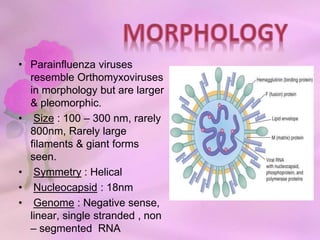
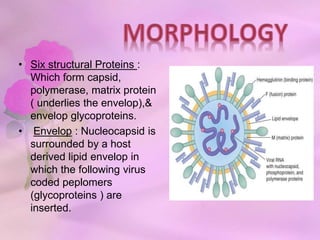
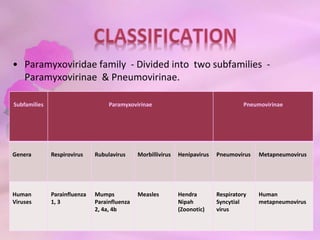
Paramyxoviridae contains viruses that are transmitted via the respiratory route and can cause localized respiratory infections or disseminate throughout the body. Parainfluenza viruses resemble orthomyxoviruses in morphology but are larger and pleomorphic, with a helical symmetry, 18nm nucleocapsid, and negative-sense RNA genome. They cause respiratory infections in children and have six structural proteins, including envelope glycoproteins, that help mediate attachment and fusion to host cells. Human parainfluenza viruses are a major cause of lower respiratory tract infections in young children.