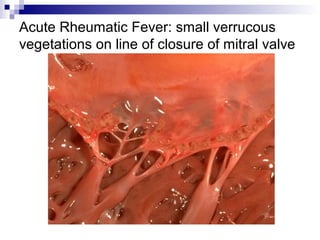
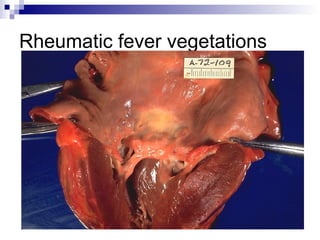
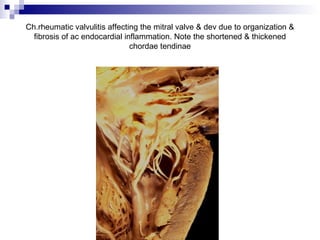
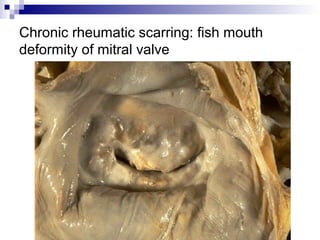
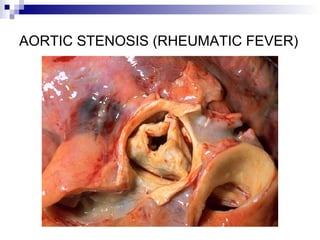
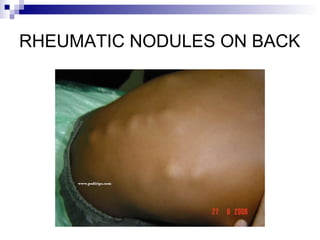
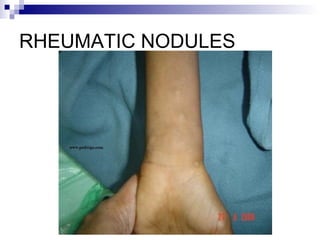
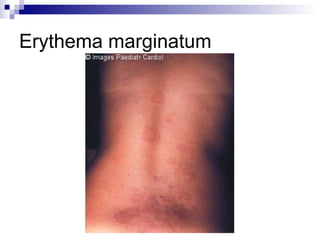
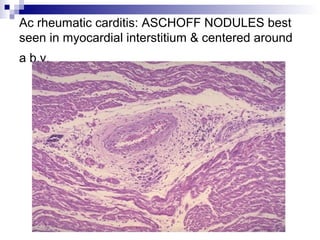
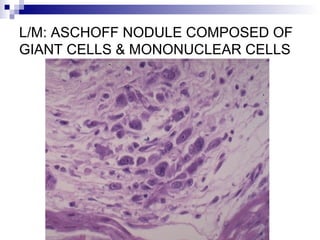
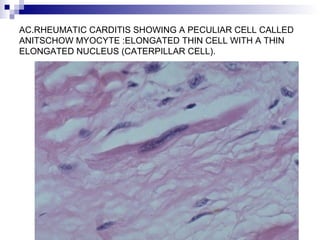
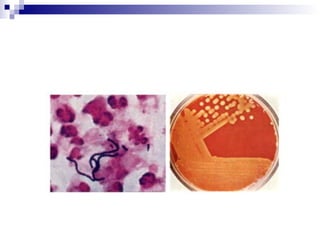
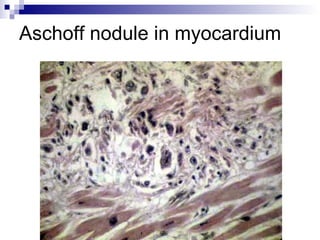
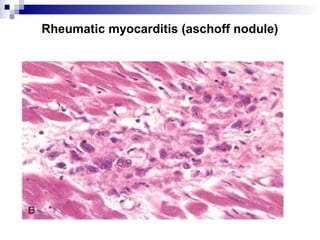
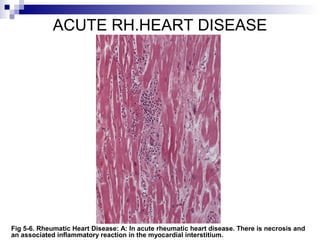
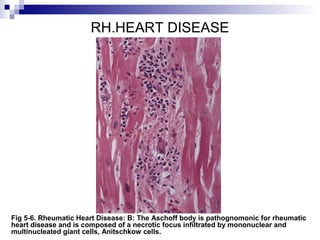
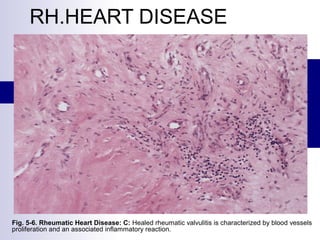
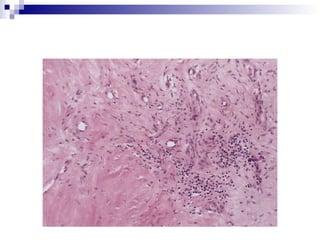
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs as a result of a prior streptococcal infection. It commonly affects children between 5-15 years old. The major systems involved are the heart, joints, skin, and brain. In the heart, it can cause inflammation of the tissues and valves, leading to scarring and deformities over time. On pathology, it is characterized by lesions called Aschoff bodies in the heart muscle. Long term, it can progress to chronic rheumatic heart disease with permanent valve damage and heart failure. Prompt treatment of streptococcal infections can help prevent recurrent cases of rheumatic fever.