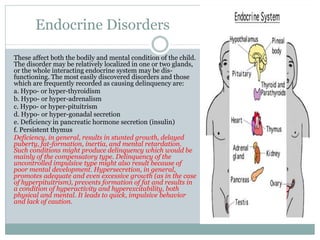
Juvenile delinquency refers to unlawful acts committed by minors under the age of 18. Theories like differential association theory and social learning theory suggest delinquent behavior is learned through interactions with peers who model criminal techniques, motives, and attitudes. Juvenile delinquency is influenced by physical, mental, home, school, neighborhood, and occupational conditions. It is a global issue associated with factors like poverty, family problems, and association with delinquent peers. Addressing the root causes early and providing a secure environment may help prevent future crimes.