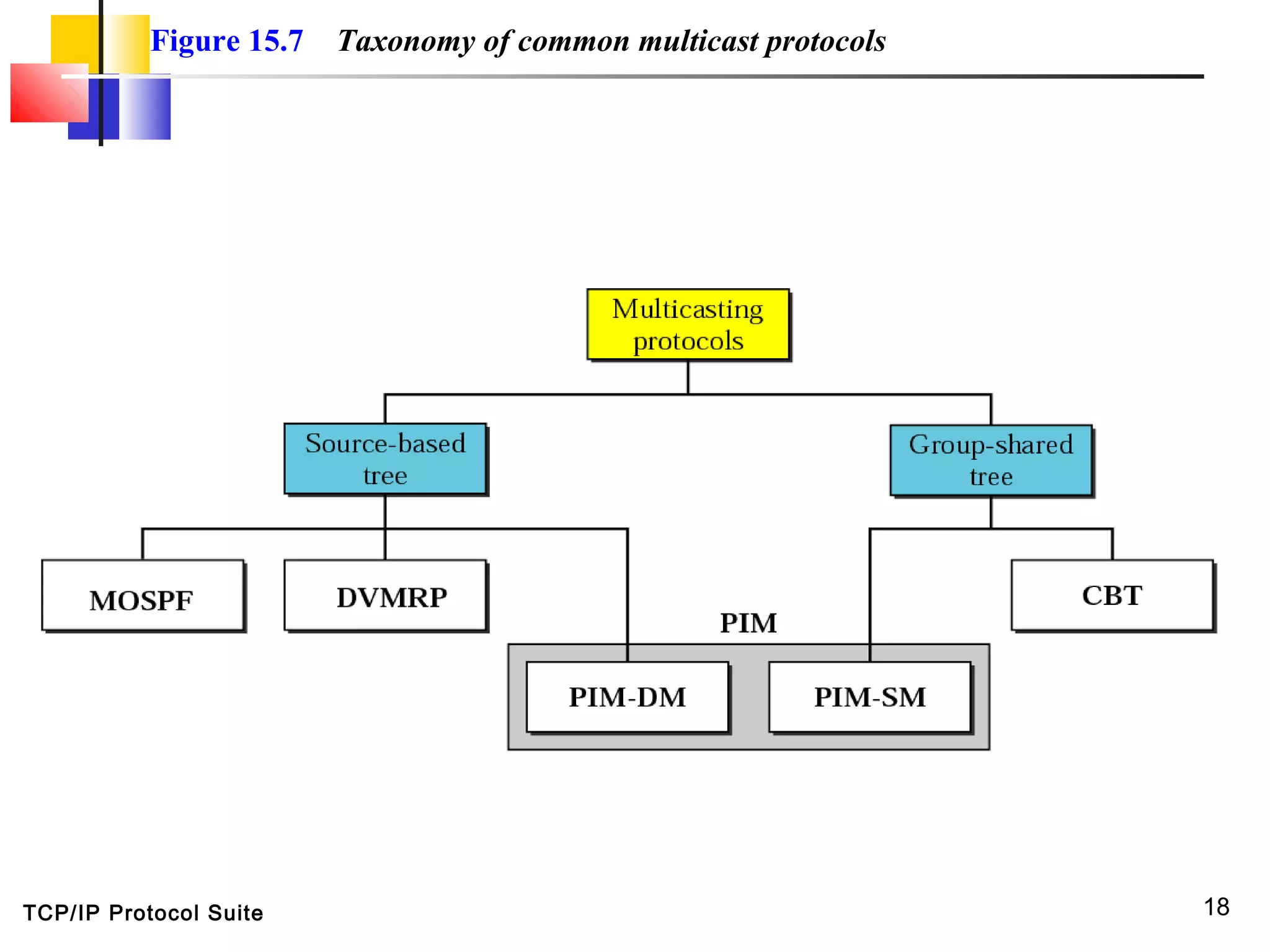
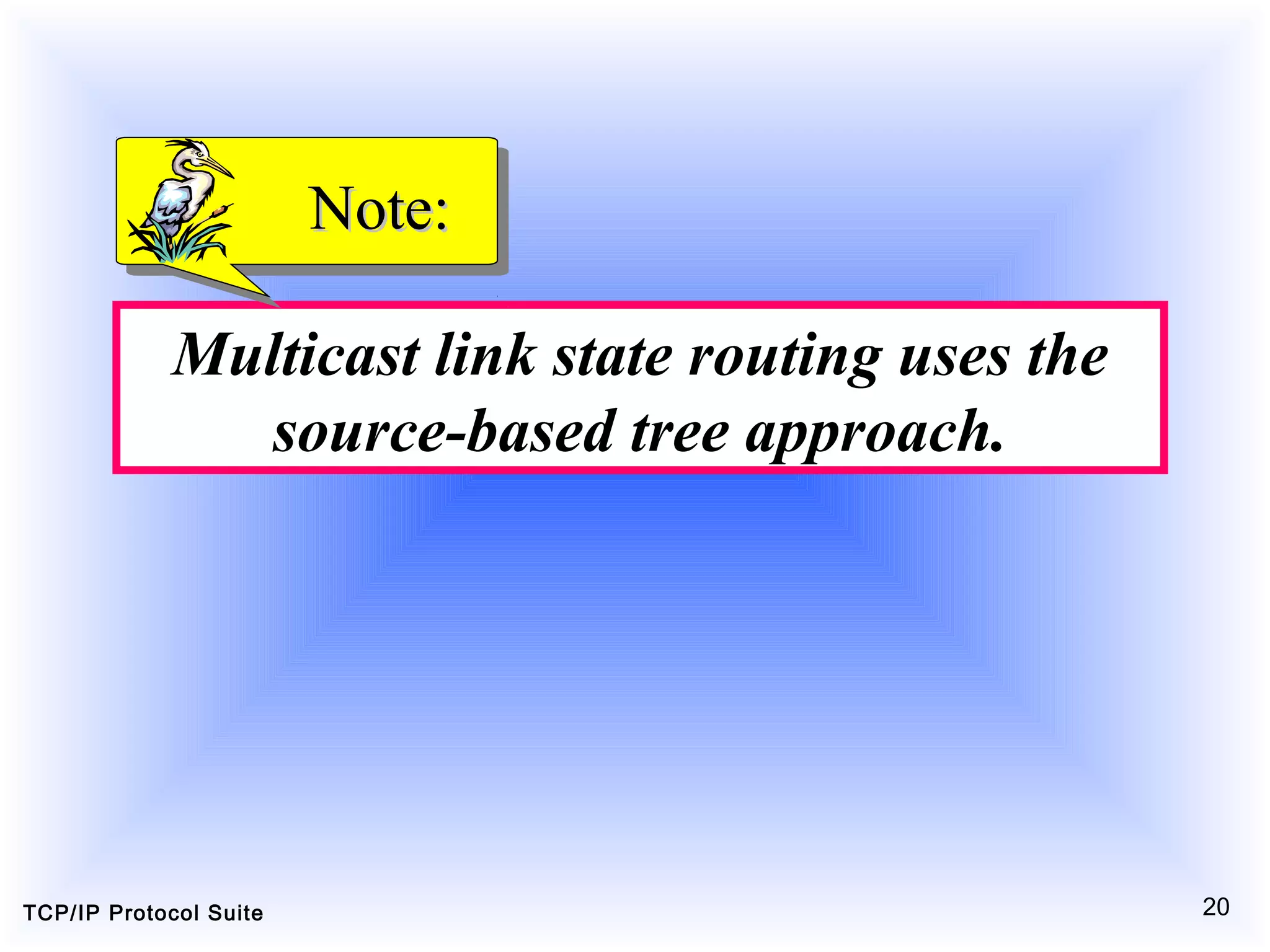
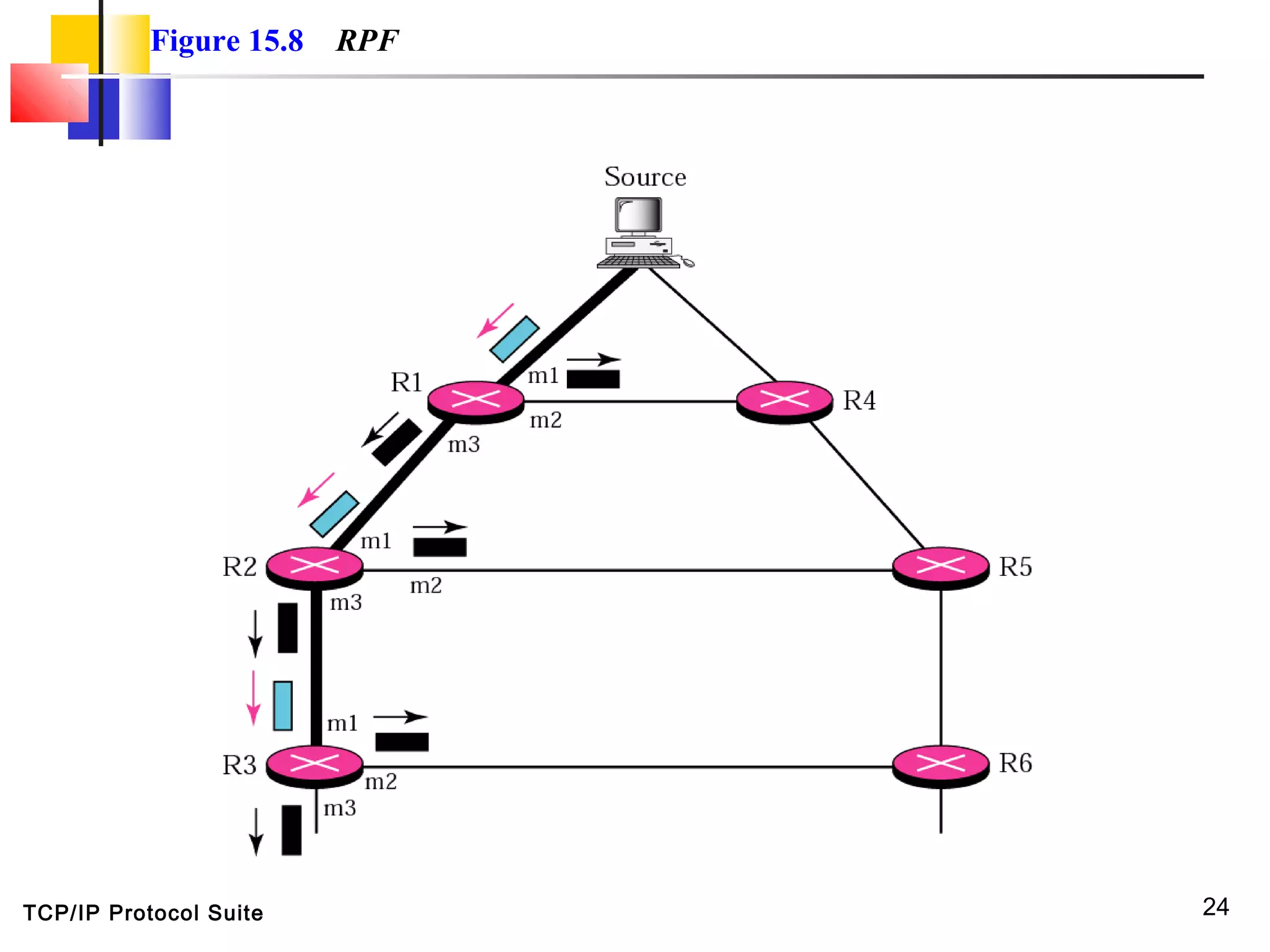
