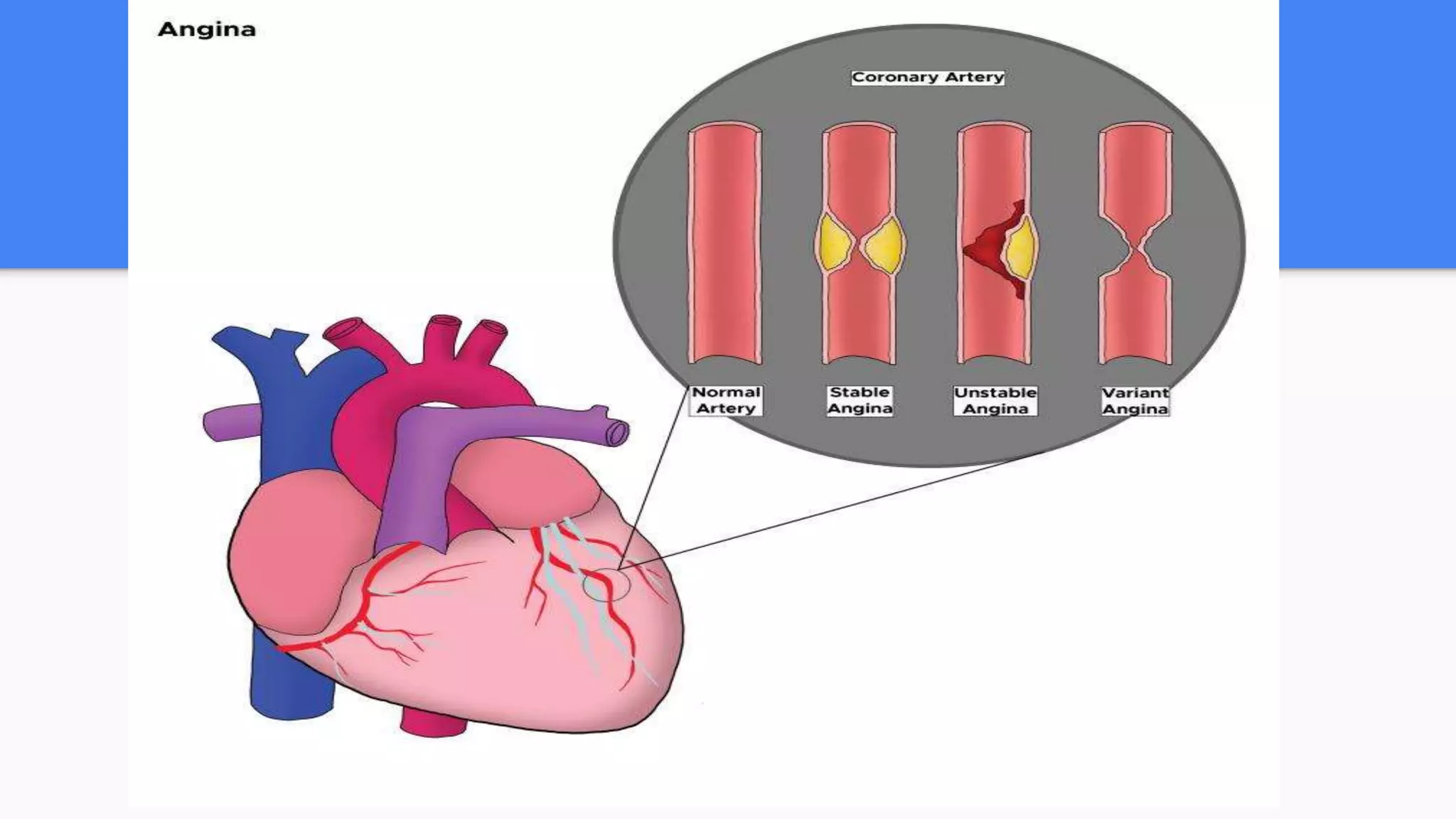
Unstable angina is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart, often due to a partially blocked artery. It can occur at rest and is considered a medical emergency. The main causes are atherosclerotic plaques that rupture or spasm of the coronary arteries. Patients experience chest pressure or pain that may radiate to the arms or jaw. Evaluation involves ECG, cardiac enzymes, and cardiac stress testing to determine the risk of a heart attack. Treatment focuses on improving blood flow through aspirin, nitroglycerin, and sometimes angioplasty or stenting of blocked arteries.