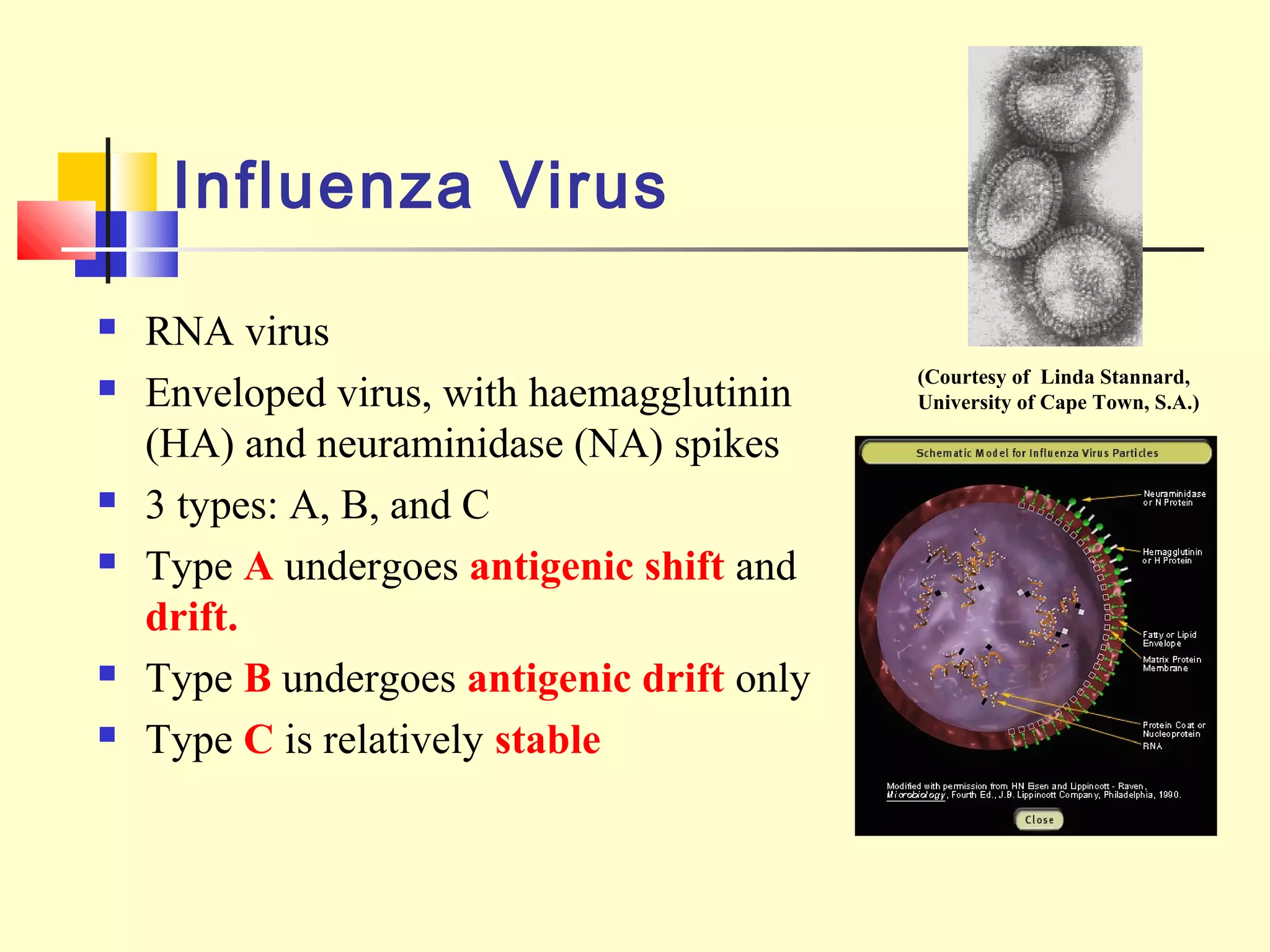
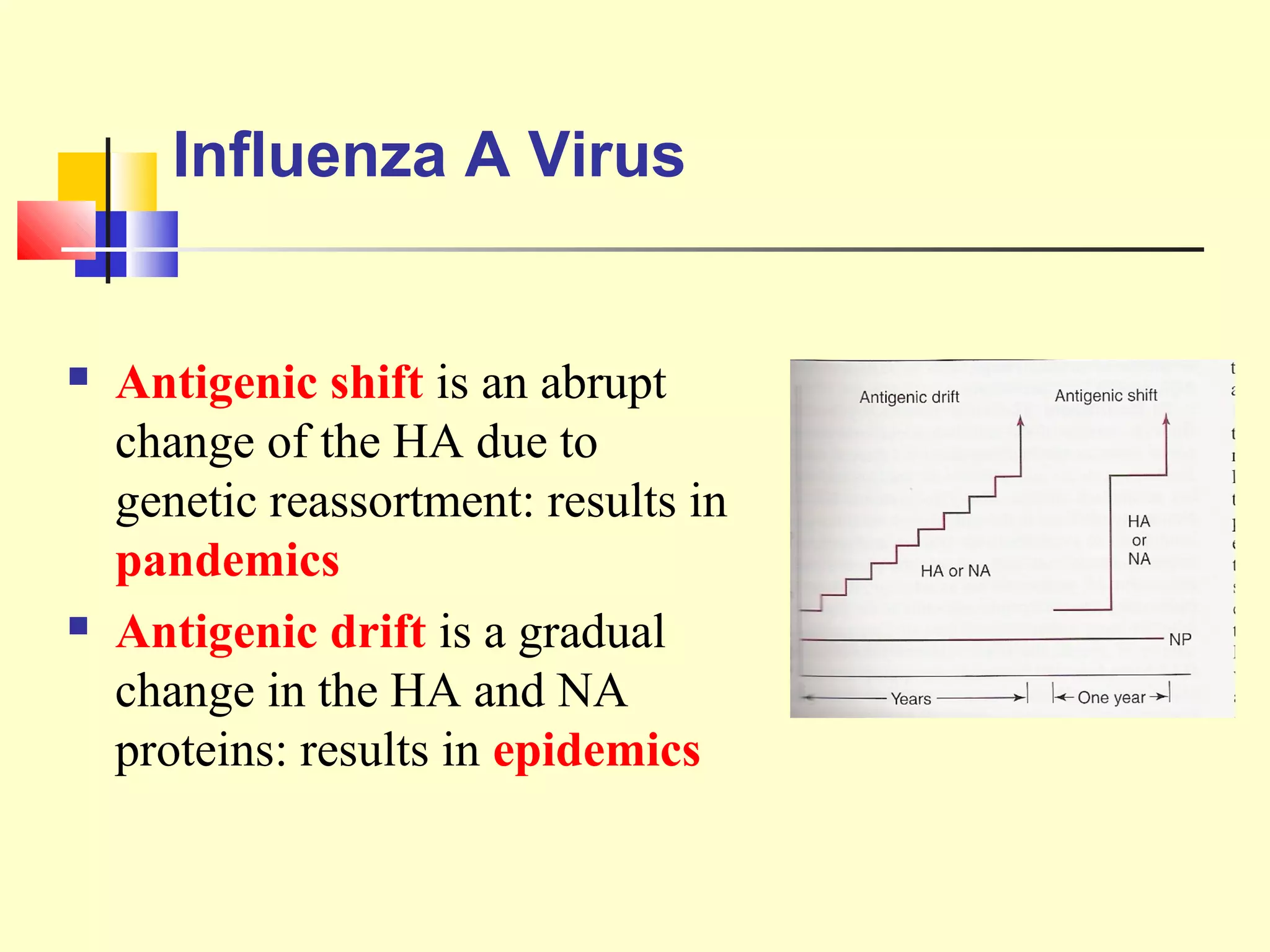
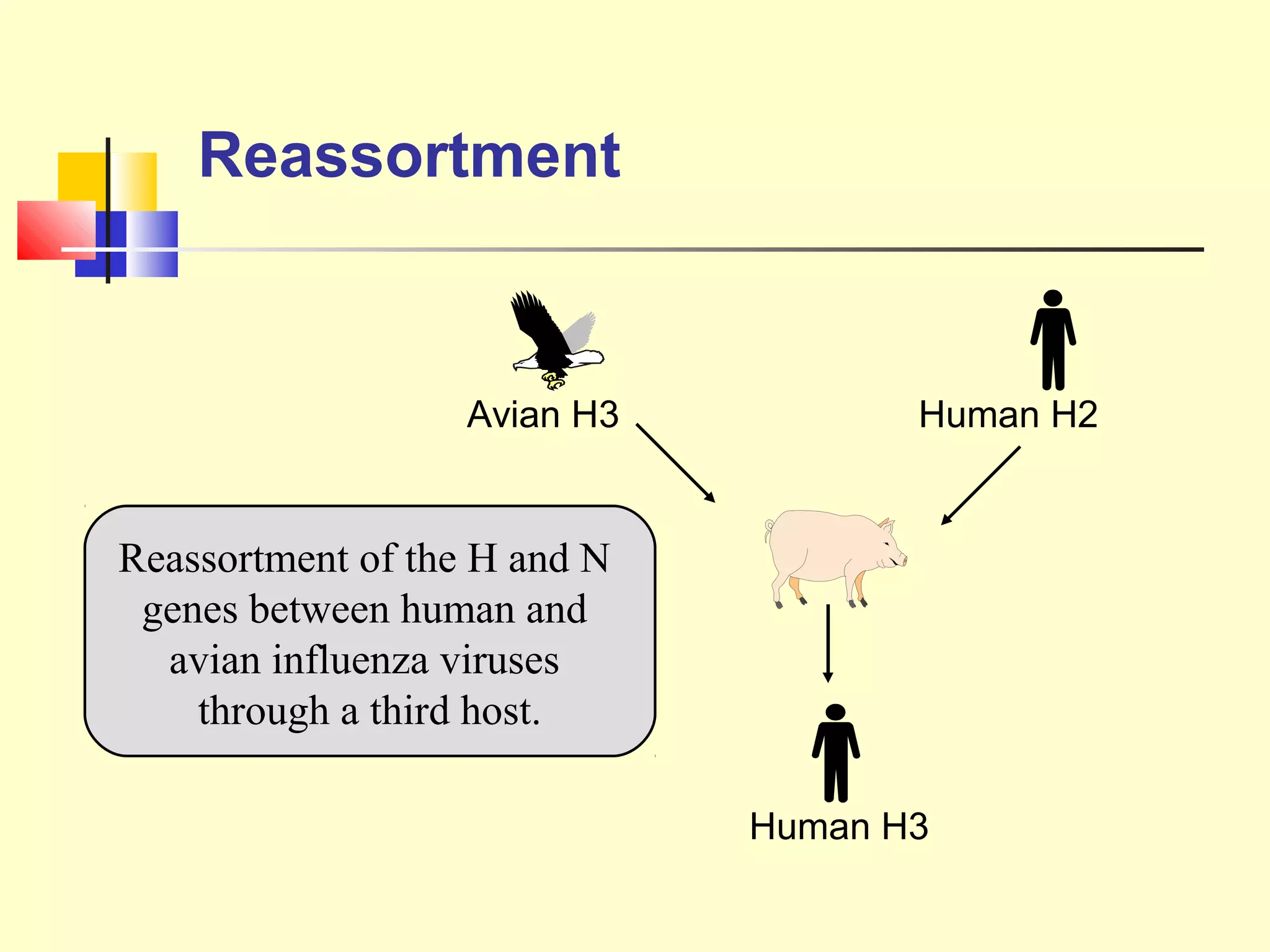