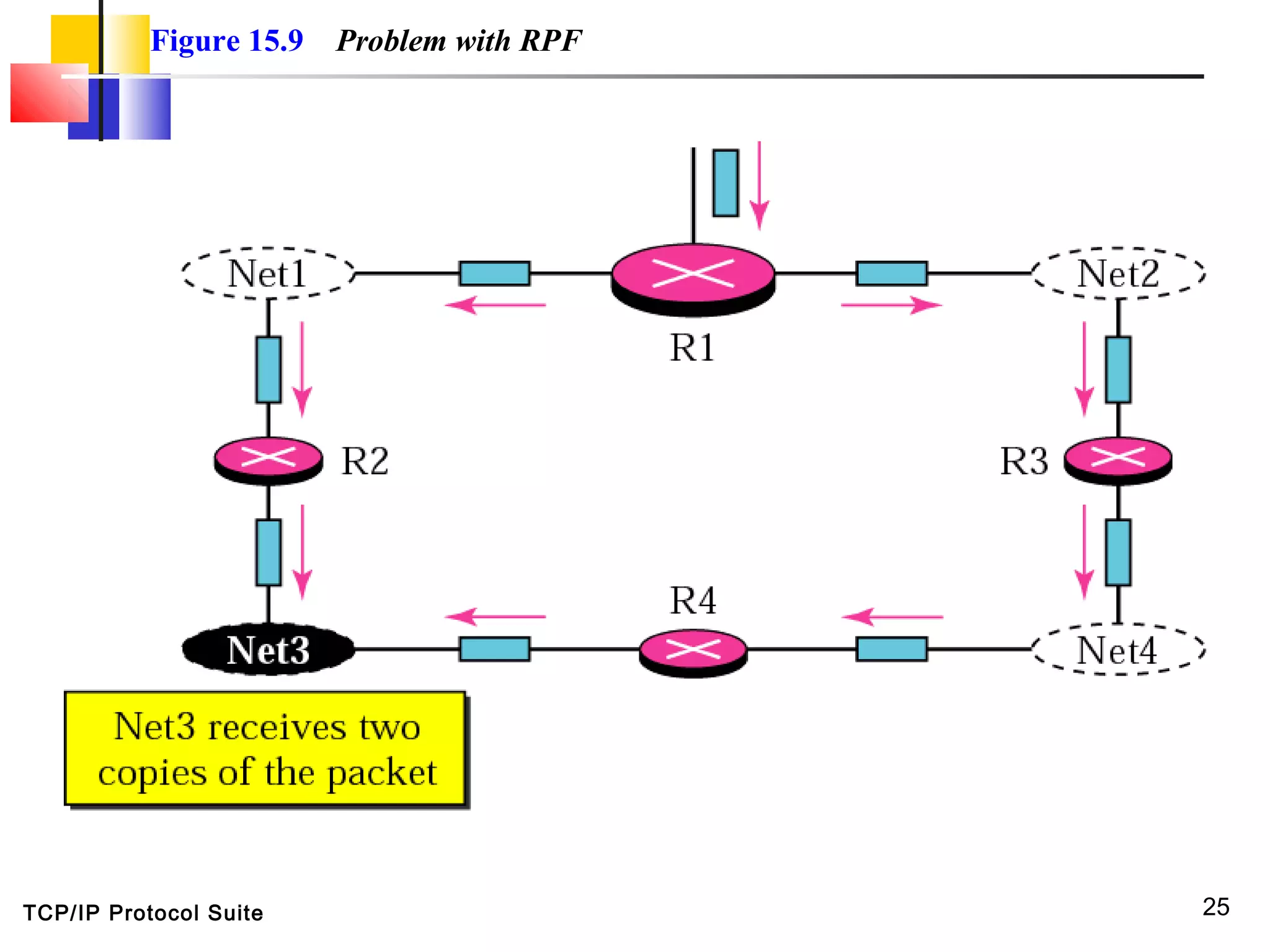
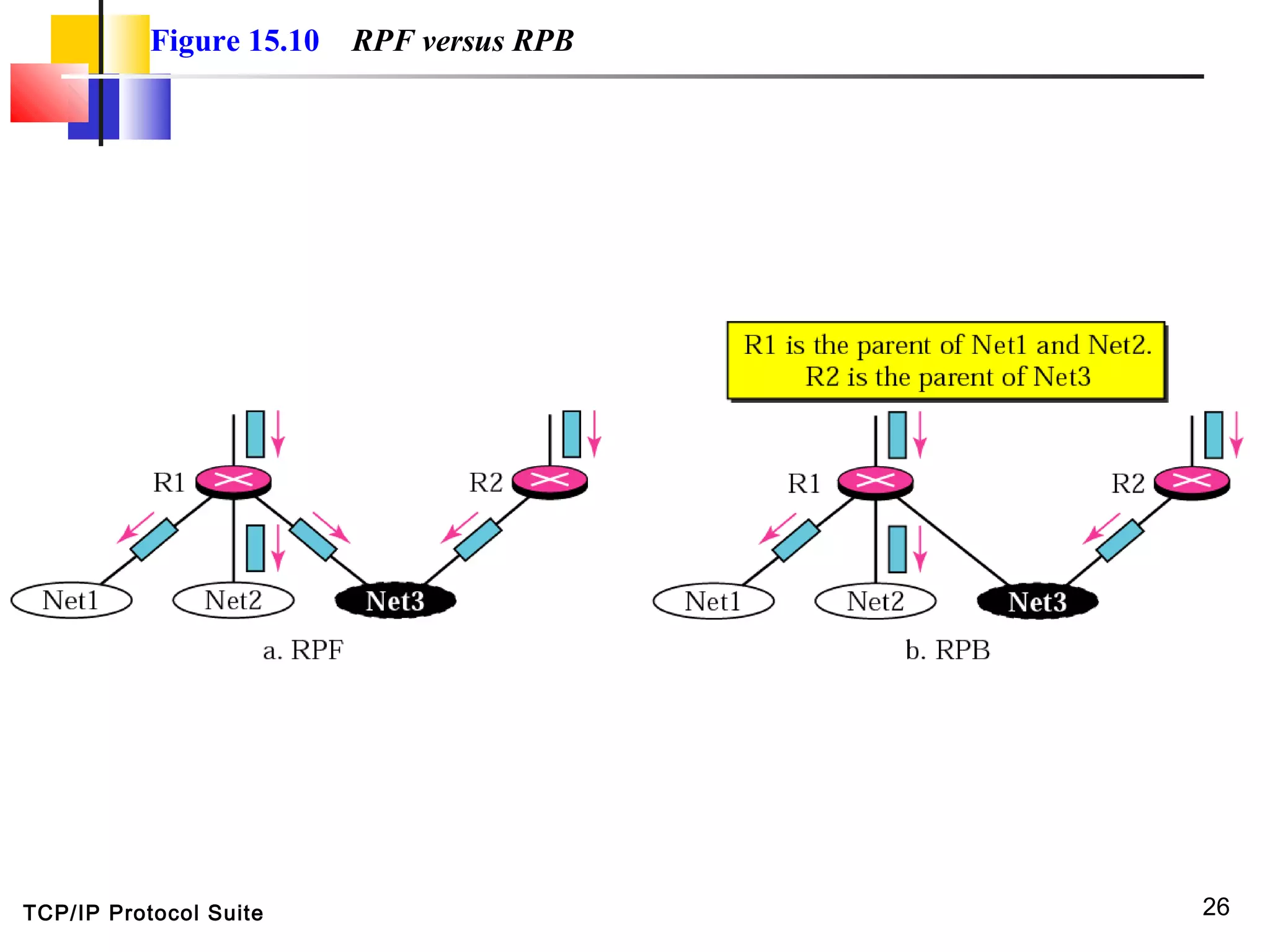
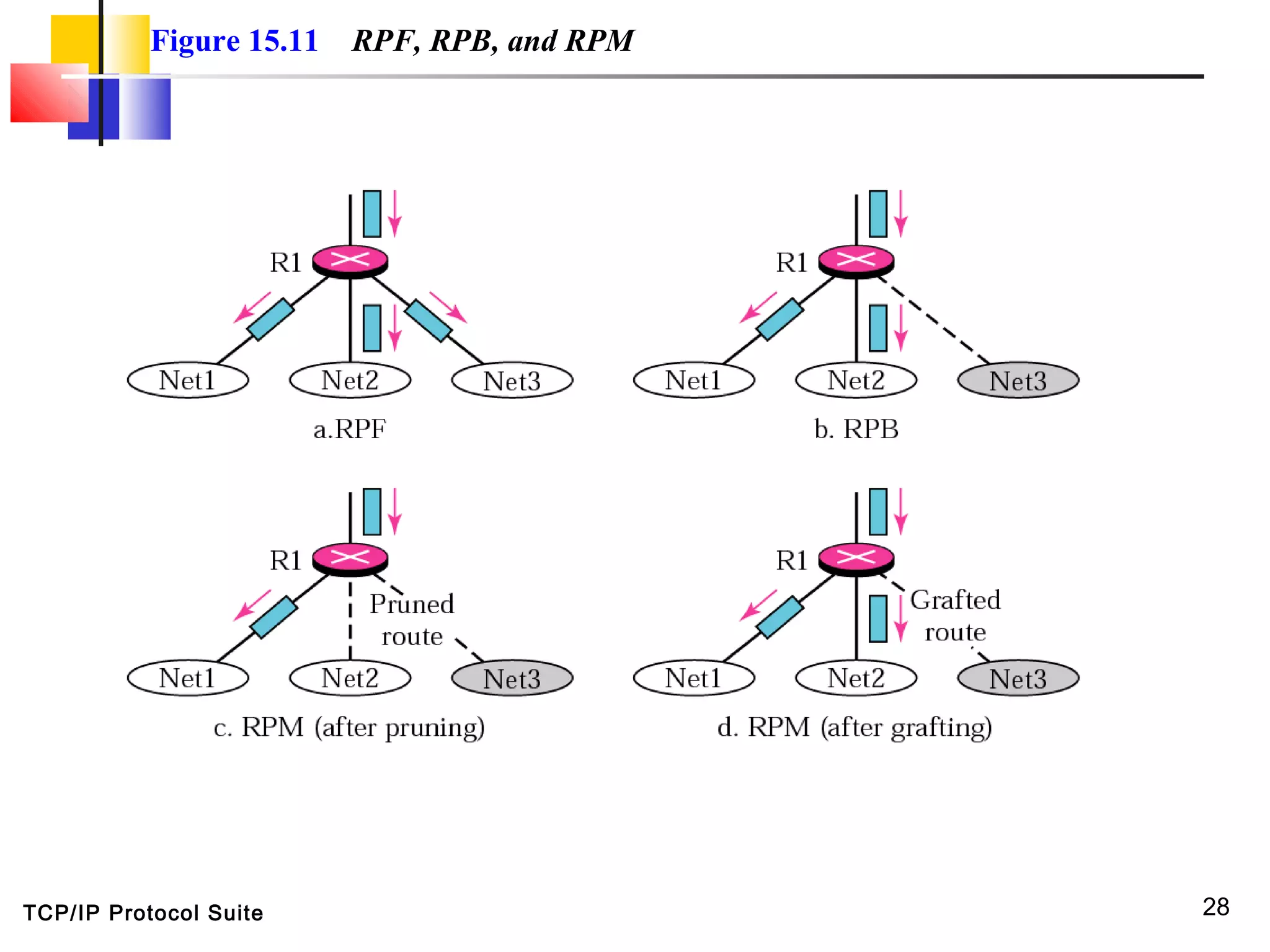
