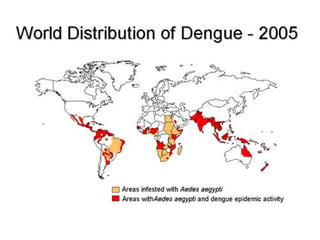
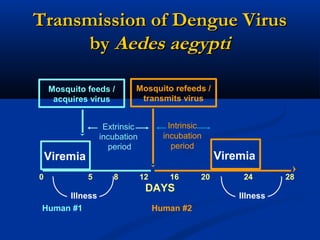
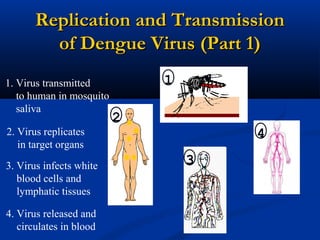
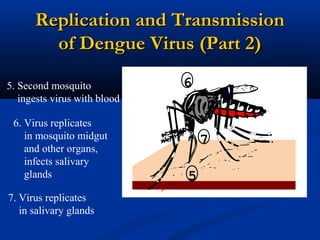
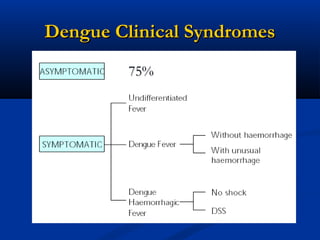
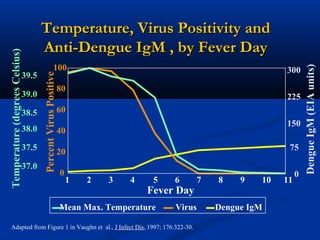
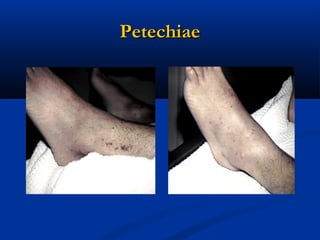
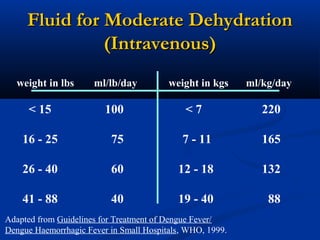
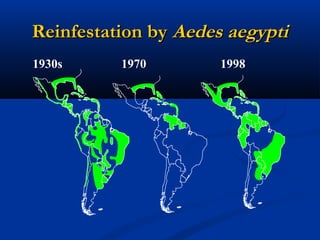
Dengue is an arbovirus transmitted by mosquitoes that causes dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever. It has 4 serotypes that provide lifetime immunity to that serotype but only short term cross-immunity. Risk of severe disease is increased in secondary infections with a different serotype due to antibody-dependent enhancement. The disease pathogenesis may involve antibodies from a previous infection forming complexes with a new infecting virus serotype, increasing virus replication in monocytes and leading to increased vascular permeability and hemorrhagic manifestations. Diagnosis involves considering travel history, signs of bleeding or increased vascular permeability, and low platelet count.