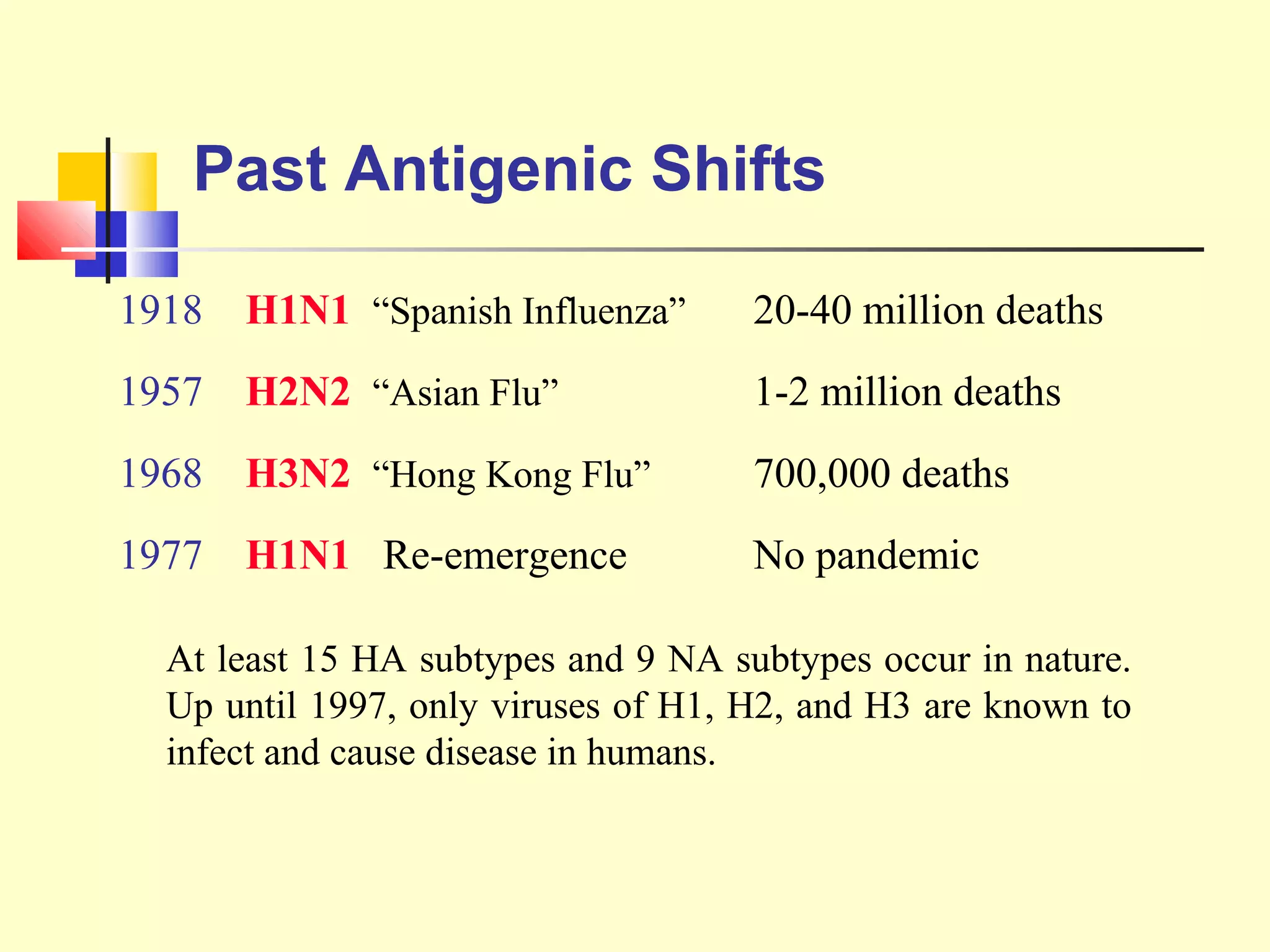
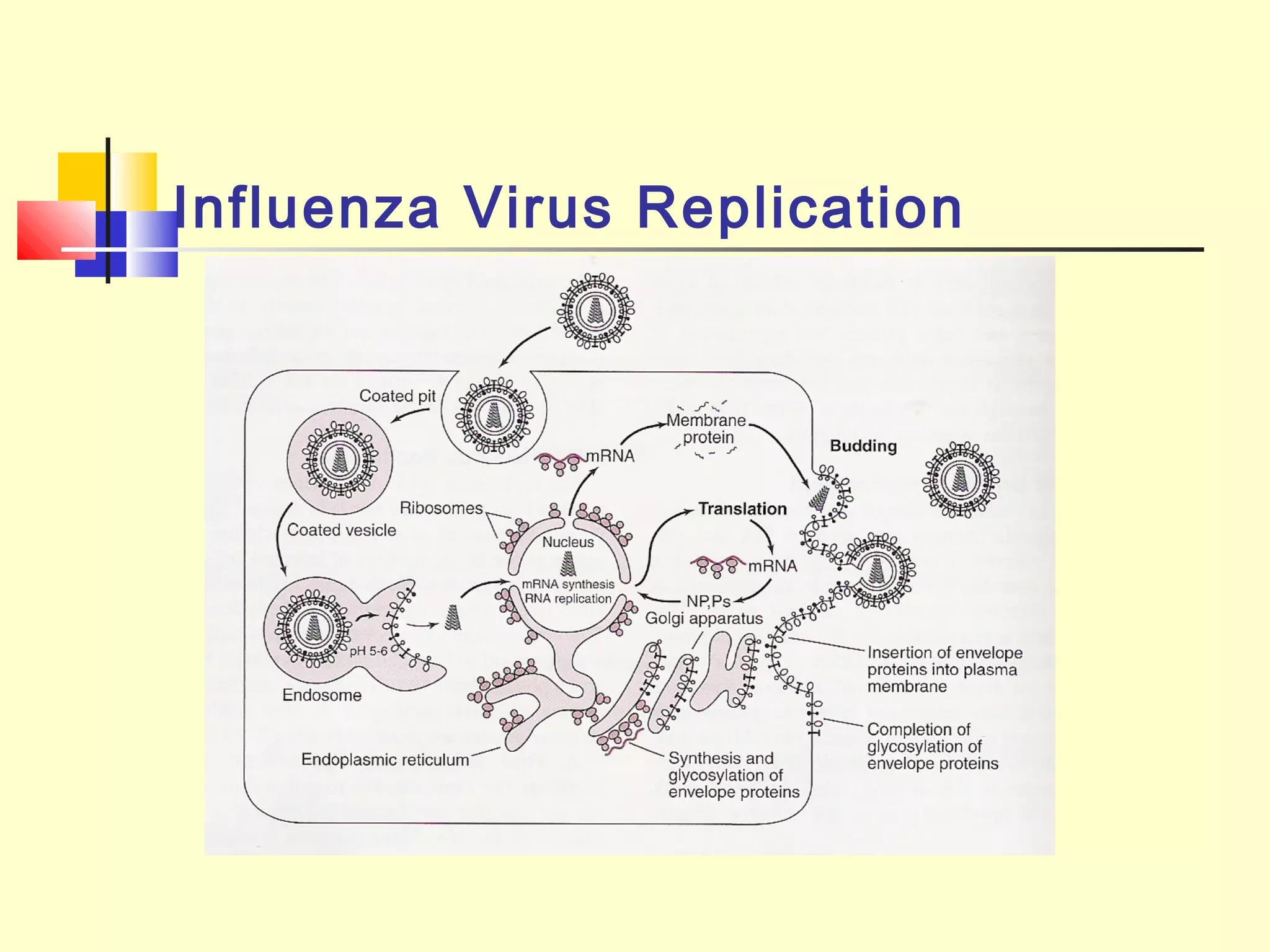
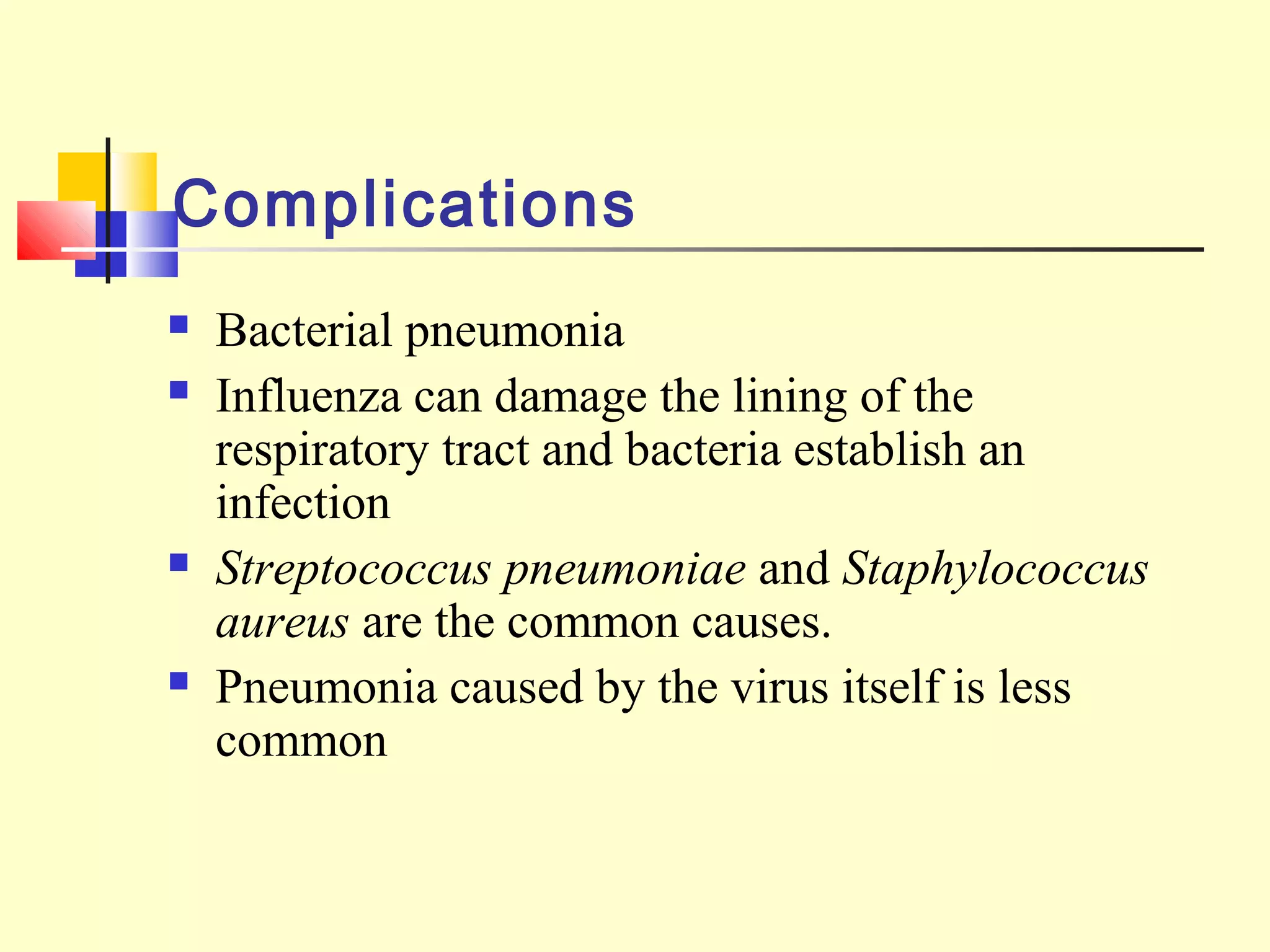