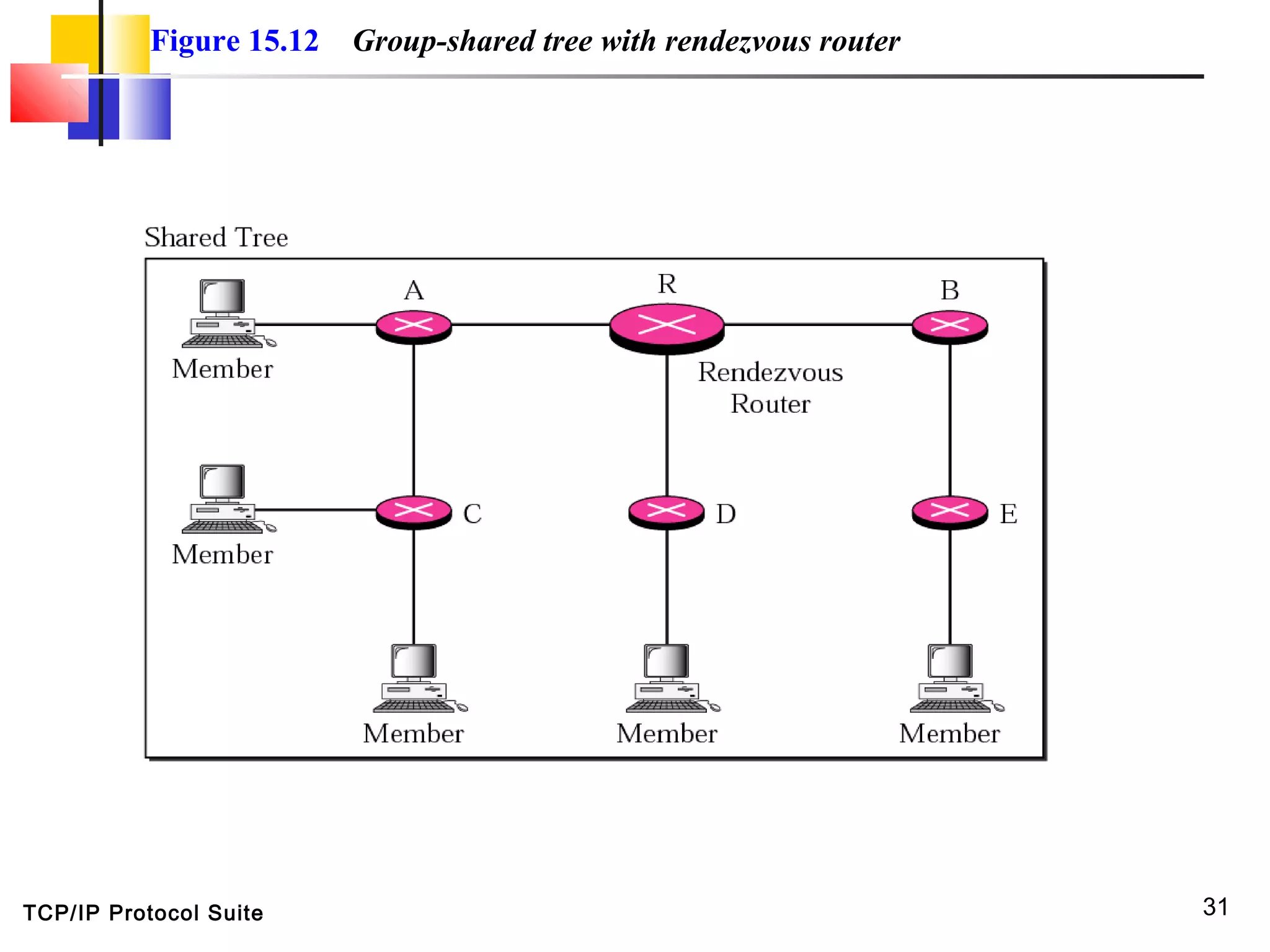
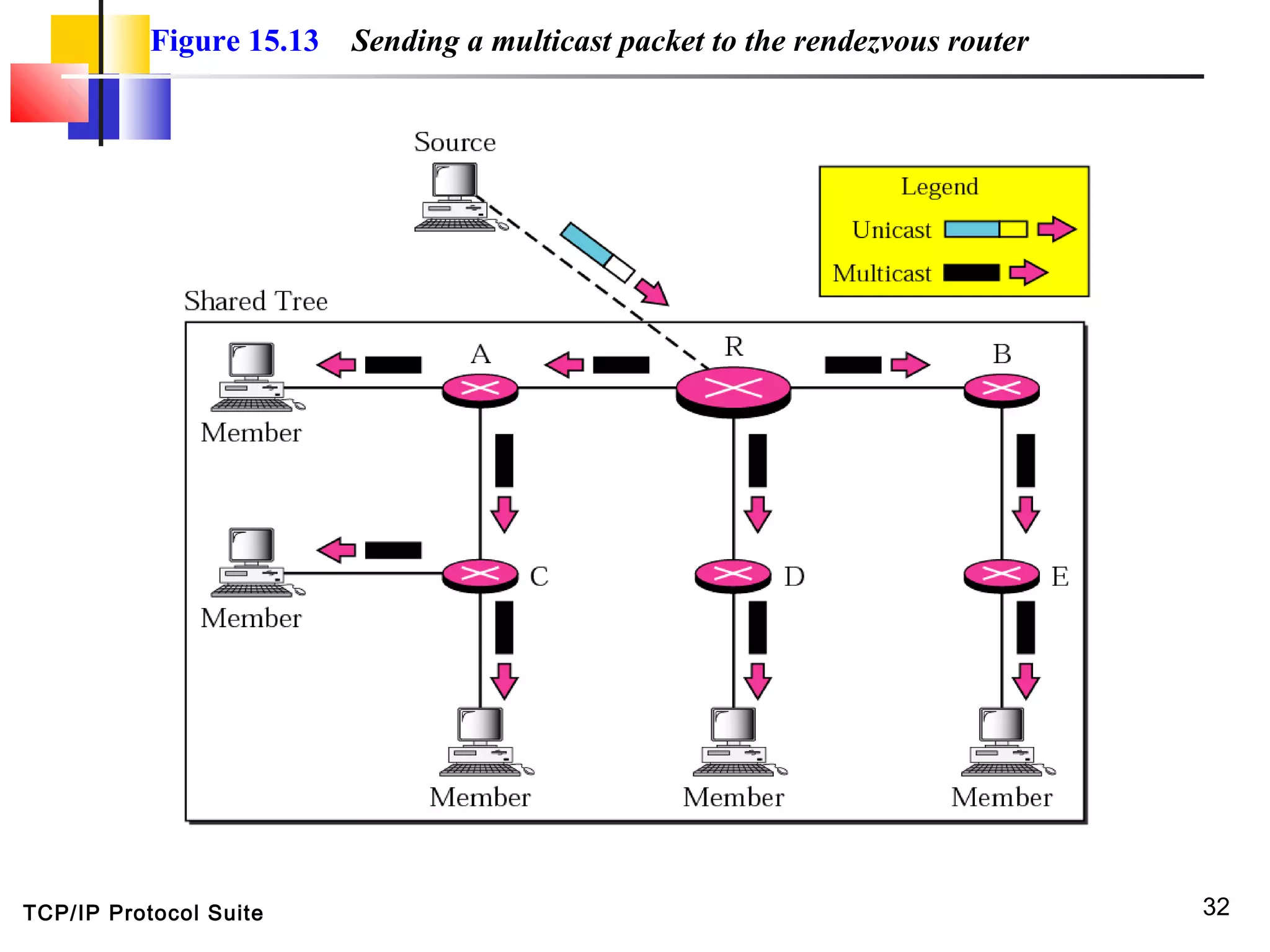
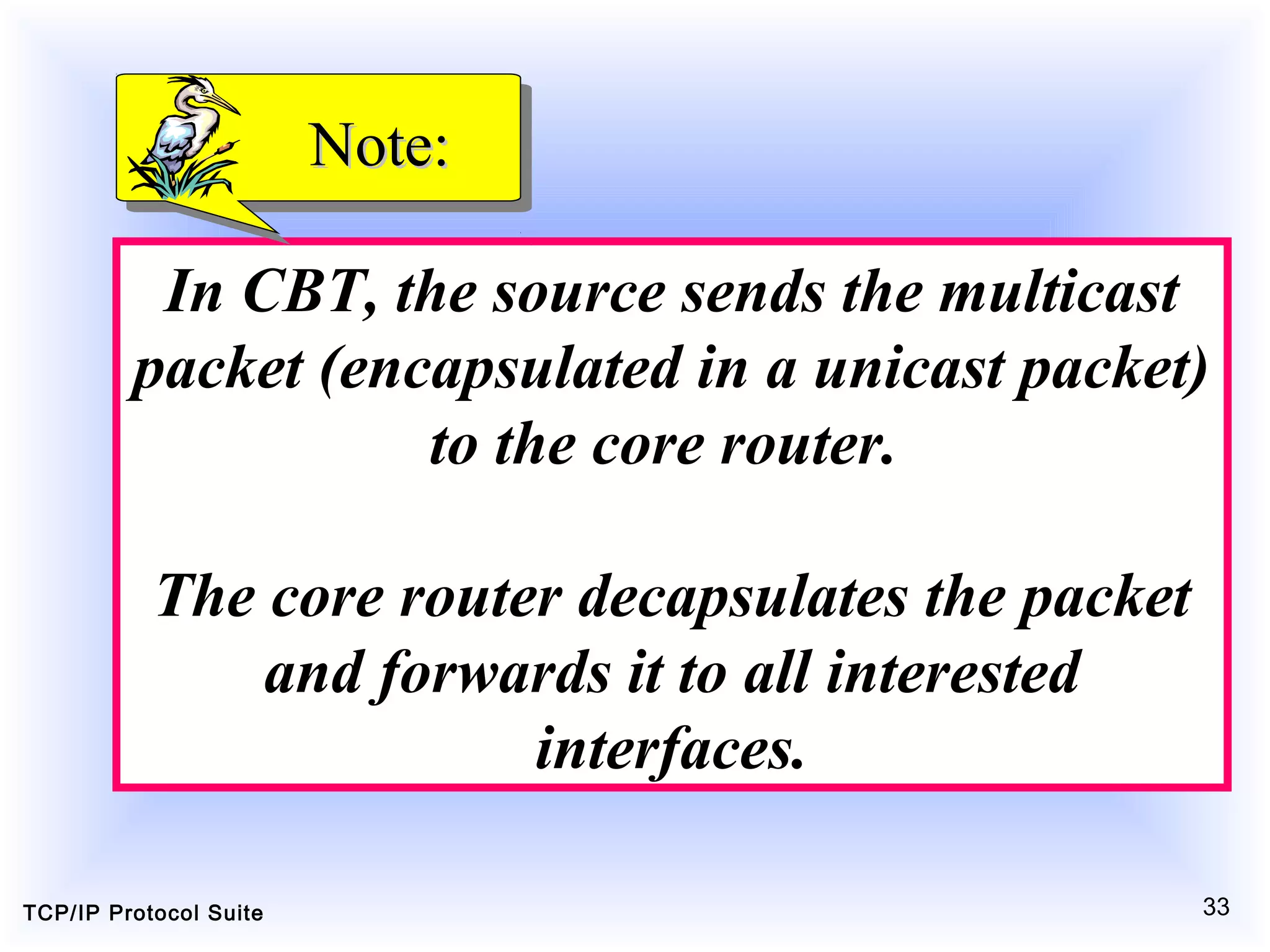
