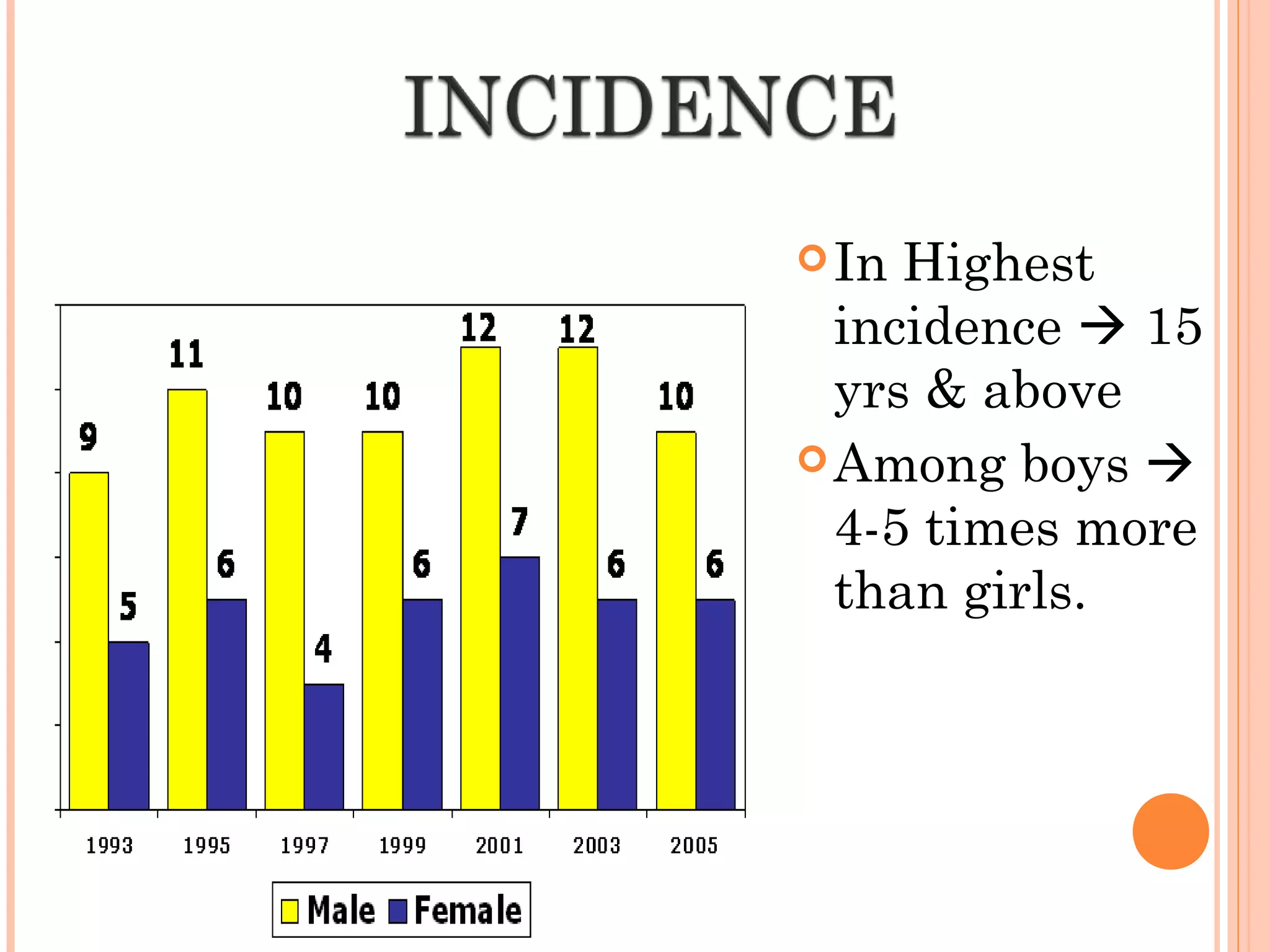
This document discusses juvenile delinquency and its causes and prevention. It defines a juvenile as a boy under 16 or a girl under 18. Delinquency includes criminal offenses as well as deviations from normal behavior like disobedience or mixing with immoral people. Incidence is higher among older teenagers and boys. Theories for the causes of delinquency include strain from inability to achieve goals, influence of delinquent peers, and labeling by authorities. Biological factors include genetics and physical defects, while social factors consist of broken homes, poverty, urbanization, and substance abuse. Preventive measures center around improving family life, schooling, and social welfare services.