- The document discusses children and issues pertaining to children in India. It aims to explain the vulnerability of children and gain knowledge on the status of children in India.
- Children are considered one of the most vulnerable populations due to factors such as dependence, innocence, lack of awareness, lack of political influence and economic power.
- In India, millions of children are involved in child labor, child marriage, trafficking and living on the streets. Malnutrition, anemia and other health issues afflict many Indian children.
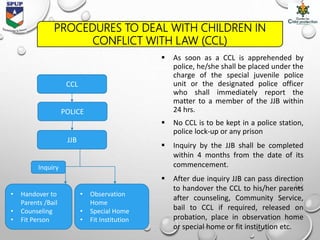
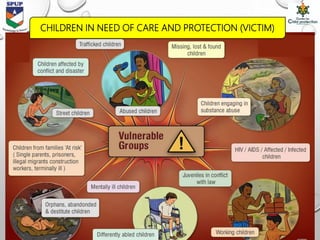
- The document categorizes vulnerable children as those in conflict with the law (offenders) and those in need of care and protection (victims). It provides statistics and discusses causes and consequences of