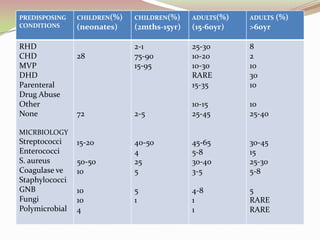
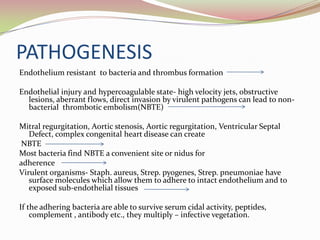
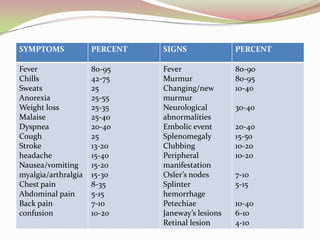
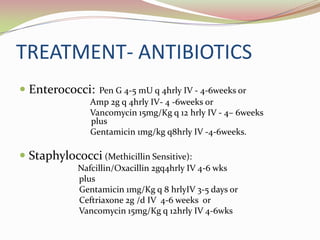
Infective endocarditis is a microbial infection of the heart valves or endocardium. It is caused by bacteria, usually streptococci or staphylococci, entering the bloodstream and colonizing injured heart valves or endothelium. Predisposing conditions include rheumatic heart disease, congenital heart disease, prosthetic heart valves, and intravenous drug use. Symptoms include fever, chills, sweats, and heart murmur. Diagnosis involves blood cultures, echocardiography, and clinical criteria. Treatment consists of intravenous antibiotics for 4-6 weeks along with surgery if needed to repair or replace damaged valves. Prophylactic antibiotics are recommended for high risk patients before certain medical procedures to prevent