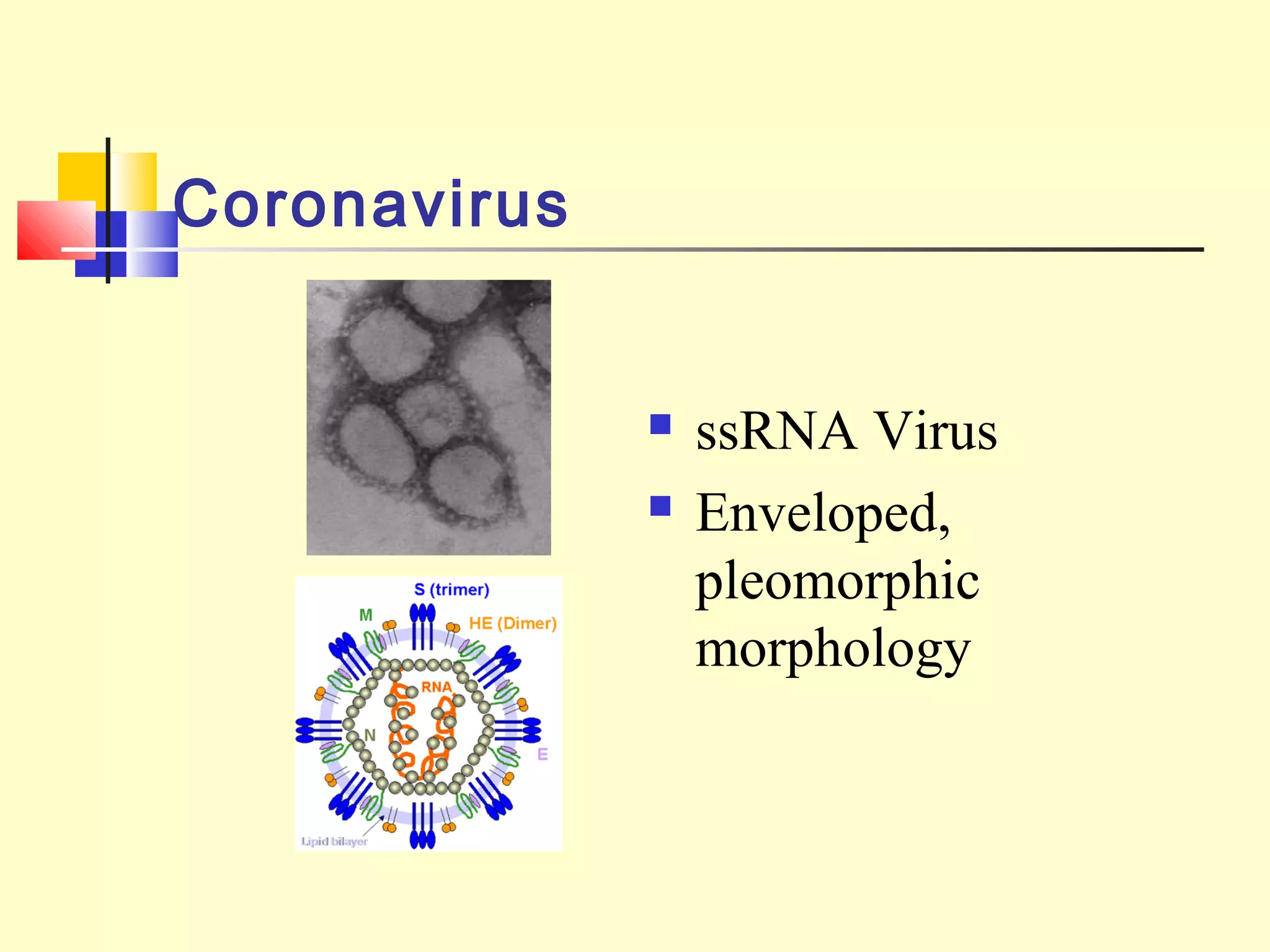
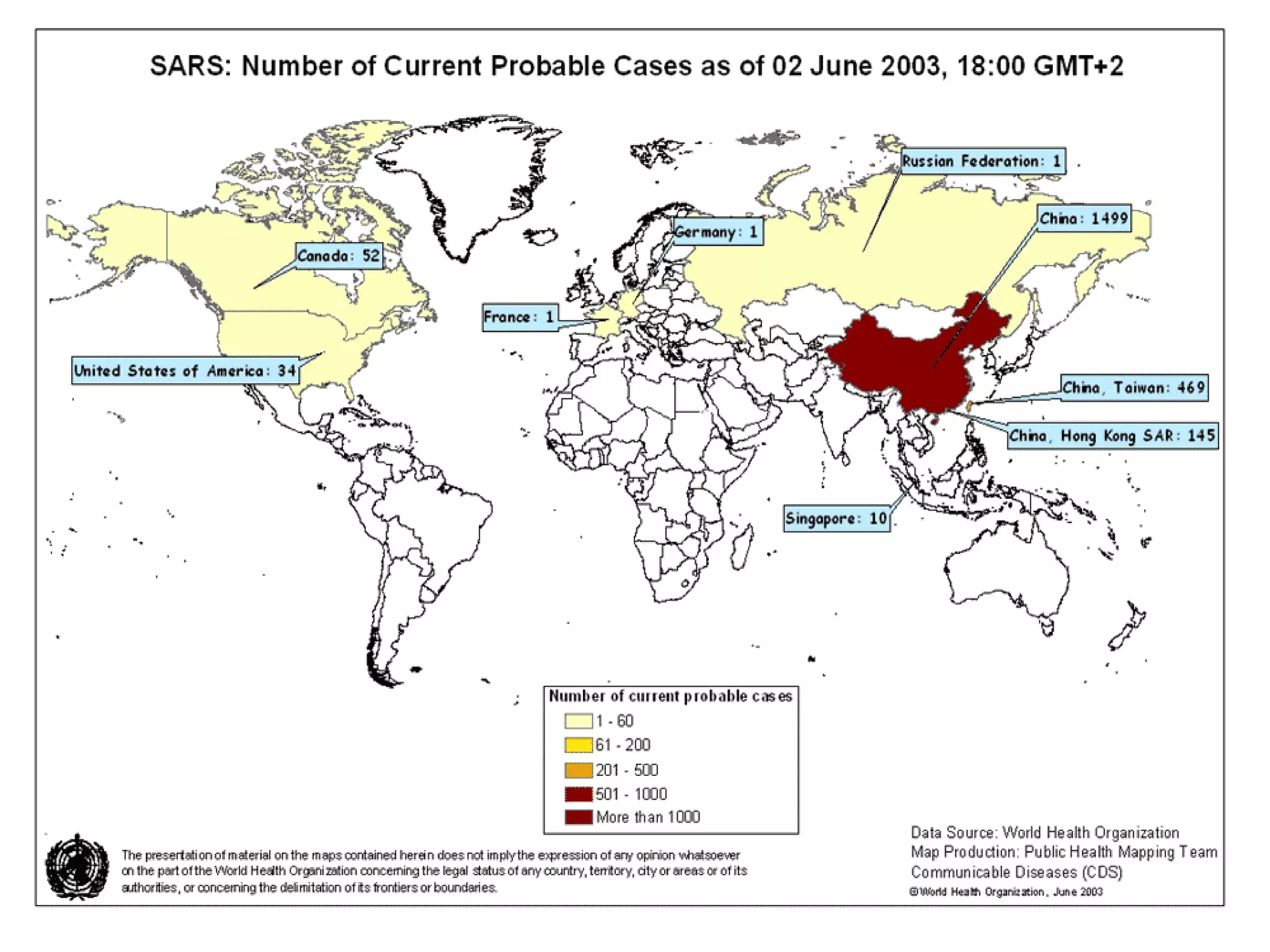
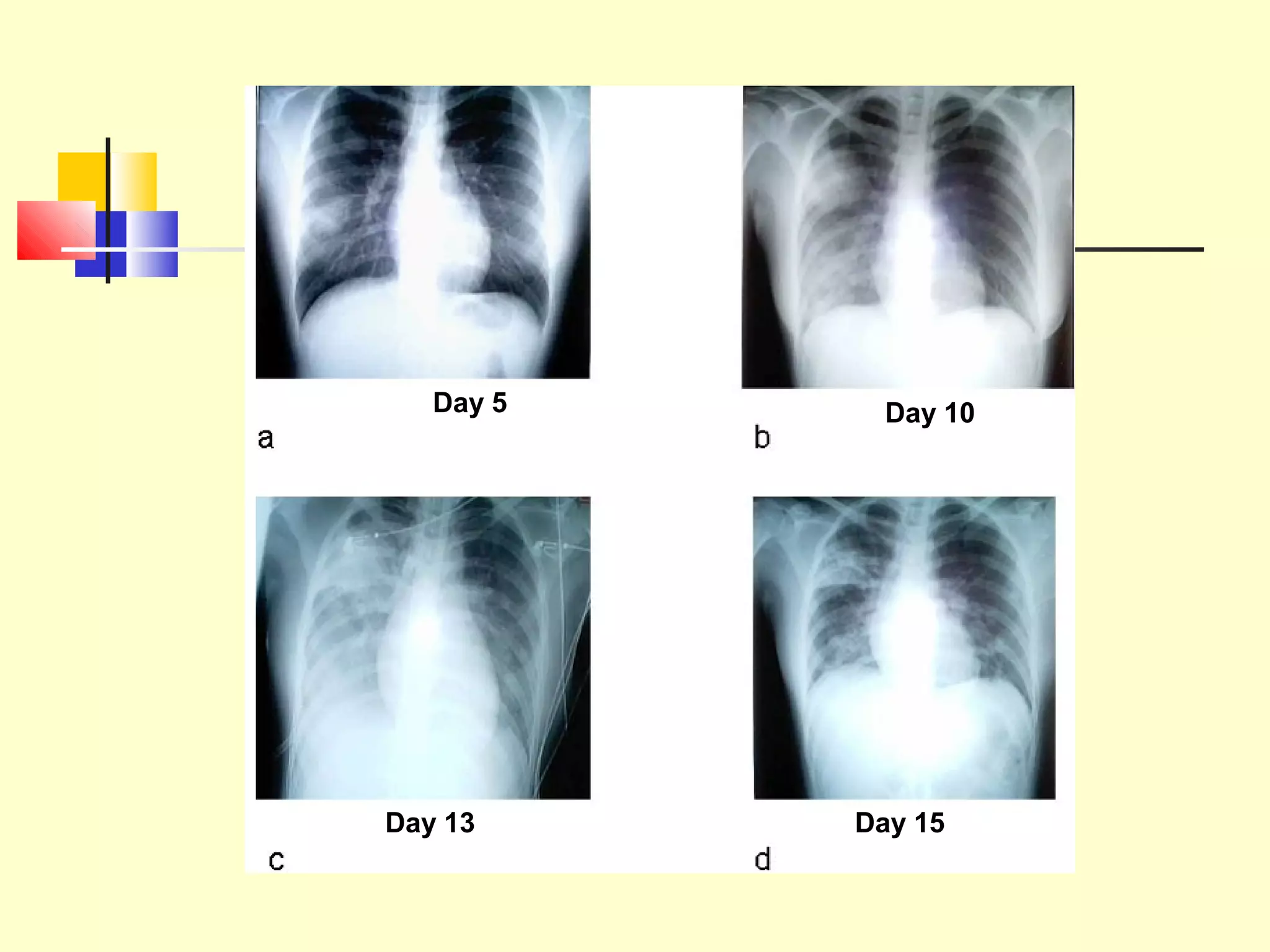