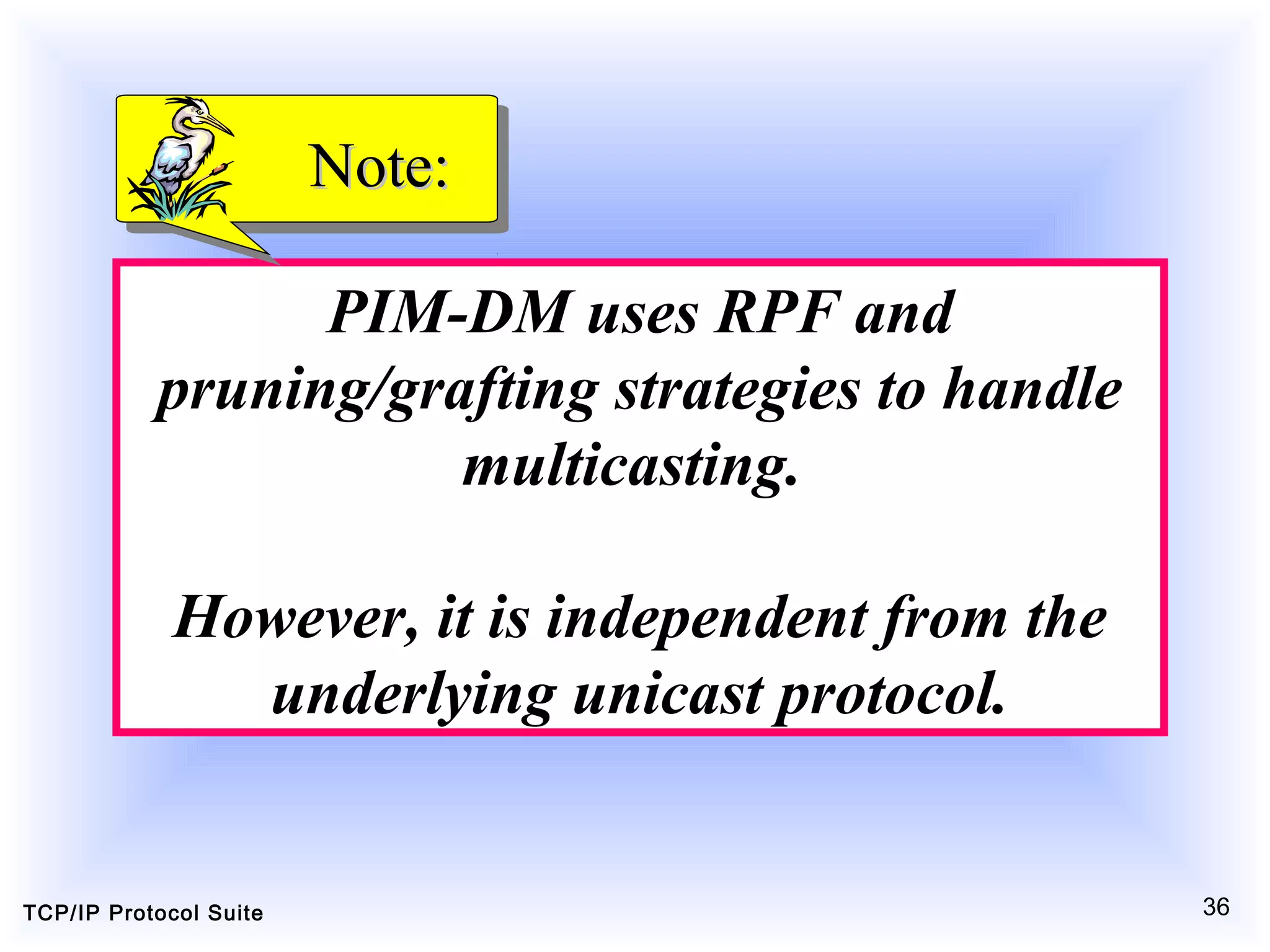
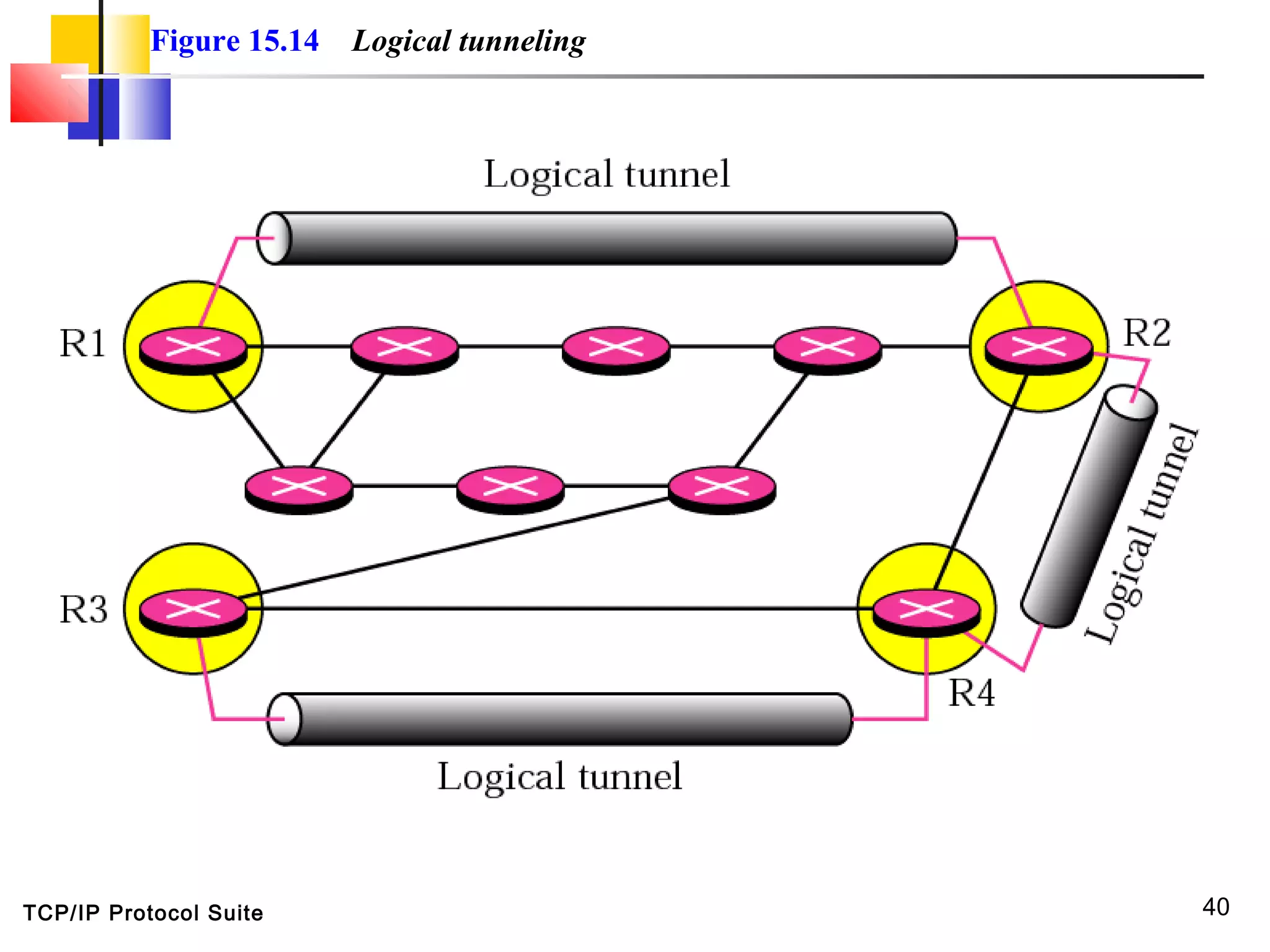
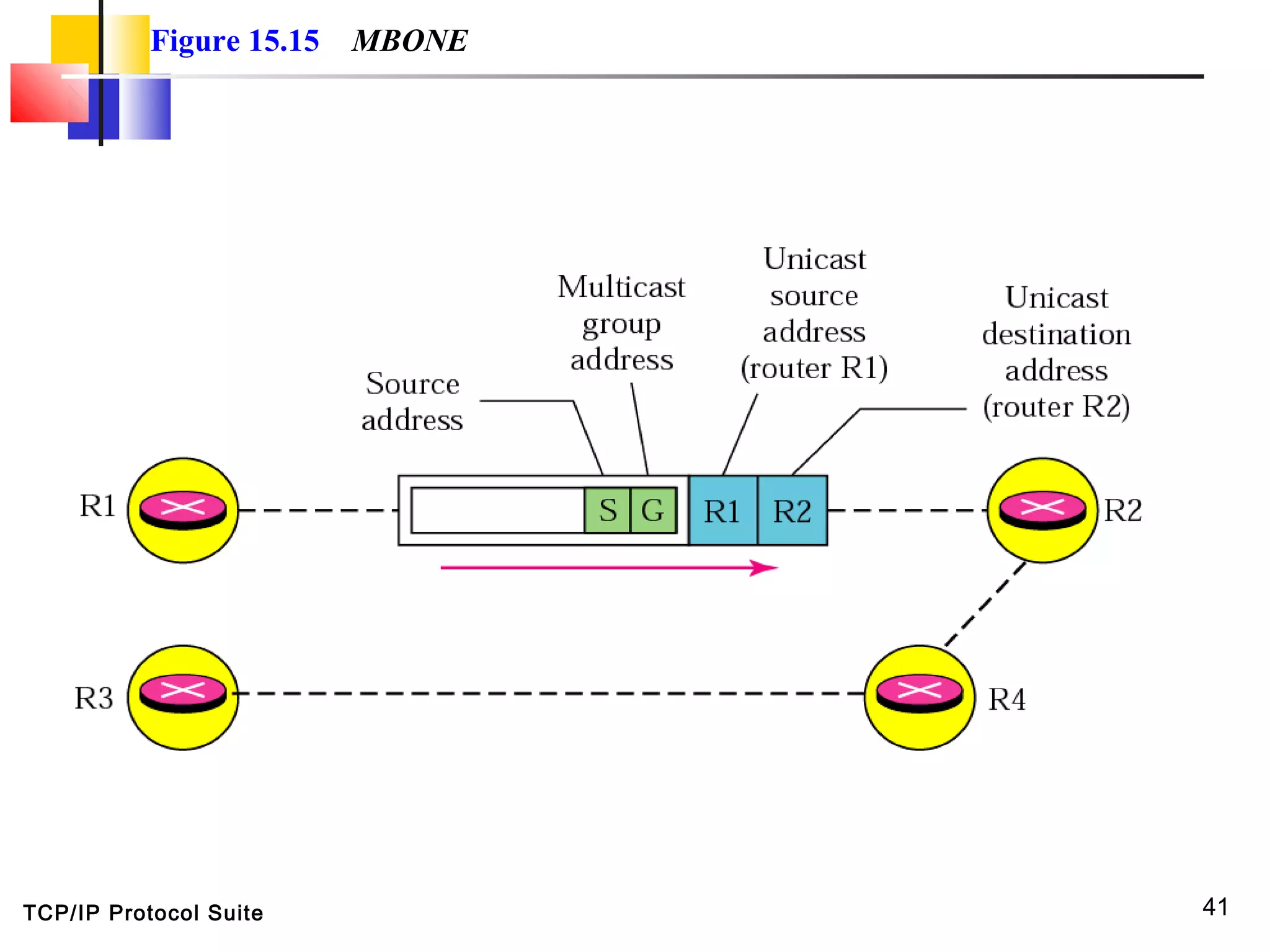
This document discusses multicasting and multicast routing protocols. It defines unicast, multicast, and broadcast messages and describes applications of multicasting like accessing distributed databases and distance learning. It also explains different multicast routing protocols including MOSPF, DVMRP, CBT, and PIM, covering concepts like shortest path trees, flooding, pruning, and grafting. Finally, it discusses MBONE and how tunneling can be used to connect isolated multicast routers.