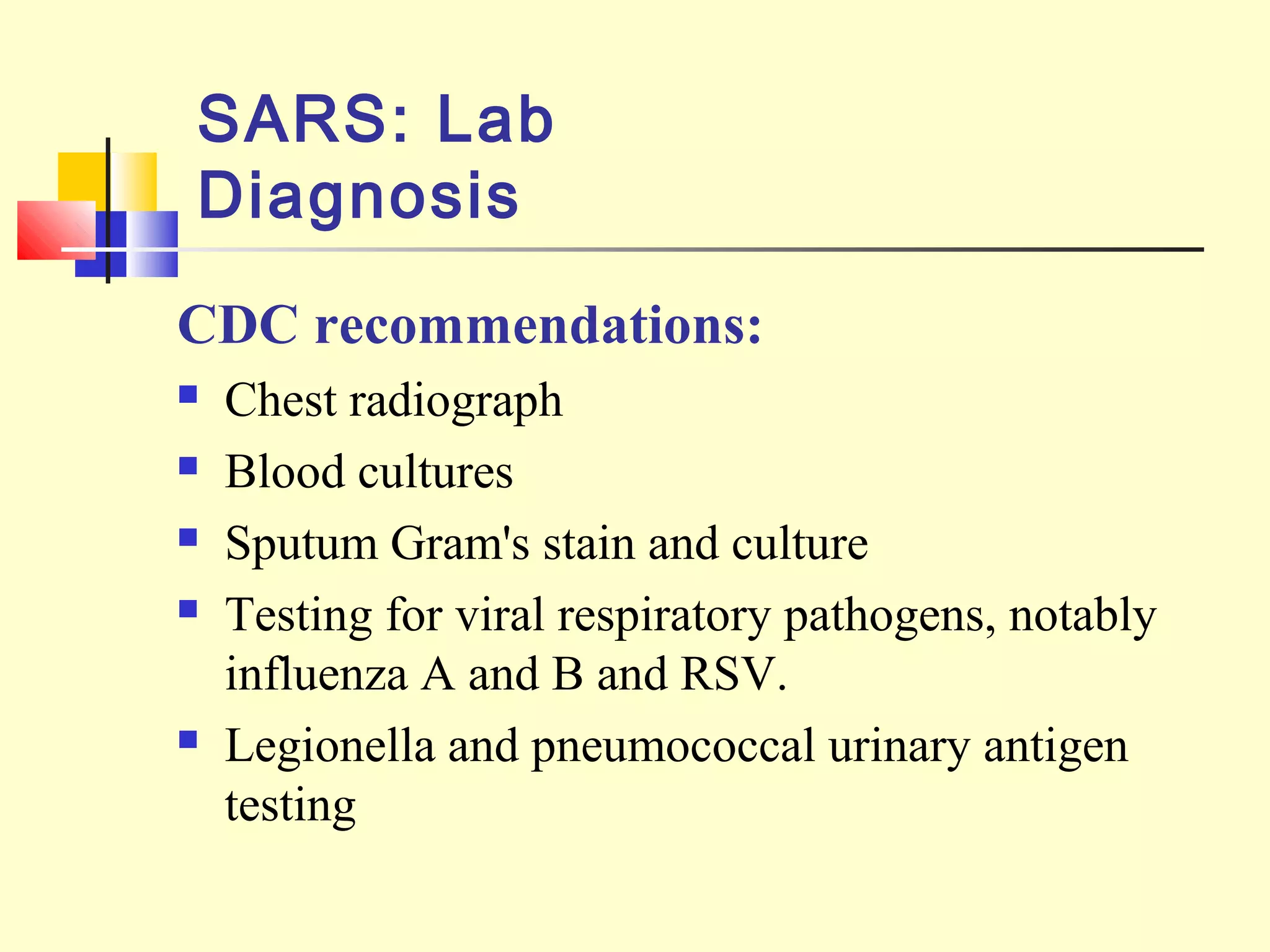
Viruses are a common cause of respiratory infections. Influenza virus is an RNA virus that causes influenza and can evolve through antigenic drift or shift, resulting in seasonal epidemics or pandemics. Other respiratory viruses include rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenoviruses. These viruses are diagnosed through antigen detection, virus isolation, or serology and treated symptomatically, though vaccines exist for some viruses. SARS is a coronavirus that emerged in 2002 and can cause severe respiratory illness.